Fig. 1
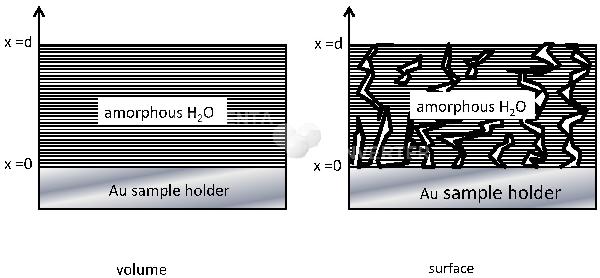
Scheme of the bilayer sample: a thin layer of the studied M molecule (M being CO, HNCO, H2CO, or NH3) is first deposited at 15 K on the gold surface, and then a thicker layer of ASW ice is deposited on top of it at 15 K. The thickness d of the ASW layer is estimated both using H2O IR absorption bands and by interferometry. The diffusion of the M molecule along the x direction is monitored at a fixed temperature by recording the evolution of one of its characteristic IR absorption bands as function of time using FTIR spectroscopy. A compact ASW ice favors a bulk (volume) diffusion (left part), while a porous ASW ice favors a surface diffusion along cracks and pores (surface).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


