| Issue |
A&A
Volume 517, July 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A85 | |
| Number of page(s) | 28 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201014156 | |
| Published online | 12 August 2010 | |
Massive star formation in Wolf-Rayet
galaxies![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png) ,
,![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
IV. Colours, chemical-composition analysis and metallicity-luminosity relations
Á. R. López-Sánchez1,2 - C. Esteban2,3
1 - CSIRO Astronomy & Space Science / Australia Telescope
National Facility, PO BOX 76, Epping,
NSW 1710, Australia
2 - Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, C/ Vía Láctea S/N, 38200 La
Laguna, Tenerife, Spain
3 - Departamento de Astrofísica de la Universidad de La Laguna, 38071
La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain
Received 29 January 2010 / Accepted 18 March 2010
Abstract
Aims. We have performed a comprehensive
multiwavelength analysis of a sample of 20 starburst galaxies that show
a substantial population of very young massive stars, most of them
classified as Wolf-Rayet (WR) galaxies. In this paper, the forth of the
series, we present the global analysis of the derived photometric and
chemical properties.
Methods. We compare optical/NIR
colours and the physical properties (reddening coefficient, equivalent
widths of the emission and underlying absorption lines, ionization
degree, electron density, and electron temperature) and chemical
properties (oxygen abundances and N/O, S/O, Ne/O, Ar/O, and Fe/O
ratios) with previous observations and galaxy evolution models. of the
electron temperature of the ionized gas.
Results. According to their absolute B-magnitude,
many of them are not dwarf galaxies, but they should be during their
quiescent phase. We found that both c(H![]() )
and
)
and ![]() increase with increasing metallicity. The differences in the N/O ratio
is explained assuming differences in the star formation histories. We
detected a high N/O ratio in objects showing strong WR features
(HCG 31 AC, UM 420, IRAS 0828+2816,
III Zw 107, ESO 566-8 and
NGC 5253). The ejecta of the WR stars may be the origin of the
N enrichment in these galaxies. We compared the abundances provided by
the direct method with those obtained through empirical calibrations,
finding that (i) the Pilyugin method is the best suited empirical
calibration for these star-forming galaxies; (ii) the relations
provided by Pettini & Pagel (2004, MNRAS, 348, 59) give
acceptable results for objects with
increase with increasing metallicity. The differences in the N/O ratio
is explained assuming differences in the star formation histories. We
detected a high N/O ratio in objects showing strong WR features
(HCG 31 AC, UM 420, IRAS 0828+2816,
III Zw 107, ESO 566-8 and
NGC 5253). The ejecta of the WR stars may be the origin of the
N enrichment in these galaxies. We compared the abundances provided by
the direct method with those obtained through empirical calibrations,
finding that (i) the Pilyugin method is the best suited empirical
calibration for these star-forming galaxies; (ii) the relations
provided by Pettini & Pagel (2004, MNRAS, 348, 59) give
acceptable results for objects with ![]() > 8.0; and (iii) the results provided by empirical calibrations
based on photoionization models are systematically 0.2-0.3 dex higher
than the values derived from the direct method. The O and N abundances
and the N/O ratios are clearly related to the optical/NIR
luminosity; the dispersion of the data is a consequence of the
differences in the star-formation histories. The L-Z
relations tend to be tighter when using NIR
luminosities, which facilitates distinguishing tidal dwarf galaxies
candidates and pre-existing dwarf objects. Galaxies with redder colours
tend to have higher oxygen and nitrogen abundances.
> 8.0; and (iii) the results provided by empirical calibrations
based on photoionization models are systematically 0.2-0.3 dex higher
than the values derived from the direct method. The O and N abundances
and the N/O ratios are clearly related to the optical/NIR
luminosity; the dispersion of the data is a consequence of the
differences in the star-formation histories. The L-Z
relations tend to be tighter when using NIR
luminosities, which facilitates distinguishing tidal dwarf galaxies
candidates and pre-existing dwarf objects. Galaxies with redder colours
tend to have higher oxygen and nitrogen abundances.
Conclusions. Our detailed analysis is fundamental to
understand the nature of galaxies that show strong starbursts, as well
as to know their star formation history and the relationships with the
environment. This study is complementary -but usually more powerful- to
the less detailed analysis of large galaxy samples that are very common
nowadays.
Key words: galaxies: starburst - galaxies: interactions - galaxies: dwarf - galaxies: abundances - galaxies: photometry - stars: Wolf-Rayet
1 Introduction
The knowledge of the chemical composition of galaxies, in particular of dwarf galaxies, is vital for understanding their evolution, star formation history, stellar nucleosynthesis, the importance of gas inflow and outflow, and the enrichment of the intergalactic medium. Indeed, metallicity is a key ingredient for modelling galaxy properties, because it determines UV, optical and NIR colours at a given age (i.e., Leitherer et al. 1999), nucleosynthetic yields (e.g., Woosley & Weaver 1995), the dust-to-gas ratio (e.g., Hirashita et al. 2001), the shape of the interstellar extinction curve (e.g., Piovan et al. 2006), or even the properties of the Wolf-Rayet stars (Crowther 2007).
The most robust method to derive the metallicity in star-forming and starburst galaxies is via the estimate of metal abundances and abundance ratios, in particular through the determination of the gas-phase oxygen abundance and the nitrogen-to-oxygen ratio. The relationships between current metallicity and other galaxy parameters, such as colours, luminosity, neutral gas content, star-formation rate, extinction or total mass, constrain galaxy-evolution models and give clues about the current stage of a galaxy. For example, is still debated whether massive star formation results in the instantaneous enrichment of the interstellar medium of a dwarf galaxy, or if the bulk of the newly synthesized heavy elements must cool before becoming part of the interstellar medium (ISM) that eventually will form the next generation of stars. Accurate oxygen abundance measurements of several H II regions within a dwarf galaxy will increase the understanding of its chemical enrichment and mixing of enriched material. The analysis of the kinematics of the ionized gas will also help to understand the dynamic stage of galaxies and reveal recent interaction features. Furthermore, detailed analyses of starburst galaxies in the nearby Universe are fundamental to interpret the observations of high-z star forming galaxies, such as Lyman Break Galaxies (Erb et al. 2003), as well as quantify the importance of interactions in the triggering of the star-formation bursts, which seem to be very common at higher redshifts (i.e., Kauffmann & White 1993; Springel et al. 2005).
The comparison of the metallicity (which reflects the gas
reprocessed by stars and any exchange of gas between the galaxy and its
environment) with the stellar mass (which reflects the amount of gas
locked up into stars) provides key clues about galaxy formation and
evolution. These analyses have shown a clear correlation between mass
and metallicity. In practice, luminosity has been used as substitute of
mass because of the difficulty of deriving reliable galaxy masses,
yielding to the so-called metallicity-luminosity relation (i.e., Rubin
et al. 1984;
Richer & McCall 1995;
Salzer et al. 2005),
although in recent years mass-metallicity relations are also explored
(i.e., Tremonti et al. 2004;
Kewley & Elisson 2008),
and are studied even at high redshifts (i.e., Kobulnicky
et al. 1999;
Pettini et al. 2001;
Kobulnicky & Kewley 2004;
Erb et al. 2006;
Liang et al. 2006).
The evolution of such relationships are now predicted by semi-analytic
models of galaxy formation within the ![]() -cold dark matter framework
that include chemical hydrodynamic simulations (De Lucia
et al. 2004;
Tissera et al. 2005;
De Rossi et al. 2006;
Davé & Oppenheimer 2007).
Ironically, today the main problem is not to estimate the mass of a
galaxy but its real metallicity, so that different methods involving
direct estimates of the oxygen abundance, empirical calibrations using
bright emission-line ratios or theoretical methods based on
photoionization models yield very different values (i.e., Yin
et al. 2007;
Kewley & Elisson 2008).
-cold dark matter framework
that include chemical hydrodynamic simulations (De Lucia
et al. 2004;
Tissera et al. 2005;
De Rossi et al. 2006;
Davé & Oppenheimer 2007).
Ironically, today the main problem is not to estimate the mass of a
galaxy but its real metallicity, so that different methods involving
direct estimates of the oxygen abundance, empirical calibrations using
bright emission-line ratios or theoretical methods based on
photoionization models yield very different values (i.e., Yin
et al. 2007;
Kewley & Elisson 2008).
Hence precise photometric and spectroscopic data, including a detailed analysis of each particular galaxy that allows conclusions about its nature, are crucial to address these issues. We performed such a detailed photometric and spectroscopic study in a sample of strong star-forming galaxies, many of them previously classified as dwarf galaxies. The majority of these objects are Wolf-Rayet (WR) galaxies, a very inhomogeneous class of star-forming objects which share at least an ongoing or recent star formation event that has produced stars sufficiently massive to evolve into the WR stage (Schaerer et al. 1999). However, WR features in the spectra of a galaxy provides useful information about the star-formation processes in the system. As the first WR stars typically appear around 2-3 Myr after the starburst is initiated and disappear within some 5 Myr (Meynet & Maeder 2005), their detection gives indications about both the youth and strength of the burst, offering the opportunity to study an approximately coeval sample of very young starbursts (Schaerer & Vacca 1998).
The main aim of our study of the formation of massive stars in
starburst galaxies and the role that the interactions with or between
dwarf galaxies and/or low surface brightness objects have in its
triggering mechanism. In Paper I (López-Sánchez &
Esteban 2008)
we described the motivation of this work, compiled the list of the 20
analysed WR galaxies (Table 1 of
Paper I), the majority of them showing several sub-regions or
objects within or surrounding them, and presented the results of the
optical/NIR broad-band and H![]() photometry. In Paper II (López-Sánchez & Esteban 2009) we presented
the results of the analysis of the intermediate resolution long-slit
spectroscopy of 16 WR galaxies of our sample - the results for the
other four galaxies were published separately. In many cases, two or
more slit positions were used to analyse the most interesting zones,
knots or morphological structures belonging to each galaxy or even
surrounding objects. Paper III (López-Sánchez &
Esteban 2010)
presented the analysis of the O and WR stellar populations within these
galaxies. In this paper, the forth of the series, we globally compile
and analyse the optical/NIR photometric data
(Sect. 2) and study the physical (Sect. 3) and
chemical (Sect. 4) properties of the ionized gas within our
galaxy sample. Thirty-one up to 41 regions have a direct estimate of
the electron temperature of the ionized gas, and hence the element
abundances were derived with the direct method.
Section 4 includes the analysis of the N/O ratio with the
oxygen abundance, a discussion of the nitrogen enrichment in WR
galaxies, a study of the
photometry. In Paper II (López-Sánchez & Esteban 2009) we presented
the results of the analysis of the intermediate resolution long-slit
spectroscopy of 16 WR galaxies of our sample - the results for the
other four galaxies were published separately. In many cases, two or
more slit positions were used to analyse the most interesting zones,
knots or morphological structures belonging to each galaxy or even
surrounding objects. Paper III (López-Sánchez &
Esteban 2010)
presented the analysis of the O and WR stellar populations within these
galaxies. In this paper, the forth of the series, we globally compile
and analyse the optical/NIR photometric data
(Sect. 2) and study the physical (Sect. 3) and
chemical (Sect. 4) properties of the ionized gas within our
galaxy sample. Thirty-one up to 41 regions have a direct estimate of
the electron temperature of the ionized gas, and hence the element
abundances were derived with the direct method.
Section 4 includes the analysis of the N/O ratio with the
oxygen abundance, a discussion of the nitrogen enrichment in WR
galaxies, a study of the ![]() -elements
to oxygen ratio with the oxygen abundance, and the comparison of the
results provided by the most common empirical calibrations with those
derived following the direct method (the Appendix compiles all
metallicity calibrations used in this work). Section 5
analyses the metallicity-luminosity relations obtained with our data.
Section 6 discusses the relations between the metallicity and
the optical/
-elements
to oxygen ratio with the oxygen abundance, and the comparison of the
results provided by the most common empirical calibrations with those
derived following the direct method (the Appendix compiles all
metallicity calibrations used in this work). Section 5
analyses the metallicity-luminosity relations obtained with our data.
Section 6 discusses the relations between the metallicity and
the optical/![]() colours. Finally, we list our main conclusions in Sect. 7.
colours. Finally, we list our main conclusions in Sect. 7.
The final paper of the series (Paper V) will compile the properties derived with data from other wavelengths (UV, FIR, radio, and X-ray) and complete a global analysis of all available multiwavelength data of our WR galaxy sample. We have produced the most comprehensive data set of these galaxies so far, involving multiwavelength results and analysed according to the same procedures.
2 Global analysis of magnitudes and colours
Table 1: Compilation of the broad-band photometric dataa for the individual galaxies analysed in this work.
