Fig. 7
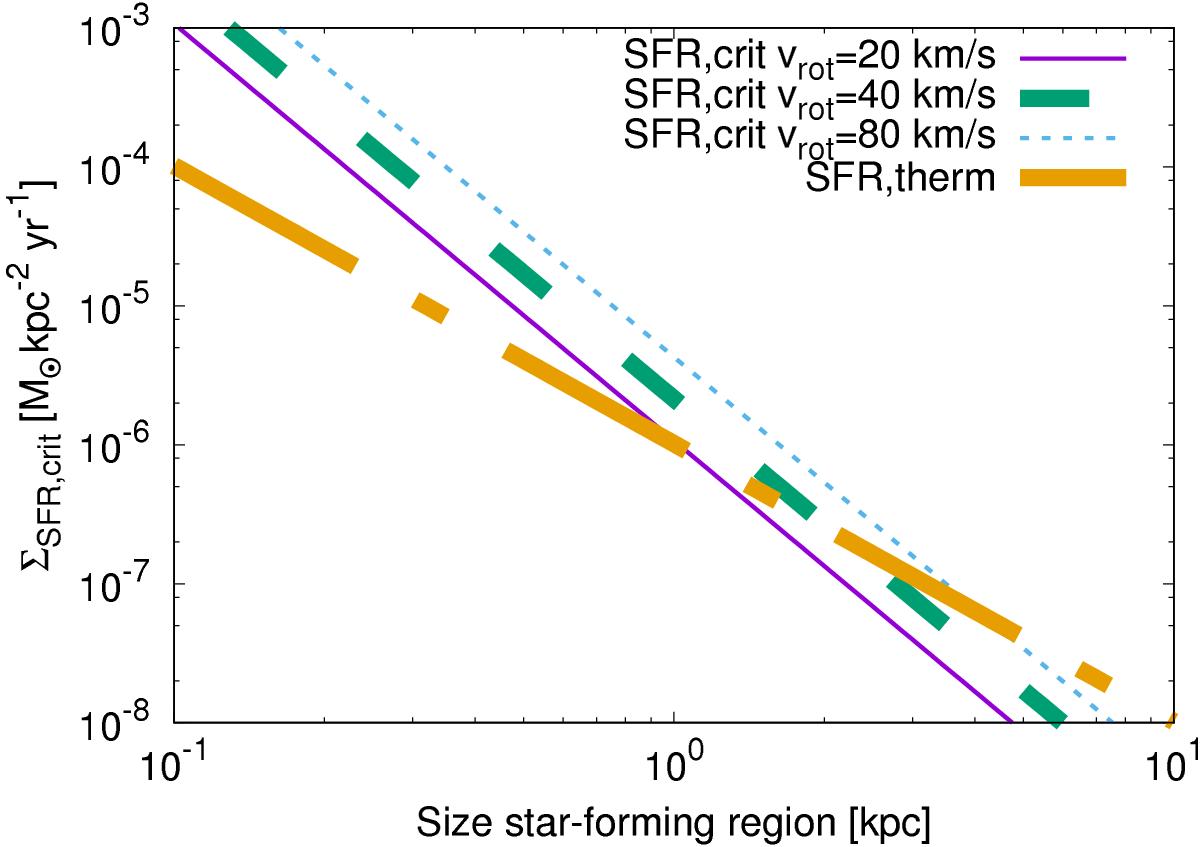
Comparison of the critical star formation surface density to maintain the relation between star formation and the magnetic field, given by Eq. (25), with the critical star formation rate to maintain thermal emission, given by Eq. (26). Critical star formation surface densities are given as functions of the size of the star-forming region. Explored are characteristic parameters for the rotational velocity of 20,40,and80 km s-1. For large star-forming regions, the critical star formation rate to maintain thermal emission eventually exceeds the critical star formation rate to maintain the correlation between star formation and the magnetic field. A comparison with Fig. 8 shows, however, that the radio emission will break down even earlier in this regime as a result of cosmic-ray diffusion losses.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


