| Issue |
A&A
Volume 574, February 2015
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | C4 | |
| Number of page(s) | 1 | |
| Section | Letters | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201424678e | |
| Published online | 03 February 2015 | |
On the radiation driven alignment of dust grains: Detection of the polarization hole in a starless core (Corrigendum)
1
Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik,
Giessenbachstrasse 1,
85748
Garching,
Germany
e-mail:
falves@mpe.mpg.de
2
Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid (CSIC),
Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz 3,
28049
Madrid,
Spain
3
Observatorio Astronómico Nacional, Alfonso XII 3, 28014
Madrid,
Spain
4
Institut de Ciències de l’Espai (CSIC-IEEC), Campus UAB, Facultat
de Ciències, C5 par
2 a,
08193 Bellaterra, Catalunya, Spain
5
Departamento de Física – ICEx – UFMG, Caixa Postal 702, 30. 123-970
Belo Horizonte,
Brazil
6
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Northwestern
University, 2145 Sheridan
Road, Evanston,
IL
60208,
USA
7
Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie,
Auf dem Hügel 69, 53121
Bonn,
Germany
Key words: stars: formation / ISM: magnetic fields / techniques: polarimetric / ISM: individual objects: Core 109 / errata, addenda
Figure 2 in the original manuscript displays the polarization efficiency for the optical, near infrared and sub-millimeter (submm) polarimetric data as P/AV, where P is the polarization degree and AV is the visual extinction traced by the data. However, the polarization efficiency for the submm data should be simply P. By dividing P by AV, we obtain a steeper and wrong slope for the decrease in polarization efficiency. The suitable form for Fig. 2 of the original document is exhibited in Fig. 1 of the present corrigendum. The submm polarization efficiency decreases as ~−1.0 with respect to AV, instead of the originally published ~−2.0.
Although the decrease in polarization efficiency at the submm regime is shallower than originally proposed, our modelling of the polarization degree with respect to the relative intensity, I/Imax, still predicts the detection of a polarization hole (Sect. 3 of the published manuscript). Therefore, the main conclusions are unchanged.
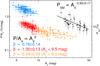 |
Fig. 1 Polarization efficiency of the optical and near-IR data (P/AV) and the submm data (PSM). |
© ESO, 2015
All Figures
 |
Fig. 1 Polarization efficiency of the optical and near-IR data (P/AV) and the submm data (PSM). |
| In the text | |
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