Our optical and NIR broad-band photometric
results for the galaxy sample were presented in Paper I. These
data allowed us the analysis of the optical and NIR
magnitudes and the colours of the galaxies and surrounding dwarf
objects. Table 1
compiles the optical/NIR results for the individual
galaxies, not considering regions within them or nearby diffuse
objects. This table shows the colour excess, E(B-V)
(derived with the Balmer decrement in our optical spectra, see
Paper II), the absolute B-magnitude (both
corrected, MB,
and uncorrected, ![]() ,
for extinction), all the optical/NIR colours, and
the age of the most recent star-formation burst (the young population,
derived from our H
,
for extinction), all the optical/NIR colours, and
the age of the most recent star-formation burst (the young population,
derived from our H![]() images) and the minimum age of the old stellar population (usually
estimated from the low luminosity component or regions without nebular
emission using our optical/NIR broad-band images).
images) and the minimum age of the old stellar population (usually
estimated from the low luminosity component or regions without nebular
emission using our optical/NIR broad-band images).
Our first result from Table 1 is that the
actual number of dwarf galaxies, defined as ![]() ,
is not as high as we had expected considering the selection criteria of
our WR galaxy sample. There are two reasons for this: (i) on the one
hand, the determination of the magnitudes was performed in a more
accurate way. As our images are deeper than those previously obtained,
the integrated magnitude of a diffuse object is lower
than that estimated before. (ii) On the other hand, we corrected all
our data for extinction, but not only considering the effect of the
dust in the Milky Way as it is usually done, but taking into account
the internal extinction derived from our spectroscopic data. That is
why only six galaxies (Mkn 5, SBS 0926+606,
SBS 1054+365, SBS 1211+540, SBS 1415+437 and
NGC 5253) are strictly classified as dwarf galaxies following
the above definition. POX 4, SBS 0948+532 and
SBS 1319+579 could be also considered dwarf galaxies because
,
is not as high as we had expected considering the selection criteria of
our WR galaxy sample. There are two reasons for this: (i) on the one
hand, the determination of the magnitudes was performed in a more
accurate way. As our images are deeper than those previously obtained,
the integrated magnitude of a diffuse object is lower
than that estimated before. (ii) On the other hand, we corrected all
our data for extinction, but not only considering the effect of the
dust in the Milky Way as it is usually done, but taking into account
the internal extinction derived from our spectroscopic data. That is
why only six galaxies (Mkn 5, SBS 0926+606,
SBS 1054+365, SBS 1211+540, SBS 1415+437 and
NGC 5253) are strictly classified as dwarf galaxies following
the above definition. POX 4, SBS 0948+532 and
SBS 1319+579 could be also considered dwarf galaxies because ![]() .
Table 1
also lists some tidal dwarf galaxy (TDG) candidates
(HCG 31 E, F1 and F2; Mkn 1087 #1 and #3,
POX 4 Comp) and nearby external objects
(Mkn 1087 N, Mkn 1199 NE,
IRAS 08309+6517 C, Tol 1457-262 #15 and #16)
surrounding a main galaxy.
However, as we remarked in Paper I and in the analysis of the
HCG 31 members (López-Sánchez et al. 2004a), we must
keep in mind that the B-magnitude of a starburst is
increased
by several magnitudes during the first 10 Myr with respect to
its brightness in the quiescent phase, so we should expect that some of
the objects with
.
Table 1
also lists some tidal dwarf galaxy (TDG) candidates
(HCG 31 E, F1 and F2; Mkn 1087 #1 and #3,
POX 4 Comp) and nearby external objects
(Mkn 1087 N, Mkn 1199 NE,
IRAS 08309+6517 C, Tol 1457-262 #15 and #16)
surrounding a main galaxy.
However, as we remarked in Paper I and in the analysis of the
HCG 31 members (López-Sánchez et al. 2004a), we must
keep in mind that the B-magnitude of a starburst is
increased
by several magnitudes during the first 10 Myr with respect to
its brightness in the quiescent phase, so we should expect that some of
the objects with ![]() are indeed defined as dwarf objects during their quiescent phase.
are indeed defined as dwarf objects during their quiescent phase.
![\begin{figure}
\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f01.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg188.png)
|
Figure 1:
Comparison between the reddening-corrected absolute B-magnitudes
(MB) and
the uncorrected ones (
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
In order to quantify the effect of the correction for extinction, we
plot the uncorrected absolute B-magnitude versus
the absolute B-magnitude corrected for extinction
in Fig. 1.
We did not consider the correction for the emission of the gas in the
absolute magnitude because (i) it is small in the B-filter,
less than 0.10 magnitudes and, more important; (ii) we are considering
the magnitude of the galaxy as a whole, taking into account both the
star-forming bursts and regions dominated by older stellar populations
that do not possess any nebular emission. From
Fig. 1,
we see that the magnitudes corrected for extinction are on average
around 0.60 magnitudes lower than when this effect is not considered.
As all data lie in a narrow band, we performed a linear fit, finding
the following relation between both magnitudes:
| (1) |
For MB=-18, the magnitude difference is
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=17cm,clip]{14156f02.eps}\vspace*{-1.5mm}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg192.png)
|
Figure 2:
Colour-colour diagrams comparing the predictions given
by evolutionary synthesis models (continous line: BC03, Bruzual
& Charlot 2003,
models; discontinuous line: PEGASE.2, Fioc & Rocca-Volmerange 1997, models; dotted
line: STARBURST 99, Leitherer et al. 1999,
assuming Z=0.4 |
| Open with DEXTER | |
As we explained in Paper I, we compared our optical/NIR
colours
(corrected for extinction and emission of the ionized gas)
with the predictions given by three different population synthesis
models, STARBURST99 (Leitherer et al. 1999), PEGASE.2
(Fioc & Rocca-Volmerange 1997)
and Bruzual & Charlot (2003),
to estimate the age of the dominant stellar population of
the galaxies, the star-forming regions, and the underlying stellar
component. We assumed an instantaneous
burst with a Salpeter IMF a total mass of 106
![]() ,
and a
metallicity of Z/
,
and a
metallicity of Z/![]() = 0.2, 0.4 and 1 (chosen as a
function of the
oxygen abundance of the galaxy derived from our spectroscopic
data, see Paper II) for all models.
= 0.2, 0.4 and 1 (chosen as a
function of the
oxygen abundance of the galaxy derived from our spectroscopic
data, see Paper II) for all models.
We found a relatively
good correspondence (see Figs. 37-39, top, in Paper I) between
the optical/NIR data and the models, especially for
compact and dwarf objects
such as HCG 31 F1 or SBS 0948+532, the ages being consistent
with a recent star-formation event (![]() 100 Myr). We remark here
100 Myr). We remark here
- 1.
- the quality of the observational data and the data reduction process, which was performed in detail and in an homogeneous way for all galaxies,
- 2.
- the we corrected the data for extinction and reddening,
considering the c(H
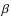 )
value derived from the spectroscopic data obtained for each region
(Paper II). As we have seen, this correction is important and
very often it is not performed in the analysis of the colours of
extragalactic objects, which only consider the extinction of the Milky
Way in the direction to the analysed galaxy,
)
value derived from the spectroscopic data obtained for each region
(Paper II). As we have seen, this correction is important and
very often it is not performed in the analysis of the colours of
extragalactic objects, which only consider the extinction of the Milky
Way in the direction to the analysed galaxy,
- 3.
- and the correction of the colours for the gas emission using our spectroscopic data. This effect is not important in some galaxies, but it seems fundamental when analysing compact objects with strong nebular emission, such as BCDGs or regions within a galaxy possessing an strong starburst.
Figure 2 shows several colour-colour diagrams comparing the predictions given by evolutionary synthesis models with the colours (corrected for both reddening and contribution of the emission lines) of our galaxy sample when the burst (blue stars) and underlying component (UC, red squares) of each system are considered independently. The correspondence has improved now. Indeed, all inferred ages of the most recent star-formation burst are lower than 25 Myr, while the data corresponding to the underlying component suggest ages higher than 100 Myr. Therefore, a proper estimate of the stellar population age for this type of galaxy using broad-band filters is only obtained when bursts and underlying components are independently considered.
There are still some discrepancies that can be explained by a
lack of good separation between regions with and without star-formation
activity. The comparison of the V-R
colour vs. the
U-B colour in data of the UC also
suggest that in some galaxies the old stellar population
colours are not explained by just one single-age population, but at
least two of them are needed (i.e., for SBS 1415+437, the UC
colour may be explained by a mix of two stellar populations with ages
of ![]() 150 Myr and
150 Myr and ![]() 500 Myr, see
Sect. 3.15.1 in Paper I). However, the best method to
analyse the colours and luminosities
of the host component in starburst systems (specially, in BCGs) is
performing a careful 2D analysis of their structural parameters (i.e.
Amorín et al. 2007,
2009). Some
of the galaxies analysed by these authors were also studied here. Their
results of the colours of the UC (the host) agree well within
the errors with those estimated here, for example, for Mkn 5
they compute
500 Myr, see
Sect. 3.15.1 in Paper I). However, the best method to
analyse the colours and luminosities
of the host component in starburst systems (specially, in BCGs) is
performing a careful 2D analysis of their structural parameters (i.e.
Amorín et al. 2007,
2009). Some
of the galaxies analysed by these authors were also studied here. Their
results of the colours of the UC (the host) agree well within
the errors with those estimated here, for example, for Mkn 5
they compute ![]() and
and ![]() ,
while in this work we derived
,
while in this work we derived ![]() and
and ![]() for the same object.
for the same object.
Figure 3
plots the H![]() equivalent width (obtained from our narrow-band images) as a function
of the U-B colour (obtained from
our broad-band images) for the bursts within the analysed galaxies. We
remark that the W(H
equivalent width (obtained from our narrow-band images) as a function
of the U-B colour (obtained from
our broad-band images) for the bursts within the analysed galaxies. We
remark that the W(H![]() derived from the H
derived from the H![]() images agree quite well with those obtained from the optical
spectroscopy (see Paper II). This figure compares the
observational data with some STARBURST 99
models (Leitherer et al. 1999) at
different metallicities. As we see, the agreement is quite good for
almost all objects. This also indicates both the quality of our data
and the success of the theoretical models to reproduce the young
star-forming populations.
images agree quite well with those obtained from the optical
spectroscopy (see Paper II). This figure compares the
observational data with some STARBURST 99
models (Leitherer et al. 1999) at
different metallicities. As we see, the agreement is quite good for
almost all objects. This also indicates both the quality of our data
and the success of the theoretical models to reproduce the young
star-forming populations.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f03.eps} %
\vspace*{-2.5mm}\vspace*{4mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg202.png)
|
Figure 3:
W(H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Table 2: Physical properties of the ionized gas for the galaxies analysed in this work.
However, if we compare the W(H![]() and the U-B colour considering
the total extension of each galaxy (and not only the burst component),
this agreement is less good. In this case, data with a fixed W(H
and the U-B colour considering
the total extension of each galaxy (and not only the burst component),
this agreement is less good. In this case, data with a fixed W(H![]() have a redder U-B colour than
that predicted by the models. This is explained because the U-B
colour is slightly contaminated with the light of older stellar
populations or regions with no nebular emission. Hence, as we
emphasized before, it is important to distinguish between the pure
starburst regions and the underlying component to get a good estimate
of the properties of these galaxies and, in particular, the strong
star-forming regions.
have a redder U-B colour than
that predicted by the models. This is explained because the U-B
colour is slightly contaminated with the light of older stellar
populations or regions with no nebular emission. Hence, as we
emphasized before, it is important to distinguish between the pure
starburst regions and the underlying component to get a good estimate
of the properties of these galaxies and, in particular, the strong
star-forming regions.
The age of the last starburst event experienced by each galaxy and the minimum age of its old stellar populations are compiled in the last two columns of Table 1. Except for a few objects (HCG 31 members E, F1 and F2 and Mkn 1087 members N and #1) for which it was not possible to estimate the colours of the UC, all analysed galaxies show an older stellar population underlying the bursts. Indeed, in many cases the colours of the UC suggest ages older than 500 Myr. This clearly indicates that all galaxies have experienced a previous star-formation events long time before those they are now hosting, as concluded in many other previous results (i.e. Cairós et al. 2001a,b; Bergvall & Östlin 2002; Papaderos et al. 2006; Amorín et al. 2009). However, as we previously said (López-Sánchez et al. 2004a), this seems not to be true in the particular case of members F of HCG 31, which clearly show no evidences of underlying old stellar populations. This was recently confirmed by deep Hubble Space Telescope imaging (Gallagher et al. 2010), and hence these two objects are very likely experiencing their very first star-formation event.
Table 3: Chemical properties of the ionized gas for the galaxies analysed in this work.
