Table B.1
Properties of the analyzed LMC stars.
| Star | Number |
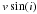
|
T eff | M evol |

|
τ H |
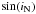
|
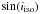
|
t N | t isochrone | Binary | Class |
| km s-1 | K | M ⊙ | dex | Myr | Myr | Myr | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| N 11–34 | L1 | 203 | 25 500 | 20 | 7.12 | 7.5 | 1.00 | – |
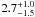
|
7.8 | yes | 1 |
| N 11–37 | L2 | 100 | 28 100 | 23 | ≤7.17 | 6.2 | 0.76 | ≥ 0.76 | 6.2 | 6.8 | yes | 2 |
| N 11–46 | L3 | 205 | 33 500 | 28 | ≤7.71 | 5.1 | 0.88 | ≥ 0.88 | 5.1-2.5 | 4.8 | yes | 2 |
| N 11–77 | L4 | 117 | 21 500 | 12 | 6.96 | 16.0 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 16.0-16.0 | 15.4 | yes | 2 |
| N 11–88 | L5 | 240 | 24 150 | 14 | ≤6.96 | 12.6 | 1.00 | – |
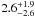
|
12.6 | – | 1 |
| N 11–89 | L6 | 117 | 21 700 | 12 | 6.91 | 16.0 | 1.00 | – |
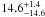
|
16.4 | yes | 1 |
| N 11–95 | L7 | 267 | 26 800 | 15 | 7.46 | 11.4 | 1.00 | – |
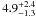
|
10.4 | – | 1 |
| N 11–102 | L8 | 218 | 31 000 | 18 | ≤7.58 | 8.6 | 1.00 | – |
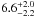
|
7.0 | – | 1 |
| N 11–104 | L9 | 153 | 25 700 | 14 | ≤7.20 | 12.5 | 0.99 | ≥0.97 | 12.5-4.2 | 11.8 | – | 2 |
| N 11–111 | L10 | 101 | 22 950 | 12 | 6.93 | 16.0 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 16.0-16.0 | 15.4 | – | 2 |
| N 11–114 | L11 | 299 | 32 500 | 19 | ≤7.92 | 8.2 | 0.91 | ≥0.90 | 8.2-4.7 | 5.8 | – | 2 |
| N 11–116 | L12 | 160 | 21 700 | 11 | 6.98 | 18.6 | 1.00 | – |
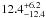
|
18.4 | – | 1 |
| N 11–117 | L13 | 247 | 26 800 | 13 | ≤7.06 | 14.2 | 1.00 | – |
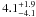
|
11.2 | – | 1 |
| N 11–118 | L14 | 150 | 25 700 | 13 | 7.39 | 14.1 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 14.1 | 12.6 | yes | 2 |
| N 11–120 | L15 | 207 | 31 500 | 17 | ≤7.56 | 9.3 | 1.00 | 0.91 |
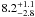
|
6.4 | – | 1 |
| N 11–121 | L16 | 265 | 27 000 | 14 | ≤7.48 | 12.6 | 1.00 | – |
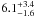
|
11.2 | – | 1 |
| N 11–122 | L17 | 173 | 33 000 | 18 | ≤7.72 | 8.6 | 0.68 | ≥ 0.61 | 8.6 | 4.6 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–20 | L18 | 145 | 22 950 | 18 | 7.46 | 8.6 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 8.6 | 9.6 | yes | 2 |
| NGC 2004–30 | L19 | 123 | 29 000 | 19 | 7.43 | 7.9 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 7.9 | 7.6 | yes | 2 |
| NGC 2004–47 | L20 | 133 | 21 700 | 12 | 7.03 | 16.0 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 16.0-16.0 | 16.4 | yes | 2 |
| NGC 2004–50 | L21 | 109 | 20 450 | 11 | 7.10 | 18.6 | 0.71 | 0.68 | 18.6-18.6 | 17.0 | yes | 2 |
| NGC 2004–54 | L22 | 114 | 21 700 | 12 | 6.97 | 16.0 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 16.0-16.0 | 16.4 | yes | 2 |
| NGC 2004–62 | L23 | 106 | 31 750 | 17 | ≤7.33 | 9.3 | 0.67 | ≥ 0.61 | 9.3 | 7.6 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–63 | L24 | 107 | 21 700 | 11 | 6.97 | 18.6 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 18.6-18.6 | 18.0 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–65 | L25 | 223 | 20 450 | 11 | ≤7.19 | 18.7 | 1.00 | – |
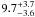
|
19.8 | – | 1 |
