Table 2
A representative portion of the ATLAS 2.3 GHz source catalogue of the ELAIS-S1 field for illustration purposes. The CDF-S catalogue contains the same information.
| IDa | RA (J2000) | Dec (J2000) | S1.4 GHz,hi | ΔS1.4 GHz,hi | S1.4 GHz,lo | ΔS1.4 GHz,lo | rms1.4 GHz,lo | S2.3 GHz | ΔS2.3 GHz | rms2.3 GHz |
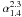
|
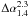
|
z | Classb |
| deg | deg | mJy | mJy | mJy | mJy | mJy | mJy | mJy | mJy | |||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| 254 | 51.770792 | –28.650297 | 1.260 | 0.084 | 1.230 | 0.093 | 0.069 | 0.561 | 0.080 | 0.075 | –1.58 | 0.11 | ||
| 178 | 51.621458 | –27.427269 | 2.740 | 0.145 | 2.220 | 0.165 | 0.122 | 1.519 | 0.107 | 0.075 | –0.76 | 0.11 | ||
| 165 | 53.319708 | –27.941922 | 1.131 | 0.054 | 0.762 | 0.158 | 0.153 | 0.828 | 0.084 | 0.073 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.685 | |
| 163 | 52.470667 | –27.492661 | 2.160 | 0.116 | 2.070 | 0.985 | 0.980 | 1.810 | 0.116 | 0.073 | –0.27 | 0.95 | ||
| 102 | 52.561167 | –28.566331 | 0.194 | 0.037 | 0.162 | 0.155 | 0.154 | 0.344 | 0.074 | 0.072 | 1.52 | 0.64 | ||
| 290 | 53.190750 | –28.520756 | 0.714 | 0.044 | 0.598 | 0.126 | 0.123 | 0.400 | 0.075 | 0.072 | –0.81 | 0.14 | 0.211 | |
| 201 | 52.399667 | –27.950881 | 1.420 | 0.087 | 1.550 | 0.153 | 0.132 | 1.154 | 0.093 | 0.072 | –0.59 | 0.06 | 0.067 | SF |
| 150 | 52.122000 | –28.030825 | 1.810 | 0.087 | 1.770 | 0.281 | 0.267 | 1.016 | 0.088 | 0.072 | –1.12 | 0.30 | 0.902 | |
| 264 | 52.105750 | –27.745814 | 0.920 | 0.054 | 0.745 | 0.176 | 0.173 | 0.674 | 0.080 | 0.072 | –0.20 | 0.46 | ||
| 323 | 52.808292 | –28.785917 | 0.834 | 0.057 | 0.818 | 0.160 | 0.155 | 0.544 | 0.077 | 0.072 | –0.82 | 0.38 | 0.140 | AGNe |
Notes. The columns are as follows: (1) unique ID; (2) degrees of J2000 right ascension; (3) degrees of J2000 declination; (4, 5) 1.4 GHz integrated flux density and flux density error as given in Hales et al. (in prep.); (6–8) integrated flux density, flux density error as calculated using Eq. (1) and local rms noise as measured from the low-resolution 1.4 GHz image; (9–11) integrated flux density, flux density error as calculated using Eq. (1) and local rms noise as measured from the 2.3 GHz image; (12, 13) spectral index calculated from the low-resolution 1.4 GHz flux density and the 2.3 GHz flux density and its error as calculated by Eq. (4); (14, 15) spectroscopic redshift and spectral classification from Mao et al. (2012) if available. The entire table is available at the CDS.
Spectroscopic classification from Mao et al. (2012). SF indicates an optical spectrum dominated by star formation activity while AGN indicates an optical spectrum typical for AGN (e.g. AGNe for an AGN with characteristic emission lines). E indicates that the spectrum is that of an early-type galaxy and hence the radio emission must originate from an AGN hosted by it.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


