Fig. 6
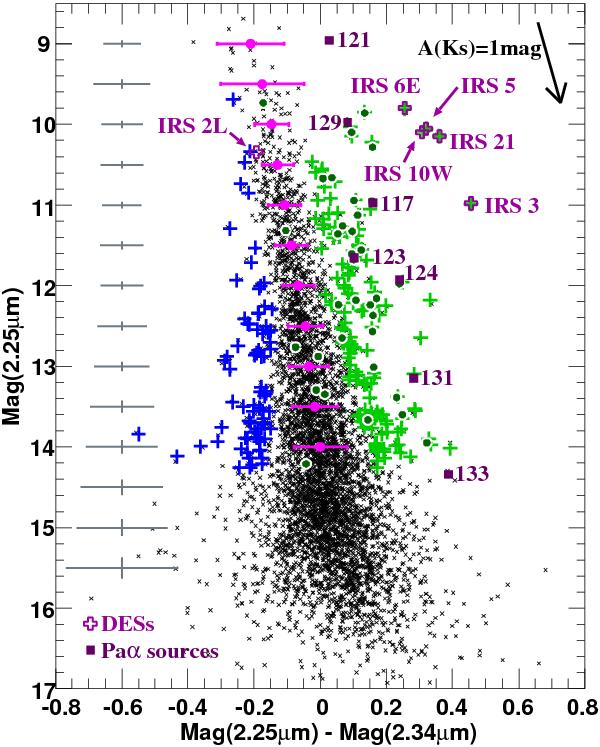
[2.25] vs. [2.25] − [2.34] color magnitude diagram. Red color (positive value) in [2.25] − [2.34] means no significant CO absorption at 2.34 μm which, together with the brightness, is an indicator for massive, early-type stars. Typical uncertainties are represented by grey crosses at the left side. Stars with photometric uncertainties larger than these typical ones are not included in this diagram. The reddening vector with a slope of Aλ ∝ λ-2.0 (Nishiyama et al. 2006) is shown at the upper right in the diagram. Dark green circles represent spectroscopically identified early-type stars. The means and sigmas of the RGB in the [2.25] − [2.34] color within bins of one magnitude width are shown by pink circles and bars, respectively. We define stars more than 2-σ redder than the red giants as early-type star candidates (light green crosses). Blue crosses, which are stars more than 2-σbluer than the RGB, are used to estimate the false detection likelihood of the early-type star candidates.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