| NGC 2004–66 | L26 | 238 | 25 700 | 13 | 7.98 | 14.2 | 0.60 | 0.59 | 14.2 | 12.0 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–69 | L27 | 178 | 28 000 | 15 | 7.84 | 11.2 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 11.2 | 9.8 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–74 | L28 | 130 | 27 375 | 14 | ≤7.42 | 12.5 | 0.72 | ≥ 0.67 | 12.5 | 10.6 | yes | 2 |
| NGC 2004–75 | L29 | 116 | 21 700 | 11 | 7.06 | 18.6 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 18.4-18.6 | 18.0 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–77 | L30 | 215 | 29 500 | 16 | 7.65 | 10.2 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 10.2-3.6 | 8.4 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–79 | L31 | 165 | 21 700 | 11 | 7.60 | 18.6 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 18.6 | 18.4 | yes | 2 |
| NGC 2004–81 | L32 | 105 | 26 800 | 13 | 7.14 | 14.0 | 0.70 | 0.63 | 14.0 | 11.2 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–82 | L33 | 161 | 25 700 | 13 | 7.47 | 14.1 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 14.1 | 12.6 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–85 | L34 | 150 | 20 450 | 10 | 7.25 | 22.0 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 22.0 | 21.4 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–88 | L35 | 200 | 20 450 | 10 | ≤7.18 | 22.0 | 1.00 | – |
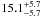
|
21.6 | yes | 1 |
| NGC 2004–95 | L36 | 138 | 25 700 | 13 | 7.13 | 14.1 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 14.1-4.8 | 12.8 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–99 | L37 | 119 | 21 700 | 10 | 7.06 | 22.0 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 22.0-22.0 | 19.6 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–100 | L38 | 323 | 26 800 | 13 | ≤7.29 | 14.5 | 1.00 | – |
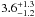
|
11.6 | – | 1 |
| NGC 2004–101 | L39 | 131 | 21 700 | 10 | 7.59 | 22.0 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 22.0 | 19.6 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–104 | L40 | 274 | 25 700 | 12 | ≤7.28 | 16.3 | 1.00 | – |
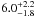
|
13.2 | – | 1 |
| NGC 2004–105 | L41 | 235 | 25 700 | 12 | ≤7.11 | 16.2 | 1.00 | – |
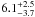
|
13.2 | – | 1 |
| NGC 2004–107 | L42 | 146 | 28 500 | 14 | ≤7.12 | 12.5 | 1.00 | 0.88 |
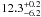
|
9.4 | yes | 1 |
| NGC 2004–110 | L43 | 121 | 21 700 | 10 | 6.95 | 22.0 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 22.0-22.0 | 19.4 | – | 2 |
| NGC 2004–113 | L44 | 307 | 20 450 | 9 | ≤7.29 | 27.1 | 1.00 | – |
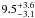
|
22.2 | – | 1 |
Notes. From left to right: the table includes catalogue number (Evans et al. 2005), reference number used in this paper, projected surface rotational velocity, effective temperature, evolutionary mass and surface nitrogen abundance (all from Hunter et al. 2008b, 2009), main sequence lifetime, nitrogen inclination angle, inclination angle derived using the nitrogen abundance and the isochrone age, maximum age based on the surface nitrogen abundance, isochrone age, identification of binarity and class. For Class 2 stars, adopting an error in the nitrogen abundance does not lead to an increased upper age limit, and in many cases also not to an decreased lower age limit.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