3 Physical properties of the ionized gas
Table 2
compiles all the high- and low-ionization electron temperatures of the
ionized gas, ![]() ,
electron density
,
electron density ![]() ,
reddenning coefficient c(H
,
reddenning coefficient c(H![]() ), equivalent width of the
underlying stellar absorption in the Balmer H I
lines
), equivalent width of the
underlying stellar absorption in the Balmer H I
lines ![]() ,
and the H
,
and the H![]() equivalent width, for the galaxies analysed in this work (see
Paper II). Thirty-one up to 41 of the objects listed in
Table 2
have a direct estimate of the electron temperature of the ionized gas.
For most, this was computed using the [O III]
ratio involving the nebular [O III]
equivalent width, for the galaxies analysed in this work (see
Paper II). Thirty-one up to 41 of the objects listed in
Table 2
have a direct estimate of the electron temperature of the ionized gas.
For most, this was computed using the [O III]
ratio involving the nebular [O III] ![]() 4959,5007
and the auroral [O III]
4959,5007
and the auroral [O III] ![]() 4363
emission lines. In most objects, the low-ionization electron
temperature was not computed directly but assuming the relation between
4363
emission lines. In most objects, the low-ionization electron
temperature was not computed directly but assuming the relation between
![]() (O III)
and
(O III)
and ![]() (O
II) provided by Garnett (1992). Half of
the objects of our galaxy sample (22) have electron densities lower
than 100 cm-3.
(O
II) provided by Garnett (1992). Half of
the objects of our galaxy sample (22) have electron densities lower
than 100 cm-3.
We explored possible correlations among some of the different
quantities compiled in Table 2 as well as the
oxygen abundance (see Table 3) computed for the
objects.
First, we checked the nature of the ionized gas of the sample galaxies.
Figure 4
plots the typical diagnostic diagrams between bright emission lines and
the predictions given by the photoionized models provided by Dopita
et al. (2000)
for extragalactic H II regions
(that assume instantaneous star-formation within star-forming regions)
and the Kewley et al. (2001)
models for starburst galaxies (which consider continuous star formation
and more realistic assumptions about the physics of starburst
galaxies). The dividing line given by the Kewley et al. (2001) models
represents an upper envelope of positions of star-forming galaxies. As
we see, in all cases the data are found below the theoretical
prediction given by this line. This indicates that photoionization is
the main excitation mechanism of the gas.
We will get the same result when we compare the relation between the FIR
and the radio-continuum luminosities (Paper V). It is
interesting to notice that the observational points included in the
diagnostic diagram involving the [O III]/H![]() and [N II]/H
and [N II]/H![]() ratios are located close to the prediction given by the Dopita
et al. (2000)
models, while points included in the diagnostic diagram that considers
the [O III]/H
ratios are located close to the prediction given by the Dopita
et al. (2000)
models, while points included in the diagnostic diagram that considers
the [O III]/H![]() and [S II]/H
and [S II]/H![]() ratios are found very close to the upper envelope given by Kewley
et al. (2001).
The left panel in Fig. 4 includes the
empirical relation between the [O III]/H
ratios are found very close to the upper envelope given by Kewley
et al. (2001).
The left panel in Fig. 4 includes the
empirical relation between the [O III]/H![]() and the [N II]/H
and the [N II]/H![]() ratios provided by Kauffmann et al. (2003) analysing
a large data sample of star-forming galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky
Survey (SDSS; York et al. 2000).
As can be seen, the comparison of the Kauffmann et al. (2003) relation
with our data points also indicates that our objects are experiencing a
pure star-formation event, despite a clear offset between both
datasets.
ratios provided by Kauffmann et al. (2003) analysing
a large data sample of star-forming galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky
Survey (SDSS; York et al. 2000).
As can be seen, the comparison of the Kauffmann et al. (2003) relation
with our data points also indicates that our objects are experiencing a
pure star-formation event, despite a clear offset between both
datasets.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f04.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg617.png)
|
Figure 4: Comparison of some observational flux ratios obtained for all available regions analysed in this work with the diagnostic diagrams proposed by Dopita et al. (2000), blue continuous line (D00), and Kewley et al. (2001), red discontinuous line (K01). The left panel also shows the empirical relation provided by Kauffmann et al. (2003) with a dotted-dashed dark yellow line (Ka03). |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f05.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg618.png)
|
Figure 5:
High ionization electron temperature, |
| Open with DEXTER | |
W(H![]() )
is a good indicator for the age of the most recent star-formation
event. The hydrogen ionizing
flux of a star cluster gradually decreases as the most massive stars
disappear with time, and hence the width of H
)
is a good indicator for the age of the most recent star-formation
event. The hydrogen ionizing
flux of a star cluster gradually decreases as the most massive stars
disappear with time, and hence the width of H![]() decreases with time (see Papers I, II and III).
Figure 5
plots the relation between the high ionization electron temperature and
the H
decreases with time (see Papers I, II and III).
Figure 5
plots the relation between the high ionization electron temperature and
the H![]() equivalent width. As we see, |W(H
equivalent width. As we see, |W(H![]() )| increases
with increasing
)| increases
with increasing ![]() ,
but we must remember that there is a strong correlation between the
electron temperature and the oxygen abundance, as high-metallicity
H II regions cool more efficiently
than low-metallicity H II regions.
To study this effect, we used colours to plot four metallicity ranges
in Fig. 5.
These colours indicate the oxygen abundance range of each object:
<7.90, 7.90-8.15, 8.15-8.40 and >8.40, in units of
,
but we must remember that there is a strong correlation between the
electron temperature and the oxygen abundance, as high-metallicity
H II regions cool more efficiently
than low-metallicity H II regions.
To study this effect, we used colours to plot four metallicity ranges
in Fig. 5.
These colours indicate the oxygen abundance range of each object:
<7.90, 7.90-8.15, 8.15-8.40 and >8.40, in units of ![]() .
Although now it is not so evident, it still seems that regions with
larger |W(H
.
Although now it is not so evident, it still seems that regions with
larger |W(H![]() )| tend to have higher
)| tend to have higher ![]() .
This indicates that younger bursts have a larger ionization budgets and
are therefore capable to heat the ionized gas to higher electron
temperatures. Another effect that we should
considered here is that galaxies with higher metallicity (and hence
with lower electron temperature) usually have a higher absorption in
the H
.
This indicates that younger bursts have a larger ionization budgets and
are therefore capable to heat the ionized gas to higher electron
temperatures. Another effect that we should
considered here is that galaxies with higher metallicity (and hence
with lower electron temperature) usually have a higher absorption in
the H![]() line than low-metallicity objects because of older stellar populations.
Indeed, it is interesting to note that objects in the metallicity range
line than low-metallicity objects because of older stellar populations.
Indeed, it is interesting to note that objects in the metallicity range
![]() may
have any value of W(H
may
have any value of W(H![]() ). This is very probably
because within this metallicity range lie both dwarf objects with no
underlying old stellar population (i.e., HCG 31 F,
SBS 0948+532) and galaxies which possess a considerable amount
of old stars (i.e, HCG 31 B, Mkn 5).
). This is very probably
because within this metallicity range lie both dwarf objects with no
underlying old stellar population (i.e., HCG 31 F,
SBS 0948+532) and galaxies which possess a considerable amount
of old stars (i.e, HCG 31 B, Mkn 5).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f06.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg620.png)
|
Figure 6:
O++/O+ ratio vs. W(H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Figure 6
shows that the ionization degree of the ionized gas of the starburts
seems to increase with the increasing of |W(H![]() )|. This is
a relation similar to that found in Fig. 5 and also indicates
that younger bursts harbour a higher proportion of massive stars and
therefore their associated H II regions
have larger ionization parameters. That is evident in
NGC 5253 A, B and HCG 31 F, which
show both the highest values of the |W(H
)|. This is
a relation similar to that found in Fig. 5 and also indicates
that younger bursts harbour a higher proportion of massive stars and
therefore their associated H II regions
have larger ionization parameters. That is evident in
NGC 5253 A, B and HCG 31 F, which
show both the highest values of the |W(H![]() )| and the O++/O+
ratio and possess the youngest star-formation bursts (see
Table 1).
The increasing of the O++/O+
ratio as increasing |W(H
)| and the O++/O+
ratio and possess the youngest star-formation bursts (see
Table 1).
The increasing of the O++/O+
ratio as increasing |W(H![]() )| seems to be independent of
the metallicity, although galaxies with higher metallicity tend to show
the lowest ionization degrees.
)| seems to be independent of
the metallicity, although galaxies with higher metallicity tend to show
the lowest ionization degrees.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f07.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg621.png)
|
Figure 7:
Reddening coefficient, c(H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f08.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg622.png)
|
Figure 8:
Equivalent width of the underlying stellar absorption in the Balmer
H I lines, |
| Open with DEXTER | |
The dependence of the reddening coefficient as a function of
other parameters is also interesting. Figure 7 plots c(H![]() )
vs. the oxygen abundance. Although the dispersion of the data is rather
scattered, we see a clear dependence: the reddening coefficient is
higher at higher metallicities. We should expect this result, because
galaxies with higher oxygen abundance are chemically more evolved and
should contain a larger proportion of dust particles that absorbs the
nebular emission.
)
vs. the oxygen abundance. Although the dispersion of the data is rather
scattered, we see a clear dependence: the reddening coefficient is
higher at higher metallicities. We should expect this result, because
galaxies with higher oxygen abundance are chemically more evolved and
should contain a larger proportion of dust particles that absorbs the
nebular emission.
Another interesting relation is shown in Fig. 8, which plots the
equivalent width of the stellar absorption underlying the H I
Balmer lines (
![]() )
as a function of the oxygen abundance. We can see that objects with
higher metallicities show larger
)
as a function of the oxygen abundance. We can see that objects with
higher metallicities show larger ![]() .
More metallic galaxies correspond to more massive and chemically
evolved systems, which means that they have consumed a larger fraction
of their gas and the stellar component should be comparatively more
important.
The data corresponding to the lowest metallicity objects analysed in
this work (SBS 1415+579 and SBS 1211+540) show a
value of
.
More metallic galaxies correspond to more massive and chemically
evolved systems, which means that they have consumed a larger fraction
of their gas and the stellar component should be comparatively more
important.
The data corresponding to the lowest metallicity objects analysed in
this work (SBS 1415+579 and SBS 1211+540) show a
value of ![]() relatively high what is to be for them. This suggests a considerable
underlying stellar population in these very low-metallicity galaxies,
as we already discussed (see Sects. 3.15 and 3.13 of
Paper I).
relatively high what is to be for them. This suggests a considerable
underlying stellar population in these very low-metallicity galaxies,
as we already discussed (see Sects. 3.15 and 3.13 of
Paper I).
Figure 9
plots W(H![]() )
vs. the oxygen abundance. The very large dispersion of W(H
)
vs. the oxygen abundance. The very large dispersion of W(H![]() )
for
)
for ![]() of about 8.0 is remarkable, but it also seems clear that galaxies with
O/H ratios higher than that value tend to have |W(H
of about 8.0 is remarkable, but it also seems clear that galaxies with
O/H ratios higher than that value tend to have |W(H![]() )
)![]() 100 Å and, conversely, galaxies with lower oxygen abundances
show |W(H
100 Å and, conversely, galaxies with lower oxygen abundances
show |W(H![]() )
)![]() 100 Å. This behaviour may be be related to the results in
Fig. 8,
in the sense that more metallic objects tend to have a higher
underlying stellar absorption that can lead to an underestimation of |W(H
100 Å. This behaviour may be be related to the results in
Fig. 8,
in the sense that more metallic objects tend to have a higher
underlying stellar absorption that can lead to an underestimation of |W(H![]() )|. Indeed,
Fig. 9
also compares our observational data with the predictions given by the
chemical evolution models of H II galaxies
provided by Martín-Manjón et al. (2008). They
assumed the star formation as a set of successive bursts, each galaxy
experiencing 11 star-formation bursts along its evolution of 13.2 Gyr.
Figure 9
includes the results for the first (t=0 Gyr), second
(t=1.3 Gyr) and last (t=13.2 Gyr)
bursts for a model that considers an attenuated bursting star-formation
mode and that 1/3 of the gas is always used to form stars in each
time-step. As we see, all the strong starbursting systems are located
between the positions of the first and second burst models, confirming
that although the dominant stellar population is certainly very young,
previous star-formation events in the last 500-1000 Myr are needed to
explain our observational data points. This agrees well with the
minimum ages of the underlying stellar component we derived using our
photometric data (see Sect. 2 and last column of
Table 1).
The Martín-Manjón et al. (2008)
models also explain the large dispersion of W(H
)|. Indeed,
Fig. 9
also compares our observational data with the predictions given by the
chemical evolution models of H II galaxies
provided by Martín-Manjón et al. (2008). They
assumed the star formation as a set of successive bursts, each galaxy
experiencing 11 star-formation bursts along its evolution of 13.2 Gyr.
