| Issue |
A&A
Volume 557, September 2013
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | C1 | |
| Number of page(s) | 1 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201218905e | |
| Published online | 28 August 2013 | |
On the massive young stellar object AFGL 4176
High-spatial-resolution multi-wavelength observations and modeling (Corrigendum)
1
Max Planck Institute for Astronomy,
Königstuhl 17,
69117
Heidelberg,
Germany
e-mail: boley@mpia.de; linz@mpia.de;
boekel@mpia.de; bouwman@mpia.de;
henning@mpia.de
2
Ural Federal University, Astronomical Observatory,
51 pr. Lenina, 620002
Ekaterinburg,
Russia
e-mail: andrey.sobolev@usu.ru
Key words: stars: formation / techniques: interferometric / techniques: high angular resolution / radiative transfer / stars: individual: AFGL 4176 / errata, addenda
We would like to correct an error in the position angle reported by Boley et al. (2012) for the disk model of the massive young stellar object AFGL 4176. The error arose due to a problem with the angle conventions used, and had no influence on the modeling of the data. The correct position angle φ is related to the previously reported (incorrect) value φ′ by φ = 270°−φ′. After correcting for this error, the position angle φ of the disk we find is 112° east of north (the value we reported previously was 158°, and should be disregarded). Although none of the other derived parameters are affected by this error, we report this corrected value in order to facilitate an easy comparison with future spatially-resolved interferometric studies in the (sub-)mm and/or near-infrared ranges for this particular object. We include here corrected versions of Fig. 12 and Table 4, and apologize for any confusion which may have occurred.
Two-dimensional geometric fit parameters.
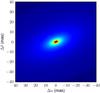 |
Fig. 12 Image of the fit of the disk model to the mid-infrared visibilities at λ = 10.6 μm. |
References
- Boley, P. A., Linz, H., van Boekel, R., et al. 2012, A&A, 547, A88 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
© ESO, 2013
All Tables
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


