Fig. 1
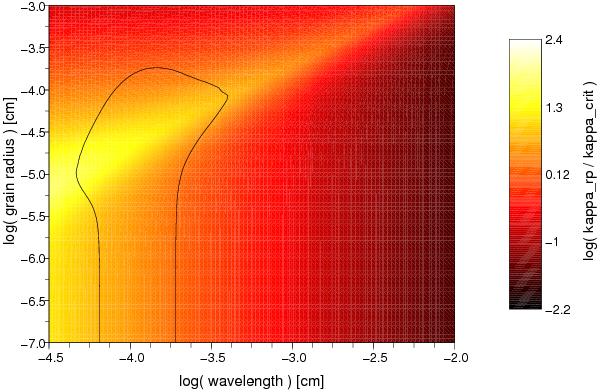
Relevant dust opacity for radiation pressure (combining effects of absorption and scattering, see Sect. 2) as function of grain radius and wavelength, computed from refractive index data for amorphous carbon by Rouleau & Martin (1991). The black contour shows the region where the flux-weighted monochromatic opacity exceeds the critical opacity, that is required in order for the radiation pressure to balance gravity (see Eqs. (12) and (11), respectively), assuming a Planckian flux distribution with Teff = 2700 K and that 30% of the carbon not bound in CO condense into carbon dust.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