Figure 9
includes the results for the first (t=0 Gyr), second
(t=1.3 Gyr) and last (t=13.2 Gyr)
bursts for a model that considers an attenuated bursting star-formation
mode and that 1/3 of the gas is always used to form stars in each
time-step. As we see, all the strong starbursting systems are located
between the positions of the first and second burst models, confirming
that although the dominant stellar population is certainly very young,
previous star-formation events in the last 500-1000 Myr are needed to
explain our observational data points. This agrees well with the
minimum ages of the underlying stellar component we derived using our
photometric data (see Sect. 2 and last column of
Table 1).
The Martín-Manjón et al. (2008)
models also explain the large dispersion of W(H![]() )
for
)
for ![]() of about 8.0, as well as the trend that more metal rich galaxies have
lower values of |W(H
of about 8.0, as well as the trend that more metal rich galaxies have
lower values of |W(H![]() )| because of the effects of
the underlying stellar populations.
)| because of the effects of
the underlying stellar populations.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f09.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg625.png)
|
Figure 9:
H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Another indication of the effect of the underlying evolved stellar
population is found in Fig. 10, which
compares the [O III] ![]() 5007 line flux with the W(H
5007 line flux with the W(H![]() )
of the sample galaxies with the model predictions by Schaerer &
Leitherer (2001). Although a general good correspondence is found, some
of the objects are slightly displaced to the left - lower W(H
)
of the sample galaxies with the model predictions by Schaerer &
Leitherer (2001). Although a general good correspondence is found, some
of the objects are slightly displaced to the left - lower W(H![]() )
- of the models predictions, suggesting that perhaps the measured
values of |W(H
)
- of the models predictions, suggesting that perhaps the measured
values of |W(H![]() )| are underestimated for some
of them that precisely coincide with those with a larger oxygen
abundance, as we also concluded before.
)| are underestimated for some
of them that precisely coincide with those with a larger oxygen
abundance, as we also concluded before.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f10.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg626.png)
|
Figure 10:
F([O III] |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f11.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg627.png)
|
Figure 11:
(Left) N/O ratio vs. oxygen abundance for all
objects with a direct estimate of |
| Open with DEXTER | |
4 Chemical abundances of the ionized gas
Table 3
compiles the oxygen abundance, the O++/O+
ratio and the N/O, S/O, Ne/O, Ar/O, and Fe/O ratios (all in logarithmic
units) for all galaxies analysed in this work. As we already said, 31
up to the 41 independent regions within the WR galaxy sample analysed
here have a direct estimate of the electron temperature (as indicated
in Table 3).
Figure 11
(left) plots the N/O ratio vs. the oxygen abundance for all our data
with a direct estimate of the electron temperature and its comparison
with previous samples involving similar objects and ![]() -based
(Izotov & Thuan 1999;
Izotov et al. 2004).
This figure shows that the position of our data agrees with that
obtained using other observations. The errors we estimated in our
objects are in general higher than those reported by Izotov &
Thuan (1999)
and Izotov et al. (2004)
basically because we used different criteria for estimating
observational errors, which are more conservative as well as more
realistic in our opinion. We also point out that our data are always of
higher spectral and spatial resolution than those obtained by the
aforementioned authors, and have a similar or even higher
signal-to-noise ratio in many cases. This is an important point to be
clarified because non-specialist in the spectra of ionized nebulae may
interpret that lower quoted uncertainties are synonymous of better
observational data, and this may not always be the case. Although the
errors in the electron temperatures derived using the empirical methods
are large, relative atomic abundances (such as the N/O ratio) are less
sensitive to the choice of
-based
(Izotov & Thuan 1999;
Izotov et al. 2004).
This figure shows that the position of our data agrees with that
obtained using other observations. The errors we estimated in our
objects are in general higher than those reported by Izotov &
Thuan (1999)
and Izotov et al. (2004)
basically because we used different criteria for estimating
observational errors, which are more conservative as well as more
realistic in our opinion. We also point out that our data are always of
higher spectral and spatial resolution than those obtained by the
aforementioned authors, and have a similar or even higher
signal-to-noise ratio in many cases. This is an important point to be
clarified because non-specialist in the spectra of ionized nebulae may
interpret that lower quoted uncertainties are synonymous of better
observational data, and this may not always be the case. Although the
errors in the electron temperatures derived using the empirical methods
are large, relative atomic abundances (such as the N/O ratio) are less
sensitive to the choice of ![]() .
Therefore they are used in many occasions to compare with the results
provided by previous observations or with the predictions given by
theoretical models.
.
Therefore they are used in many occasions to compare with the results
provided by previous observations or with the predictions given by
theoretical models.
4.1 The N/O ratio
Figure 11 (right) plots the N/O ratio vs. abox for all objects analysed in this work; the chemical abundances were derived either from the direct method or via empirical calibrations. We compare our data with the two galaxy samples previously indicated (Izotov & Thuan 1999; Izotov et al. 2004) and with other galaxy samples whose data have been obtained using empirical calibrations: Izotov et al. Izotov et al. 2006, whose data were extracted from the SDSS, and van Zee et al. (1998), who study data from H II regions within spiral galaxies with chemical abundances computed via the direct method or using the McGaugh 1994 empirical calibration. In some sense, the N/O ratio of a galaxy is an indicator of the time that has elapsed since the bulk of star formation occurred, or of the nominal age of the galaxy as suggested by Edmunds & Pagel 1978. Following the position of our data points in Fig. 11 we see that they follow the expected trend:
- 1.
- The N/O ratio is rather constant for
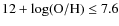 .
In our case, for the galaxies SBS 1211+540 and
SBS 1415+437 we derive log
.
In our case, for the galaxies SBS 1211+540 and
SBS 1415+437 we derive log 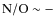 1.6, similar
values as those found by Izotov & Thuan (1999). These
authors explained the constant N/O ratio in very low-metallicity
objects assuming that the nitrogen is produced only as a primary
element in massive, short-life stars. However, other authors have
claimed that this may be not completely true (i.e., Henry
et al. 2000;
Pilyugin et al. 2003;
Mollá et al. 2006)
because of the lack of a clear mechanism that produces N in massive
stars besides the effect or the stellar rotation (Meynet &
Maeder 2005).
Furthermore, these galaxies already host old stellar populations, and
hence low- and intermediate-mass stars should be also releasing N to
the ISM. Henry et al. (2000)
explained the constancy of the N/O ratio in metal-poor galaxies by a
historically low star-formation rate, where almost all the nitrogen is
produced by 4-8
1.6, similar
values as those found by Izotov & Thuan (1999). These
authors explained the constant N/O ratio in very low-metallicity
objects assuming that the nitrogen is produced only as a primary
element in massive, short-life stars. However, other authors have
claimed that this may be not completely true (i.e., Henry
et al. 2000;
Pilyugin et al. 2003;
Mollá et al. 2006)
because of the lack of a clear mechanism that produces N in massive
stars besides the effect or the stellar rotation (Meynet &
Maeder 2005).
Furthermore, these galaxies already host old stellar populations, and
hence low- and intermediate-mass stars should be also releasing N to
the ISM. Henry et al. (2000)
explained the constancy of the N/O ratio in metal-poor galaxies by a
historically low star-formation rate, where almost all the nitrogen is
produced by 4-8 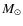 stars.
Additionally, Izotov et al. (2006) suggested
that the low dispersion of the data in this part of the diagram is
probably explained by the low number of WR stars that are expected at
very low-metallicity regimes.
stars.
Additionally, Izotov et al. (2006) suggested
that the low dispersion of the data in this part of the diagram is
probably explained by the low number of WR stars that are expected at
very low-metallicity regimes.
- 2.
- However, there is an important dispersion of the data in
the interval
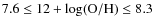 .
This problem has been analysed by several authors in the past (i.e.,
Kobulnicky & Skillman 1998;
Izotov & Thuan 1999;
Pilyugin et al. 2003;
Mollá et al. 2006).
Two main scenarios have been proposed for explaining this dispersion:
.
This problem has been analysed by several authors in the past (i.e.,
Kobulnicky & Skillman 1998;
Izotov & Thuan 1999;
Pilyugin et al. 2003;
Mollá et al. 2006).
Two main scenarios have been proposed for explaining this dispersion:
- (a)
- a loss of heavy element via galactic winds. In
particular, it should be a loss of
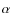 -elements via supernova
explosions.
-elements via supernova
explosions. 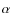 -elements,
such as oxygen, are produced in massive short-lived stars (Edmunds
& Pagel 1978;
Clayton & Pantelaki 1993).
Hence, the effect of supernova explosions would produce a
underabundance of oxygen (Esteban & Peimbert 1995), increasing
the N/O ratio. However, the observational evidence for low-mass
galaxies with galactic winds is still unclear (i.e. Marlowe
et al. 1995;
Bomans et al. 2007;
Dubois & Teyssier 2008; van Eymeren et al. 2008, 2009, 2010) and even the
numerical simulations give very discrepant results (i.e.,
Mac Low & Ferrara 1999;
Springel & Hernquist 2003;
Tenorio-Tagle et al. 2006;
Dubois & Teyssier 2008);
-elements,
such as oxygen, are produced in massive short-lived stars (Edmunds
& Pagel 1978;
Clayton & Pantelaki 1993).
Hence, the effect of supernova explosions would produce a
underabundance of oxygen (Esteban & Peimbert 1995), increasing
the N/O ratio. However, the observational evidence for low-mass
galaxies with galactic winds is still unclear (i.e. Marlowe
et al. 1995;
Bomans et al. 2007;
Dubois & Teyssier 2008; van Eymeren et al. 2008, 2009, 2010) and even the
numerical simulations give very discrepant results (i.e.,
Mac Low & Ferrara 1999;
Springel & Hernquist 2003;
Tenorio-Tagle et al. 2006;
Dubois & Teyssier 2008); - (b)
- a delayed release of nitrogen and elements produced in
low-mass long-lived stars compared to the
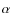 -elements. The N/O ratio drops
and the O/H ratio increases as supernovae release the
-elements. The N/O ratio drops
and the O/H ratio increases as supernovae release the 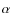 -elements
into the ISM. Consequently, the chemical properties of these galaxies
would vary very fast (few tens of Myr) during the starburst phase
(Kobulnicky & Skillman 1998). The
delayed-release hypothesis also predicts that BCDGs with high N/O
ratios are experiencing their first burst of massive star formation
after a relatively long quiescent
interval (oxygen has still not been completely delayed by massive stars
and mixed with the surrounding ISM), while those objects with low N/O
ratios have had little or no quiescent interval. However, recent
chemical evolution models suggest that the releasing and mixing of the
oxygen occurs almost instantaneously, and hence the delayed-release
scenario cannot explain BCDGs with high N/O ratio. If this is the case,
the most plausible explanation of the high N/O ratio observed in these
objects is the chemical pollution due to the winds of WR stars, which
are indeed ejecting N to the ISM, as we will discuss below.
-elements
into the ISM. Consequently, the chemical properties of these galaxies
would vary very fast (few tens of Myr) during the starburst phase
(Kobulnicky & Skillman 1998). The
delayed-release hypothesis also predicts that BCDGs with high N/O
ratios are experiencing their first burst of massive star formation
after a relatively long quiescent
interval (oxygen has still not been completely delayed by massive stars
and mixed with the surrounding ISM), while those objects with low N/O
ratios have had little or no quiescent interval. However, recent
chemical evolution models suggest that the releasing and mixing of the
oxygen occurs almost instantaneously, and hence the delayed-release
scenario cannot explain BCDGs with high N/O ratio. If this is the case,
the most plausible explanation of the high N/O ratio observed in these
objects is the chemical pollution due to the winds of WR stars, which
are indeed ejecting N to the ISM, as we will discuss below.
- 3.
- For moderate high-metallicities objects,
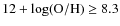 ,
the N/O ratio clearly increases with increasing oxygen abundance. This
trend seems to be a consequence of the metallicity-dependence of
nitrogen production in both massive and intermediate-mass stars (e.g.,
Pilyugin et al. 2003),
the N/O ratio increases at higher metallicities. Hence, nitrogen is
essentially a secondary element in this metallicity regime
(Torres-Peimbert 1989;
Vila-Costas & Edmunds 1993;
Henry et al. 2000;
van Zee & Haynes 2006).
Besides the uncertainties (that are higher than those estimated in
other objects because the
,
the N/O ratio clearly increases with increasing oxygen abundance. This
trend seems to be a consequence of the metallicity-dependence of
nitrogen production in both massive and intermediate-mass stars (e.g.,
Pilyugin et al. 2003),
the N/O ratio increases at higher metallicities. Hence, nitrogen is
essentially a secondary element in this metallicity regime
(Torres-Peimbert 1989;
Vila-Costas & Edmunds 1993;
Henry et al. 2000;
van Zee & Haynes 2006).
