Fig. 1
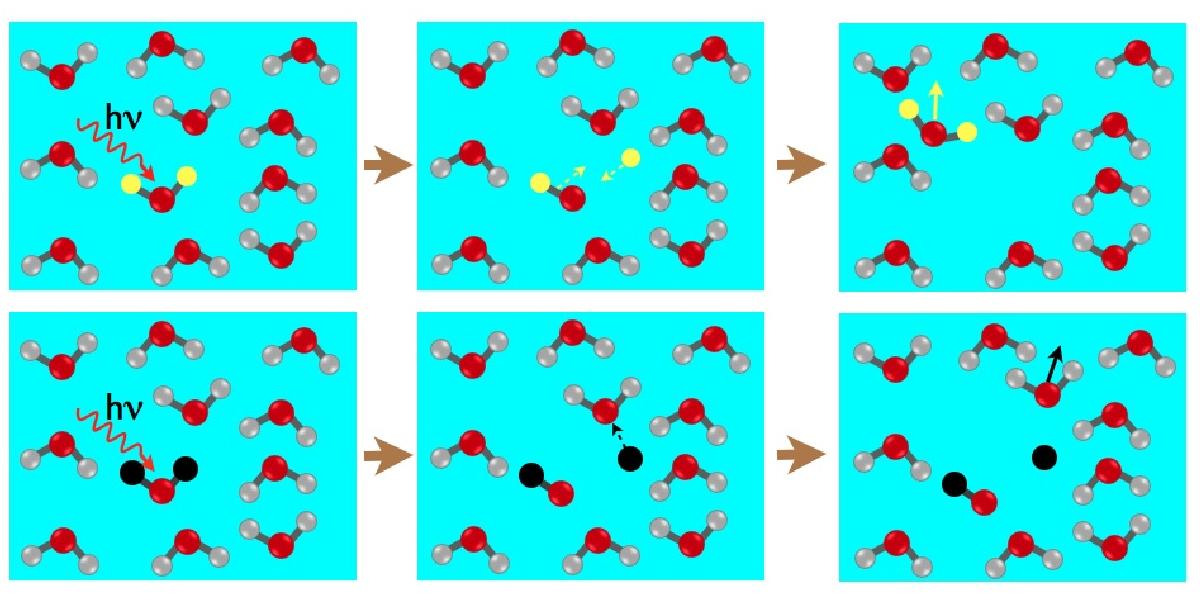
Top: a H2O molecule (with H atoms in yellow) surrounded by water molecules absorbs an UV photon and dissociates into H and OH. H and OH recombine to form H2O that eventually desorbs from the ice surface via the direct mechanism. Bottom: a D2O molecule (with D atoms in black) surrounded by water molecules absorbs an UV photon and dissociates into D and OD. The heavier D atom transfers its momentum to one of the surrounding H2O molecules that desorbs from the ice via the “kick-out” mechanism.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


