Table 3
Comparison between the flow parameters derived from CO (2 − 1) and H2O.
| Method 1a (i = 80°) | Method 2b (i = 75°) | ||||
|
|
|
||||
| Parameterc | Symbol and unit | CO (2 − 1) | H2O (red) | H2O (red) | |
|
|
|||||
| Length to width ratio | Rcoll | 14 | 7.5 | 7.5 | |
| Total mass | Mtot (M⊙) | 10 × 10-3 | 1.6 × 10-3 | 1.6 × 10-3 | |
| Extent | Rmax (pc) | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | |
| Characteristic velocity | υchar (km s-1) | 50 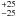 |
90 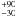 |
60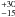 |
|
| Dynamical time scale | td (yr) | 1.7 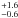 × 103 × 103 |
1.0 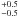 × 103 × 103 |
7.4 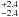 × 102 × 102 |
|
| Momentum | P (M⊙ km s-1) | 0.6 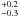 |
0.1 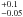 |
0.03 | |
| Kinetic energy | E (erg) | 3 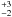 × 1044 × 1044 |
1 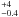 × 1044 × 1044 |
2.0 × 1043 | |
| Momentum rate | Ṗ (M⊙ km s-1 yr-1) | 3.4 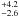 × 10-4 × 10-4 |
1.5 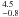 × 10-4 × 10-4 |
3.4 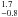 × 10-5 × 10-5 |
|
| Mechanical luminosity | Ė (L⊙) | 1.4 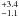 |
1.1 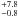 |
0.2 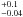 |
|
| Wind mass-loss rate | Ṁ (M⊙ yr-1) | 1.7 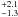 × 10-6 × 10-6 |
0.7 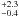 × 10-6 × 10-6 |
1.7 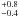 × 10-7 × 10-7 |
|
Notes. The uncertainty on the inclination is assumed to be 5° and the velocity of the wind is set to 200 km s-1.
The parameters derived from CO (2−1) were presented in André et al. (1990) and have here been scaled to the distance 120 pc.
The inclination corrections are based on the work presented in Downes & Cabrit (2007). The dynamical time-scale is derived from the maximum velocity of the H2O gas, i.e. ~30 km s-1.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