Besides the uncertainties (that are higher than those estimated in
other objects because the 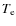 error is higher at higher metallicities) our data agree with the
tendency found in other galaxy samples, as that compiled by Pilyugin
et al. (2003).
However, notice that the galaxy sample compiled by van Zee
et al. (1998)
does not agree with our data, as her data have a systematically lower
N/O ratio. In some cases, differences higher than 0.5 dex in the N/O
ratio are found for a particular oxygen abundance. This discrepancy may
be partially explained by the fact that empirical calibrations from
photoionized models - van Zee et al. (1998) used McGaugh (1991) models -
seem to overestimate the actual oxygen abundance by at least 0.2 dex
(see below), and hence the derived N/O ratio is lower than the actual
value.
error is higher at higher metallicities) our data agree with the
tendency found in other galaxy samples, as that compiled by Pilyugin
et al. (2003).
However, notice that the galaxy sample compiled by van Zee
et al. (1998)
does not agree with our data, as her data have a systematically lower
N/O ratio. In some cases, differences higher than 0.5 dex in the N/O
ratio are found for a particular oxygen abundance. This discrepancy may
be partially explained by the fact that empirical calibrations from
photoionized models - van Zee et al. (1998) used McGaugh (1991) models -
seem to overestimate the actual oxygen abundance by at least 0.2 dex
(see below), and hence the derived N/O ratio is lower than the actual
value.
4.2 Nitrogen enrichment in WR galaxies
From Fig. 11, it is evident that there are some objects in the low-intermediate metallicity regime with a higher N/O ratio than expected for their oxygen abundance. An excess of nitrogen abundance has been reported in a few cases (e.g. Kobulnicky et al. 1997; Pustilnik et al. 2004). Remarkably, the common factor observed in all galaxies with a high N/O ratio is the detection of Wolf-Rayet features. Indeed, as we demonstrated in our analysis of NGC 5253 (López-Sánchez et al. 2007), the ejecta of WR stars may be the origin of a localized N (and probably also He) enrichment of the ISM in these galaxies.
The analysis of the WR populations within our sample galaxy
was performed in Paper III. The numbers of WNL and WCE stars
were computed assuming metallicity-dependent WR luminosities (Crowther
& Hadfield 2006).
We detected the blue WR bump (the broad He II
![]() 4686
emission line) in all objects with high N/O ratio: UM 420,
NGC 5253 A,B, HCG 31 AC,
IRAS 08208+2816, III Zw 107 and
ESO 566-8, indicating that these bursts host an important WNL
star population.
4686
emission line) in all objects with high N/O ratio: UM 420,
NGC 5253 A,B, HCG 31 AC,
IRAS 08208+2816, III Zw 107 and
ESO 566-8, indicating that these bursts host an important WNL
star population.
Figure 12
plots the observed nitrogen overabundance, ![]() ,
as a function of the derived WNL/(WNL+O) ratio. We do not see any clear
trend in this diagram, merely that the objects with a high N/O ratio do
not show a particularly high WNL/(WNL+O) ratio.
,
as a function of the derived WNL/(WNL+O) ratio. We do not see any clear
trend in this diagram, merely that the objects with a high N/O ratio do
not show a particularly high WNL/(WNL+O) ratio.
Galaxies HCG 31 AC and
III Zw 107 seem to show a slight nitrogen excess [
![]() dex]. Three of the galaxies with high N/O ratio compiled by Pustilnik
et al. (2004)
are plotted in Fig. 12:
NGC 5253 (already discussed), Mkn 1089
(HCG 31 AC) and UM 420. Our data confirm the
nitrogen overabundance in UM 420 [
dex]. Three of the galaxies with high N/O ratio compiled by Pustilnik
et al. (2004)
are plotted in Fig. 12:
NGC 5253 (already discussed), Mkn 1089
(HCG 31 AC) and UM 420. Our data confirm the
nitrogen overabundance in UM 420 [
![]() dex], but not a significant N/O ratio in HCG 31 AC [
dex], but not a significant N/O ratio in HCG 31 AC [
![]() dex; Pustilnik et al. (2004)
quoted
dex; Pustilnik et al. (2004)
quoted ![]() 0.5 dex].
We also find a relatively high N/O ratio in ESO 566-8 [
0.5 dex].
We also find a relatively high N/O ratio in ESO 566-8 [
![]() dex].
dex].
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f12.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg637.png)
|
Figure 12:
Observed nitrogen overabundance, |
| Open with DEXTER | |
The very rare occurrence of objects with a large N overabundance
suggests the general idea of the short-time scales for the localized
N pollution and its fast dispersal. Brinchmann et al. (2008) used
SDSS data to find that for |W(H![]() )
)![]() Å, WR galaxies show a high N/O compared to non-WR galaxies.
Quantitatively these authors found that on average
Å, WR galaxies show a high N/O compared to non-WR galaxies.
Quantitatively these authors found that on average ![]() (N/O)
(N/O)
![]() .
They interpreted this result as a rapid enrichment of the ISM from WR
winds. Brinchmann et al. (2008) also
found that WR galaxies are in general more metal-rich at a given
|W(H
.
They interpreted this result as a rapid enrichment of the ISM from WR
winds. Brinchmann et al. (2008) also
found that WR galaxies are in general more metal-rich at a given
|W(H![]() )|
than similar galaxies without WR features, which likely is a reflection
of WR stars being more abundant at higher metallicities (see
Fig. 5 of Paper III).
)|
than similar galaxies without WR features, which likely is a reflection
of WR stars being more abundant at higher metallicities (see
Fig. 5 of Paper III).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f13.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg642.png)
|
Figure 13:
H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Although we do not dismiss the statistical analysis performed by
Brinchmann et al. (2008)
comparing WR and non-WR galaxy data, we would like to warn about the
use of data with low spectral resolution in order to derive an accurate
nitrogen abundance in individual objects. This is commonly done via the
analysis of the [N II] ![]() 5683
emission line, very close to H
5683
emission line, very close to H![]() .
Lack of sufficient spectral resolution will derive a blending of both
lines and a probable over-estimation of the [N II]
.
Lack of sufficient spectral resolution will derive a blending of both
lines and a probable over-estimation of the [N II]
![]() 5683 flux,
that would be even higher if broad low-intensity wings in the H
5683 flux,
that would be even higher if broad low-intensity wings in the H![]() profile exist, which are actually rather common in WR galaxies (e.g.
Méndez & Esteban 1997).
On the other hand, as explained by Izotov et al. (2006), the bright
doublet [O II]
profile exist, which are actually rather common in WR galaxies (e.g.
Méndez & Esteban 1997).
On the other hand, as explained by Izotov et al. (2006), the bright
doublet [O II] ![]() 3726,3729 is
not observed in the SDSS spectra for nearby galaxies, and hence the
estimate of the total oxygen abundance has to be done via the [O II]
3726,3729 is
not observed in the SDSS spectra for nearby galaxies, and hence the
estimate of the total oxygen abundance has to be done via the [O II]
![]() 7319,7330, which is much
fainter, very dependent on the electron density and severely affected
by sky emission features.
Therefore their associated errors are usually larger than for the [O II]
7319,7330, which is much
fainter, very dependent on the electron density and severely affected
by sky emission features.
Therefore their associated errors are usually larger than for the [O II]
![]() 3726,3729 lines.
More data and a re-analysis of the chemical abundances in galaxies
where WR features are detected, with a similar analysis of a sample of
non-WR galaxies, are needed to get any definitive results.
3726,3729 lines.
More data and a re-analysis of the chemical abundances in galaxies
where WR features are detected, with a similar analysis of a sample of
non-WR galaxies, are needed to get any definitive results.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f14.eps}
\vspace*{2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg643.png)
|
Figure 14: Ne/O, S/O, Ar/O ang Fe/O ratios vs the oxygen abundance for the galaxies analysed in this work. We compare with the results provided by the galaxy samples considered by Izotov & Thuan (1999) and Izotov et al. (2006). The dashed dark-blue lines indicate a fit to our data. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Some authors (i.e. Izotov et al. 2006) suggest that
there is a dependence between the N/O ratio and the H![]() equivalent width: the N/O ratio should increase with decreasing |W(H
equivalent width: the N/O ratio should increase with decreasing |W(H![]() )|.
This trend was also observed by Brinchmann et al. (2008), but
only for objects with |W(H
)|.
This trend was also observed by Brinchmann et al. (2008), but
only for objects with |W(H![]() )
)![]() Å. Figure 13
plots the N/O ratio vs. W(H
Å. Figure 13
plots the N/O ratio vs. W(H![]() )
for the objects analysed here. In this figure we distinguish between
objects with high N/O ratio for their oxygen abundance and WR features
(yellow diamonds), and galaxies with a normal N/O ratio with (red
squares) or without (blue circles) WR features.
)
for the objects analysed here. In this figure we distinguish between
objects with high N/O ratio for their oxygen abundance and WR features
(yellow diamonds), and galaxies with a normal N/O ratio with (red
squares) or without (blue circles) WR features.
From Fig. 13
it is evident that non-WR galaxies only show high N/O ratios when their
|W(H![]() )|<
50 Å. Their N/O ratio becomes low for larger equivalent widths.
Brinchmann et al. (2008)
suggested that the non-detection of high N/O ratios in objects with
small equivalent widths is consistent with very young bursts where the
WR stars have not yet had a change to enrich the surrounding ISM to a
noticeable degree. However, this is probably a consequence of both the
complex star-formation histories and the high relative importance of
the old underlying stellar populations in these systems.
)|<
50 Å. Their N/O ratio becomes low for larger equivalent widths.
Brinchmann et al. (2008)
suggested that the non-detection of high N/O ratios in objects with
small equivalent widths is consistent with very young bursts where the
WR stars have not yet had a change to enrich the surrounding ISM to a
noticeable degree. However, this is probably a consequence of both the
complex star-formation histories and the high relative importance of
the old underlying stellar populations in these systems.
On the other hand it is remarkable that the WR galaxies with |W(H![]() )|<50
Å show systematically high N/O ratios, but a large dispersion when |W(H
)|<50
Å show systematically high N/O ratios, but a large dispersion when |W(H![]() )|>
50 Å. This dispersion becomes substantially smaller when we consider
the N/O ratio expected for their O abundance for those objects with a
high
)|>
50 Å. This dispersion becomes substantially smaller when we consider
the N/O ratio expected for their O abundance for those objects with a
high ![]() (N/O).
If the high N/O ratios in these galaxies are produced by the chemical
pollution due to winds of WR stars, objects would move to the right in
Fig. 13
once the burst is finished
because of the decreasing of |W(H
(N/O).
If the high N/O ratios in these galaxies are produced by the chemical
pollution due to winds of WR stars, objects would move to the right in
Fig. 13
once the burst is finished
because of the decreasing of |W(H![]() )|. If the
chemical pollution is very localized, we should also expect that
objects with a N excess would move towards lower values of the N/O
ratio as the fresh released material is dispersed and mixed with the
existing gas of the galaxy.
Hence, detailed analyses of galaxies with a localized high N/O ratio,
such as we performed in NGC 5253 (López-Sánchez 2007), are
fundamental to solve these unsolved questions, which will definitely be
key elements to the evolution of the galaxies.
)|. If the
chemical pollution is very localized, we should also expect that
objects with a N excess would move towards lower values of the N/O
ratio as the fresh released material is dispersed and mixed with the
existing gas of the galaxy.
Hence, detailed analyses of galaxies with a localized high N/O ratio,
such as we performed in NGC 5253 (López-Sánchez 2007), are
fundamental to solve these unsolved questions, which will definitely be
key elements to the evolution of the galaxies.
4.3 The 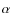 -elements to
oxygen ratio
-elements to
oxygen ratio
Figure 14
plots the Ne/O, S/O, Ar/O, and Fe/O ratios as a function of ![]() for all objects analysed in this work. We compare our observational
results with those found in samples with similar characteristics
(Izotov & Thuan 1999;
Izotov et al. 2006).
We remark again that although the estimates of our errors are higher
than those provided by other samples, they are not a consequence of the
quality of our data but derive from the different formalism we used to
estimate the uncertainties.
In any case, our results completely agree with those previously
reported in the literature. The relative abundance ratios of the
for all objects analysed in this work. We compare our observational
results with those found in samples with similar characteristics
(Izotov & Thuan 1999;
Izotov et al. 2006).
We remark again that although the estimates of our errors are higher
than those provided by other samples, they are not a consequence of the
quality of our data but derive from the different formalism we used to
estimate the uncertainties.
In any case, our results completely agree with those previously
reported in the literature. The relative abundance ratios of the ![]() -elements
(neon, sulfur, and argon) to oxygen are approximately constant,
as expected because all four elements (O, Ne, S and Ar) are mainly
produced by massive stars. For our sample, the mean
-elements
(neon, sulfur, and argon) to oxygen are approximately constant,
as expected because all four elements (O, Ne, S and Ar) are mainly
produced by massive stars. For our sample, the mean ![]() (Ne/O),
(Ne/O), ![]() (S/O), and
(S/O), and ![]() (Ar/O)
ratios are
(Ar/O)
ratios are ![]() ,
,
![]() and
and ![]() ,
respectively. These values are comparable to the values reported for
starbursting dwarf galaxies
(e.g., Izotov & Thuan 1999;
Izotov et al. 2006)
and for other dwarf irregular galaxies (e.g., van Zee et al. 1998; van Zee
& Haynes 2006).
For example, Izotov & Thuan (1999) found mean
values of
,
respectively. These values are comparable to the values reported for
starbursting dwarf galaxies
(e.g., Izotov & Thuan 1999;
Izotov et al. 2006)
and for other dwarf irregular galaxies (e.g., van Zee et al. 1998; van Zee
& Haynes 2006).
For example, Izotov & Thuan (1999) found mean
values of ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
and
,
and ![]() for the
for the ![]() (Ne/O),
(Ne/O),
![]() (S/O), and
(S/O), and ![]() (Ar/O)
ratios, respectively.
(Ar/O)
ratios, respectively.
Despite their higher uncertainties, we notice that the Ne/O ratio seems to increase slightly with increasing oxygen abundance. This effect was reported by Izotov et al. (2006), who interpreted it as due to a moderate depletion of oxygen onto grains in the most metal-rich galaxies. Verma et al. (2003) observed an underabundance of sulphur in relatively high-metallicity starburst galaxies. These authors interpreted this effect as a consequence of the depletion of sulphur onto dust grains. However, we do not see any underabundance of sulphur; quite the opposite, the sulphur abundance is well correlated with both neon and argon abundances.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f15.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg651.png)
|
Figure 15:
Comparison between the oxygen abundances derived using the direct
method ( |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f16.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg652.png)
|
Figure 16:
Comparison between the oxygen abundances derived using the direct
method ( |
| Open with DEXTER | |
On the other hand, it seems that the Fe/O ratio slightly decreases with increasing oxygen abundance. This effect was previously observed by Izotov et al. (2006), who suggested that it may be a consequence of the iron depletion in dust grains, which is more important for galaxies with higher metallicities.
Finally we remark how important is to use high-quality data
and a proper estimate of all the physical parameters (including ![]() via the direct method) in an homogeneous sample of objects to get
reasonable conclusions about these topics (i.e., this work; Hägele
et al. 2008).
via the direct method) in an homogeneous sample of objects to get
reasonable conclusions about these topics (i.e., this work; Hägele
et al. 2008).
4.4 Comparison with empirical calibrations
We used the data of the 31 regions for which we have a direct estimate
of ![]() and, hence, a direct estimate of the oxygen abundance, to check the
reliability of several empirical calibrations.
A recent review of 10 metallicity calibrations, including theoretical
and empirical methods, was presented by Kewley & Ellison (2008).
Appendix A gives an overview of the most common empirical
calibrations and defines the typical parameters that are used to
estimate the oxygen abundance following these relations. These
parameters are ratios between bright emission lines, the most commonly
used are R23, P,
y, N2, and O3N2
(see definitions in Appendix A). Table A.1 lists the
values of all these parameters derived for each region with a direct
estimate of the oxygen abundance (see Paper II for details).
Table A.1
also includes the value derived for the q parameter
(in units of cm s-1) obtained from the optimal
calibration provided by Kewley & Dopita (2002). The results
for the oxygen abundances derived for each object and empirical
calibration are listed in Table A.2. This table
also indicates the branch (high or low metallicity) considered in each
region when using the R23
parameter (see Appendix A), although, as is clearly specified
in the table, for some objects with
and, hence, a direct estimate of the oxygen abundance, to check the
reliability of several empirical calibrations.
A recent review of 10 metallicity calibrations, including theoretical
and empirical methods, was presented by Kewley & Ellison (2008).
Appendix A gives an overview of the most common empirical
calibrations and defines the typical parameters that are used to
estimate the oxygen abundance following these relations. These
parameters are ratios between bright emission lines, the most commonly
used are R23, P,
y, N2, and O3N2
(see definitions in Appendix A). Table A.1 lists the
values of all these parameters derived for each region with a direct
estimate of the oxygen abundance (see Paper II for details).
Table A.1
also includes the value derived for the q parameter
(in units of cm s-1) obtained from the optimal
calibration provided by Kewley & Dopita (2002). The results
for the oxygen abundances derived for each object and empirical
calibration are listed in Table A.2. This table
also indicates the branch (high or low metallicity) considered in each
region when using the R23
parameter (see Appendix A), although, as is clearly specified
in the table, for some objects with ![]() we assumed the average value
found for the lower and upper branches.
we assumed the average value
found for the lower and upper branches.
Looking at the data compiled in Table A.2 the huge range of oxygen abundance found for the same object using different calibrations is evident. As Kewley & Ellison (2008) concluded, it is critical to use the same metallicity calibration when comparing properties from different data sets or investigate luminosity-metallicity or mass-metallicity relations. Furthermore, abundances derived with such strong-line methods may be significantly biased if the objects under study have different structural properties (hardness of the ionizing radiation field, morphology of the nebulae) than those used to calibrate the methods (Stasinska 2010).
Figures 15 and 16 plots the ten most common calibrations and their comparison with the oxygen abundance obtained using the direct method. We performed a simple statistic analysis of the results to quantify the goodness of these empirical calibrations. Table 4 compiles the average value and the dispersion (in absolute values) of the difference between the abundance given by empirical calibration and that obtained using the direct method. We check that the empirical calibration that provides the best results is that proposed by Pilyugin (2001a,b), which gives oxygen abundances very close to the direct values (the differences are lower than 0.1 dex in the majority of the objects), and furthermore it possesses a low dispersion. We note however that the largest divergences found using this calibration are in the low-metallicity regime. The update of this calibration presented by Pilyugin & Thuan (2005) seems to partially solve this problem, the abundances provided by this calibration also agree very well with those derived following the direct method. We therefore conclude that the Pilyugin & Thuan (2005) calibration is nowadays the best suitable method to derive the oxygen abundance of star-forming galaxies when auroral lines are not observed.
Table 4:
Results of the comparison between the oxygen abundance given by several
empirical calibrations and the oxygen abundance derived here following
the direct (![]() )
method.
)
method.
On the other hand, the results given by the empirical
calibrations provided by McGaugh (1991),
Kewley & Dopita (2002)
and Kobulnicky & Kewley (2004), that
are based on photoionization models, are systematically higher than the
values derived from the direct method. This effect is even more marked
in the last two calibrations, which usually are between 0.2 and 0.3 dex
higher than the expected values. These empirical calibrations also have
a higher dispersion than that estimated for Pilyugin (2001a,b) or
Pilyugin & Thuan (2005)
calibrations. Yin et al. (2007)
also found high discrepancies when comparing the theoretical
metallicities using the theoretical models of Tremonti et al. (2004) with the ![]() -based
metallicites obtained from Pilyugin (2001a,b) and
Pilyugin & Thuan (2005).
-based
metallicites obtained from Pilyugin (2001a,b) and
Pilyugin & Thuan (2005).
One of the possible explanations for the different
metallicities obtained between the direct method and those derived from
the empirical calibrations based on photoionization models are
temperature fluctuations in the ionized gas. Temperature gradients or
fluctuations indeed cause the true metallicities based on the ![]() -method to
be underestimated (i.e. Peimbert 1967; Stasinska 2002, 2005; Peimbert
et al. 2007).
Temperature fluctuations can also explain our results for
NGC 5253 (López-Sánchez et al. 2007): the ionic
abundances of O++/H+ and C++/H+
derived from recombination lines are systematically 0.2-0.3 dex higher
than those determined from the direct method -based on the intensity
ratios of collisionally excited lines. This abundance discrepancy has
been also found in Galactic (García-Rojas & Esteban 2007) and other
extragalactic (Esteban et al. 2009) H II
regions and interestingly this discrepancy is in all
cases of the same order as the differences between abundances derived
from the direct methods and empirical calibrations based on
photoionization models.
-method to
be underestimated (i.e. Peimbert 1967; Stasinska 2002, 2005; Peimbert
et al. 2007).
Temperature fluctuations can also explain our results for
NGC 5253 (López-Sánchez et al. 2007): the ionic
abundances of O++/H+ and C++/H+
derived from recombination lines are systematically 0.2-0.3 dex higher
than those determined from the direct method -based on the intensity
ratios of collisionally excited lines. This abundance discrepancy has
been also found in Galactic (García-Rojas & Esteban 2007) and other
extragalactic (Esteban et al. 2009) H II
regions and interestingly this discrepancy is in all
cases of the same order as the differences between abundances derived
from the direct methods and empirical calibrations based on
photoionization models.
The conclusion that temperature fluctuations do exist in the ionized gas of starburst galaxies is very important for the analysis of the chemical evolution of galaxies and the Universe. Indeed, if that is correct, the majority of the abundance determinations in extragalactic objects following the direct method, including those provided in this work, have been underestimated by at least 0.2 to 0.3 dex. Deeper observations of a large sample of star-forming galaxies - that allow us to detect the faint recombination lines, such as those provided by Esteban et al. (2009) - and more theoretical work - including a better understanding of the photoionization models, such as the analysis provided by Kewley & Ellison (2008) - are needed to confirm this puzzling result.
On the other hand, we have checked the validity of the recent
relation provided by Nagao et al. (2006), which merely
considers a cubic fit between the R23
parameter and the oxygen abundance. This calibration was obtained
combining data from several large galaxy samples, the majority from the
SDSS, which includes all kinds of star-forming objects. As it is
clearly seen in Table A.2
and in Fig. 16,
the Nagao et al. (2006)
relation is not suitable to derive a proper estimate of the oxygen
abundance for the majority of the objects in our galaxy sample. In
general, this calibration provides lower oxygen abundances in
low-metallicity regions and higher oxygen abundances in
high-metallicity regions. Objects located in the metallicity range ![]() have systematically 12 + log(O/H)
have systematically 12 + log(O/H)
![]() because we have to use an average value between the low and the high
branches. Furthermore, many of the regions do not have a formal
solution to the Nagao et al. (2006) equation,
such as the maximum value for R23
is 8.39 at
because we have to use an average value between the low and the high
branches. Furthermore, many of the regions do not have a formal
solution to the Nagao et al. (2006) equation,
such as the maximum value for R23
is 8.39 at ![]() .
We consider that the use of an ionization parameter - P
as introduced by Pilyugin (2001a,b)
or q as followed by Kewley & Dopita (2002) - is
fundamental to obtain a real estimate of the oxygen abundance in
star-forming galaxies, especially in objects showing strong starbursts.
In the same sense, the direct method and not the formulae provided by
Izotov et al. (2006)
(which assumes a low-density approximation in order not to have to
solve the statistical equilibrium equations of the O+2
ion) provides a good approximation to the actual oxygen abundance when
the auroral line [O III]
.
We consider that the use of an ionization parameter - P
as introduced by Pilyugin (2001a,b)
or q as followed by Kewley & Dopita (2002) - is
fundamental to obtain a real estimate of the oxygen abundance in
star-forming galaxies, especially in objects showing strong starbursts.
In the same sense, the direct method and not the formulae provided by
Izotov et al. (2006)
(which assumes a low-density approximation in order not to have to
solve the statistical equilibrium equations of the O+2
ion) provides a good approximation to the actual oxygen abundance when
the auroral line [O III] ![]() 4653 is
observed.
4653 is
observed.
Empirical calibrations considering a linear fit to the N2
ratio (Denicoló et al. 2002;
Pettini & Pagel 2004)
give results that are systematically ![]() 0.15 dex higher that the oxygen abundances
derived from the direct method. The difference is higher at higher
metallicities. We do not consider that this trend is a consequence of
comparing different objects: both Denicoló et al. (2002) and
Pettini & Pagel (2004)
calibrations are obtained using a sample of star-forming galaxies
similar to those analysed in this work, many of which are WR galaxies.
Denicoló et al. (2002)
compared the N2 ratio with the ionization
parameter together with the results of photoionization models and
concluded that most of the observed trend of N2
with the oxygen abundance is caused by metallicity changes.
The cubic fit to N2 performed by Pettini
& Pagel (2004)
better reproduces the oxygen abundance, especially in the intermediate-
and high-metallicity regime (
0.15 dex higher that the oxygen abundances
derived from the direct method. The difference is higher at higher
metallicities. We do not consider that this trend is a consequence of
comparing different objects: both Denicoló et al. (2002) and
Pettini & Pagel (2004)
calibrations are obtained using a sample of star-forming galaxies
similar to those analysed in this work, many of which are WR galaxies.
Denicoló et al. (2002)
compared the N2 ratio with the ionization
parameter together with the results of photoionization models and
concluded that most of the observed trend of N2
with the oxygen abundance is caused by metallicity changes.
The cubic fit to N2 performed by Pettini
& Pagel (2004)
better reproduces the oxygen abundance, especially in the intermediate-
and high-metallicity regime (
![]() ),
where it has an average error of
),
where it has an average error of ![]() 0.08 dex. However, the cubic fit to N2
provided by Nagao et al. (2006)
gives systematically lower values for the oxygen abundance than those
derived using the direct method, having an average error of
0.08 dex. However, the cubic fit to N2
provided by Nagao et al. (2006)
gives systematically lower values for the oxygen abundance than those
derived using the direct method, having an average error of ![]() 0.18 dex.
0.18 dex.
The empirical calibration between the oxygen abundance and the
O3N2 parameter proposed
by Pettini & Pagel (2004)
gives acceptable results for objects with ![]() ,
with the average error
,
with the average error ![]() 0.1
dex. However, the new relation provided by Nagao et al. (2006) involving the
O3N2 parameter gives
systematically lower values for the oxygen abundance. As we commented
before, we consider that the Nagao et al. (2006) calibrations
are not suitable for studying galaxies with strong star-formation
bursts. Their procedures must be taken with caution, galaxies with
different ionization parameters, different chemical evolution
histories, and different star formation histories should have different
relations between the bright emission lines and the oxygen abundance.
This issue is even more important when estimating the metallicities of
intermediate- and high-redshift galaxies, because the majority of their
properties are highly unknown.
0.1
dex. However, the new relation provided by Nagao et al. (2006) involving the
O3N2 parameter gives
systematically lower values for the oxygen abundance. As we commented
before, we consider that the Nagao et al. (2006) calibrations
are not suitable for studying galaxies with strong star-formation
bursts. Their procedures must be taken with caution, galaxies with
different ionization parameters, different chemical evolution
histories, and different star formation histories should have different
relations between the bright emission lines and the oxygen abundance.
This issue is even more important when estimating the metallicities of
intermediate- and high-redshift galaxies, because the majority of their
properties are highly unknown.
5 Metallicity-luminosity relations
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f17.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg662.png)
|
Figure 17:
Metallicity-luminosity diagrams for the objects analysed in this work.
The oxygen abundance is expressed in units of |
| Open with DEXTER | |
The metallicity of normal disc galaxies is strongly correlated with the galaxy mass. The first mass-metallicity relation was found for irregular and blue compact galaxies (Lequeux et al. 1979; Kinman & Davidson 1981). However, luminosity is often used instead of mass because obtaining reliable mass estimates is difficult. Rubin et al. (1984) provided the first evidence that metallicity is correlated with luminosity in disk galaxies. Further work using larger samples of nearby disk galaxies confirmed this result (Bothum et al. 1984; Wyse & Silk 1985; Skillman et al. 1989; Vila-Costas & Edmunds 1992; Zaritsky et al. 1994; Garnett 2002). Despite the huge observational effort, the origin of the luminosity-metallicity is still not well understood. The two basic ideas are (i) it represents an evolutionary sequence - more luminous galaxies have processed a larger fraction of their raw materials (McGaugh & deBlok 1997; Bell & deJong 2000; Boselli et al. 2001) - or (ii) it is related to a mass-retention sequence - more massive galaxies retain a larger fraction of their processed material (Garnett 2002; Tremonti et al. 2004; Salzer et al. 2005). Furthermore, other factors may play a key role in the variation of the metal content of a galaxy, remarking the quick metal enrichment that strong star-formation events in dwarf galaxies, such as BCDGs, may experience. In these objects, the freshly processed material may be expelled into the intergalactic medium via galactic winds or be mixed with the reservoirs of non-synthesized gas, in both cases decreasing the global metallicity of the galaxy.
In addition, luminosity-metallicity relations are very useful to discern between pre-existing dwarf galaxies and tidal dwarf galaxy (TDG) candidates (Duc & Mirabel 1998; Duc et al. 2000) because these objects should have a metallicity similar to that observed in their parent spiral galaxies (Weilbacher et al. 2003) and not a low-metallicity as it is found in dwarf objects.
We studied the metallicity-luminosity relation using the data
provided by our analysis. Figure 17 plots the oxygen
abundance vs absolute magnitude in B and NIR
filters and including some relationships found by previous studies. In
this figure we distinguish between galaxies (blue points) and TDGs
candidates (red triangles) found in HCG 31 and
Mkn 1087 groups. We also distinguish the dwarf object
surrounding POX 4 (labeled POX 4 comp in
figures and tables) because it may be another TDG, and the galaxy
SBS 1054+365 because, as we will see later, its position in
the metallicity-luminosity diagrams is quite unusual. We estimated the NIR
absolute magnitudes for SBS 0948+532 and SBS 1211+540
assuming ![]() ,
,
![]() and
and ![]() ,
that are the average values found in objects with properties similar to
these two galaxies (see Paper I).
,
that are the average values found in objects with properties similar to
these two galaxies (see Paper I).
The MB-O/H
diagram includes the relation given by Richer & McCall (1995) for dwarf
and irregular galaxies (
![]() )
extrapolated to high luminosities and the van Zee & Haynes (2006) relation found
for isolated dwarf irregular galaxies. Both relations have a similar
slope (-0.147 and -0.149, respectively) and intercept (5.67 and 5.65,
respectively). Our observational data have a rather high dispersion,
but the tendency of increasing oxygen abundance with increasing
absolute B-magnitude is clear. Most of the objects
fainter than MB=-18
are located above those relations, but many of them are TDG candidates.
On the other hand, a substantial fraction of the brighter objects tend
to be clearly below the metallicity-luminosity relations obtained by
previous authors. The best linear fit to our data excluding the TDG
candidates - it is well-known that they should not follow the
metallicity-luminosity relation (Duc & Mirabel 1998) - provides a
slope of
)
extrapolated to high luminosities and the van Zee & Haynes (2006) relation found
for isolated dwarf irregular galaxies. Both relations have a similar
slope (-0.147 and -0.149, respectively) and intercept (5.67 and 5.65,
respectively). Our observational data have a rather high dispersion,
but the tendency of increasing oxygen abundance with increasing
absolute B-magnitude is clear. Most of the objects
fainter than MB=-18
are located above those relations, but many of them are TDG candidates.
On the other hand, a substantial fraction of the brighter objects tend
to be clearly below the metallicity-luminosity relations obtained by
previous authors. The best linear fit to our data excluding the TDG
candidates - it is well-known that they should not follow the
metallicity-luminosity relation (Duc & Mirabel 1998) - provides a
slope of ![]() and an intercept of
and an intercept of ![]() .
The slope we derive for our galaxy sample is shallower than those
provided by the Richer & McCall (1995) and van Zee
& Haynes (2006)
relations. However, the Tremonti et al. (2004) MB-O/H
relation for all kinds of galaxies using SDSS data (plotted with a blue
dotted line in Fig. 17)
show the steepest slope of all relations, which has a value of -0.185.
That disagree with the conclusions reached by Tremonti et al. (2004), who
explained the flattening of the M-Z
relation at higher masses because efficient galactic winds are able to
remove metals from low-mass galaxies.
.
The slope we derive for our galaxy sample is shallower than those
provided by the Richer & McCall (1995) and van Zee
& Haynes (2006)
relations. However, the Tremonti et al. (2004) MB-O/H
relation for all kinds of galaxies using SDSS data (plotted with a blue
dotted line in Fig. 17)
show the steepest slope of all relations, which has a value of -0.185.
That disagree with the conclusions reached by Tremonti et al. (2004), who
explained the flattening of the M-Z
relation at higher masses because efficient galactic winds are able to
remove metals from low-mass galaxies.
Some authors (Campos-Aguilar et al. 1993; Peña & Ayala 1993; McGaugh 1994) have already questioned the validity of the luminosity-metallicity relation in starbursting galaxies. As we explained in previous papers (López-Sánchez et al. 2004a,b), we consider that the emission of the dominant young stellar population in these galaxies is increasing their B-luminosity, and hence the use of the standard metallicity-luminosity relation is not appropriate for starburst-dominated galaxies. Indeed, the increment of the B-luminosity is moving all star-forming objects away - towards more negative magnitudes - from the usual relations valid for non-starbursting galaxies, and even producing - incidentally - the TDG candidates to agree with the relations.
As proposed by Hidalgo-Gámez & Olofsson (1998) and
reviewed by Salzer et al. (2005), perhaps NIR
magnitudes are more suitable than the optical B-magnitude
to built metallicity-luminosity diagrams. Indeed, NIR
magnitudes are less affected by extinction and more directly related to
the stellar mass of the galaxy than the optical luminosities.
Furthermore, the effect of variations in star-formation histories and
stellar populations is less pronounced in the NIR
than in the optical.
We analysed the behaviour of the oxygen abundance with the J,
H and ![]() absolute magnitudes (see Fig. 17).
As we expected, the oxygen abundance increases with the luminosity.
The slopes,
absolute magnitudes (see Fig. 17).
As we expected, the oxygen abundance increases with the luminosity.
The slopes, ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
and
,
and ![]() for MJ, MH,
and
for MJ, MH,
and ![]() ,
respectively, and intercepts,
,
respectively, and intercepts, ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
and
,
and ![]() ,
of the lineal fits are remarkably similar to the fit parameters of our MB-O/H
relation. However, these fits
have a better correlation coefficient (0.773, 0.779 and 0.790) and
dispersion (0.18, 0.17 and 0.17) than those derived for the MB-O/H
relation (r=0.719 and
,
of the lineal fits are remarkably similar to the fit parameters of our MB-O/H
relation. However, these fits
have a better correlation coefficient (0.773, 0.779 and 0.790) and
dispersion (0.18, 0.17 and 0.17) than those derived for the MB-O/H
relation (r=0.719 and ![]() ). Salzer
et al. (2005)
found a notable decreasing of the rms scatter of the
metallicity-luminosity relation between the blue and the NIR.
). Salzer
et al. (2005)
found a notable decreasing of the rms scatter of the
metallicity-luminosity relation between the blue and the NIR.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f18.eps}
\vspace{1.5mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg675.png)
|
Figure 18:
Nitrogen abundance vs. luminosity for the galaxies analysed in this
work. The nitrogen abundance is expressed in units of 12+log(N/H); the
luminosity is expressed as the absolute magnitude in B
( left) and |
| Open with DEXTER | |
The ![]() -O/H diagram shown in
Fig. 17
includes the relations obtained by Salzer et al. (2005) -which
consider two different empirical calibrations of their oxygen
abundance, one following the Edmunds & Pagel (1984) method and
another considering the Kennicutt et al. (2003)
relationships - and Mendes de Oliveira (2006). These
relationships have a very different slope (-0.212, -0.195, and -0.14,
respectively) and intercept (3.919, 4.029, and 5.55, respectively) than
that derived in our analysis of the
-O/H diagram shown in
Fig. 17
includes the relations obtained by Salzer et al. (2005) -which
consider two different empirical calibrations of their oxygen
abundance, one following the Edmunds & Pagel (1984) method and
another considering the Kennicutt et al. (2003)
relationships - and Mendes de Oliveira (2006). These
relationships have a very different slope (-0.212, -0.195, and -0.14,
respectively) and intercept (3.919, 4.029, and 5.55, respectively) than
that derived in our analysis of the ![]() -O/H
relation. However, for objects with
-O/H
relation. However, for objects with ![]() ,
the relations provided by Salzer et al. (2005) agree fairly
well with the position of our data points. These authors found that the
slopes of the metallicity-luminosity relations change systematically
from the shortest to the longest wavelengths, in that the relation is
steepest in the blue and more shallow in the NIR.
In fact, Salzer et al. (2005)
also noted that their derived MB-O/H
relation has a much steeper slope than those found by previously
relations (i.e., Skillman et al. 1989, Richer
& McCall 1995).
,
the relations provided by Salzer et al. (2005) agree fairly
well with the position of our data points. These authors found that the
slopes of the metallicity-luminosity relations change systematically
from the shortest to the longest wavelengths, in that the relation is
steepest in the blue and more shallow in the NIR.
In fact, Salzer et al. (2005)
also noted that their derived MB-O/H
relation has a much steeper slope than those found by previously
relations (i.e., Skillman et al. 1989, Richer
& McCall 1995).
The disagreement between our data and previous metallicity-luminosity relations may arise because our sample was chosen considering WR galaxies, which host strong starbursts, while other samples consider any star-forming galaxies. It may also occur because dwarf galaxies and normal galaxies have different relations (i.e. Tremonti et al. 2004). Another fact that can contribute to the aforementioned disagreement is that the oxygen abundances derived in previous analyses have been usually computed via photoionization-based empirical calibrations. As we discussed before, they seem to overestimate the actual O/H ratio by about 0.2 dex.
In Fig. 17
we can see that the separation between the positions of TDG candidates
and dwarf galaxies is somewhat more evident in the
metallicity-luminosity diagrams involving NIR
magnitudes. POX 4 comp agrees with the relations, and
hence further analysis of this object is needed to understand its real
nature. On the other hand, SBS 1054+365 has a higher oxygen
abundance for its optical and NIR absolute
luminosities. We do not consider the O/H to be overestimated because of
the high quality of our spectra (Paper II) and because
previous studies derived the same metallicity (i.e., Izotov &
Thuan 1998).
We are also quite confident of the correct determination of its optical
and NIR magnitudes because of the detailed analysis
we already presented in Paper I. Hence we consider that this
nearby (8 Mpc) BCDG may have experienced a recent a strong
pollution of heavy elements which probably has not had enough time to
disperse and mix with the surrounding ISM. In Paper V we will
see that this galaxy also possesses a very high ![]() ratio, suggesting that the neutral gas is quite disturbed. Further
analysis of this intriguing object, including H I
radio data and optical spectroscopy, would be necessary to ascertain
its true nature.
ratio, suggesting that the neutral gas is quite disturbed. Further
analysis of this intriguing object, including H I
radio data and optical spectroscopy, would be necessary to ascertain
its true nature.
Finally, another aspect that should also be addressed is the possibility that some of the sample objects may be a recent merger of two galaxies. In this case, the integrated luminosity would be higher than that expected for a single galaxy, and hence its position would be also far from the metallicity-luminosity relations. That may be happening in UM 420 - see Sect. 3.9 in Paper I, Sect. 3.9.3 in Paper II and James et al. (2009) - and Tol 1457-262 (see Sect. 3.18.3 in Paper II), which show a considerable high luminosity given their low oxygen abundances. Hence it is more appropriate to compare the stellar mass (and not the B or the NIR luminosities) with the metallicity to reach any conclusions about this topic, as we will explain in Paper V.
The nitrogen abundance also has a strong correlation with the
luminosity. Figure 18
plots the nitrogen abundance, expressed in units of 12+log(N/H), as a
function of the absolute B and ![]() magnitudes. As in Fig. 17,
we distinguish the TDG candidates and the intriguing objects
POX 4 comp and SBS 1054+365. From
Fig. 18
it is also evident that the nitrogen abundance increases with
increasing luminosity. We performed a linear fit to our data (without
considering the problematic objects already discussed), which is
plotted with a continuous red line. In the MB-N/H
diagram this fit yields a slope of
magnitudes. As in Fig. 17,
we distinguish the TDG candidates and the intriguing objects
POX 4 comp and SBS 1054+365. From
Fig. 18
it is also evident that the nitrogen abundance increases with
increasing luminosity. We performed a linear fit to our data (without
considering the problematic objects already discussed), which is
plotted with a continuous red line. In the MB-N/H
diagram this fit yields a slope of ![]() and an intercept of
and an intercept of ![]() .
This result is virtually identical to that found by van Zee &
Haynes (2006),
their relation is shown with a green dashed line in the left diagram of
Fig. 18.
The scatter of the MB-N/H
relation is higher than that found in the MB-O/H
relation, actually, we may distinguish between two kinds of objects in
this figure, because the more evolved galaxies (such as
Mkn 1199, Mkn 1087, Tol 9,
ESO 566-8) and the non-starbursting systems
(Mkn 1199 NE, IRAS 08339+6517 c,
ESO 566-7) have a higher N/H value at a given absolute B-luminosity
than the very starbursting (i.e. IRAS 08339+6517,
HCG 31 AC) and blue compact dwarf (i.e.
UM 420, POX 4, SBS 0926+606 A)
galaxies. TDG candidates do not lie far from this relation. These
differences are probably a consequence of the different star-formation
histories of the galaxies, as we also explained the scatter in the
observed N/O ratio at
.
This result is virtually identical to that found by van Zee &
Haynes (2006),
their relation is shown with a green dashed line in the left diagram of
Fig. 18.
The scatter of the MB-N/H
relation is higher than that found in the MB-O/H
relation, actually, we may distinguish between two kinds of objects in
this figure, because the more evolved galaxies (such as
Mkn 1199, Mkn 1087, Tol 9,
ESO 566-8) and the non-starbursting systems
(Mkn 1199 NE, IRAS 08339+6517 c,
ESO 566-7) have a higher N/H value at a given absolute B-luminosity
than the very starbursting (i.e. IRAS 08339+6517,
HCG 31 AC) and blue compact dwarf (i.e.
UM 420, POX 4, SBS 0926+606 A)
galaxies. TDG candidates do not lie far from this relation. These
differences are probably a consequence of the different star-formation
histories of the galaxies, as we also explained the scatter in the
observed N/O ratio at ![]() (see Fig. 11).
(see Fig. 11).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f19.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg681.png)
|
Figure 19: Metallicity-colour diagrams for the galaxies analysed in this work. A linear fit is shown with a continuous red line. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
As it happened in the previous diagrams involving the oxygen abundance,
the luminosity-metallicity diagram using NIR data
has a smaller scatter (Fig. 18,
right). The fit to our data in the ![]() -N/H
diagram, neglecting TDG candidates and problematic objects, gives a
slope of
-N/H
diagram, neglecting TDG candidates and problematic objects, gives a
slope of ![]() and an intercept of
and an intercept of ![]() .
The correlation coefficient is r=0.813 and the
dispersion is
.
The correlation coefficient is r=0.813 and the
dispersion is ![]() .
In comparison, the MB-N/H
diagram has r=0.707 and
.
In comparison, the MB-N/H
diagram has r=0.707 and ![]() .
We note that again TDG candidates and the galaxy SBS 1054+365
lie far from this fit, which is plotted in Fig. 18 (right) with a
continuous red line. POX 4 comp agrees quite nicely
with the relation. In both diagrams, the position of
Tol 1457-262 is far from the relation, having a considerable
high luminosity for its N/H ratio. As we already discussed, we consider
that this object may correspond to a recent merger of two independent
galaxies. Hence we conclude that luminosity-metallicity relations using
NIR band magnitudes are very suitable to understand
galaxy properties and evolution, providing tighter correlations than
those relations involving optical magnitudes.
.
We note that again TDG candidates and the galaxy SBS 1054+365
lie far from this fit, which is plotted in Fig. 18 (right) with a
continuous red line. POX 4 comp agrees quite nicely
with the relation. In both diagrams, the position of
Tol 1457-262 is far from the relation, having a considerable
high luminosity for its N/H ratio. As we already discussed, we consider
that this object may correspond to a recent merger of two independent
galaxies. Hence we conclude that luminosity-metallicity relations using
NIR band magnitudes are very suitable to understand
galaxy properties and evolution, providing tighter correlations than
those relations involving optical magnitudes.
6 Metallicity-colour relations
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f20.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg686.png)
|
Figure 20:
N/O ratio vs. the reddening-corrected B-V
colour considering all the galaxy (left) or just the underlying stellar
population (right). A linear fit to our data is shown with a continuous
red line. The relationship found by van Zee & Haynes (2006) in their
analysis of dwarf irregular galaxies is plotted with a dashed green
line. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f21.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg687.png)
|
Figure 21: N/O ratio vs. the reddening-corrected V-R ( left) and J-H ( right) colours. A linear fit to our data is shown with a continuous red line. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
We analysed the relationship between the optical and NIR colours observed in each galaxy and its metallicity. Figure 19 plots the results for all colours (from Table 1) vs. the oxygen abundance and a fit to the data. Although the dispersion is large, the general trend is that galaxies with redder colours have a higher oxygen abundance in their ionized gas. This suggests again the relative importance of the evolved stellar populations existing in the galaxies, and agrees both with models of galaxy evolution (i.e., Leitherer et al. 1999; Bruzual & Charlotte 2003) and previous observational analysis (i.e. Jansen et al. 2000; Lilly et al. 2003). Neglecting other effects (such as extinction), the birth of new generations of stars within a galaxy will continuously increase the number of intermediate and low-mass stars, which are the typical stellar population that constitutes the low-luminosity component in starburst galaxies. Hence it should be expected that as the system evolves - increasing its metallicity - its optical and NIR colours are more dominated by the evolved population, and therefore they are redder. Another interesting comment regarding these correlations is to remark how important it is to have an estimate of the metallicity of the galaxies when comparing the optical/NIR colours with the predictions of theoretical evolutionary models (see Paper I).
Besides the N/O ratio has a large dispersion in our sample objects, we checked whether a correlation exists between this ratio and the B-V colour. Figure 20 plots both quantities considering the B-V colour of the complete galaxy (left panel) and that derived for the old underlying population (right panel). Both diagrams include a fit to our data (continuous red line). Figure 20 shows the large dispersion of the data points, but there seems to be a suggestion of a tendency of increasing N/O with increasing B-V colour. This tendency does not become clearer when considering the data of the underlying stellar component. However, the relation found using our data disagrees with that obtained by van Zee & Haynes (2006) analysing a sample of dwarf irregular galaxies. We note that they referred to the B-V colour of the underlying population, but actually it is just the integrated colour of the galaxy. The significant difference found between both samples may be a consequence of two reasons: (i) we are comparing different objects - our sample is composed by starbursting galaxies, many of them BCDGs, but van Zee & Haynes (2006) analysed quiescent dwarf irregular galaxies with star-formation histories that are correctly modelled by simple changes in the SFR - and (ii) the N/O ratios tabulated by these authors, who used McGaugh (1991) photoionization models in many cases, are not well estimated - as we saw before, these models overestimate the oxygen abundance, and hence underestimate the N/O ratio, as it is clearly seen in the O/H-N/O diagram (Fig. 11, right) when comparing the van Zee et al. (1998) sample with the results provided by other authors -. We consider that the first reason may be the most reasonable explanation: objects with different star-formation histories have different relationships between the N/O ratio and other global characteristics such as optical colours.
However, as we commented before, using the B-magnitude may be not ideal to compare the colours and the chemical properties of these galaxies. Hence we also compared the N/O ratio with other optical and NIR colours, two of them (V-R and J-H) are shown in Fig. 21. As we already explained when analysing the N/H-L relationship (Fig. 18), there are two kinds of objects with similar optical luminosities but with different nitrogen abundances. This is also reflected in the N/O ratio (Fig. 20, left), where normal and dwarf non-starbursting galaxies show a higher N/O ratio than starbursts (which have a lower N/O ratio in Fig. 20, left). This segregation is not so evident when comparing the N/O ratio with the NIR luminosities (Fig. 21, right), perhaps because the underlying component makes a higher contribution to the NIR magnitudes, but more data are needed to quantify this effect.
Finally, we also note that we do not see any clear
relationship between the underlying population colours and the N/O
ratio: for example, the V-R
colour of the low luminosity component is ![]() for all ranges of N/O. It was not possible to analyse the NIR
colours of the low-luminosity component in the majority of the cases
(see Table 5 in Paper I), but for the few available
data it also seems that they are metallicity-independent, showing
for all ranges of N/O. It was not possible to analyse the NIR
colours of the low-luminosity component in the majority of the cases
(see Table 5 in Paper I), but for the few available
data it also seems that they are metallicity-independent, showing ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
7 Conclusions
We compiled and analysed globally the optical/NIR
colours and the physical and chemical properties of the ionized gas for
a sample of 20 Wolf-Rayet galaxies. The individual analysis of the
photometry of each galaxy was presented in Paper I, while the
individual spectroscopic analysis was discussed in Paper II.
The metallicity of these galaxies lies between 7.58 and 8.75 - in units
of ![]() -. The most important conclusions found in this study are
-. The most important conclusions found in this study are
- 1.
- The colours estimated for our galaxy sample, which were corrected for both extinction and nebular emission using our spectroscopic data, agree quite well with the predictions given by evolutionary synthesis models, especially in compact and dwarf objects. Small discrepancies are explained because of the existence of several stellar populations within each galaxy and differences in their star-formation history. All galaxies show evidence of an old stellar population underlying the starburst, with ages older than 500 Myr.
- 2.
- We checked that all objects can be classified as pure
star-forming galaxies. In total, we compiled 41 independent
star-forming regions, of which 31 have a direct estimate of the
electron temperature of the ionized gas, and hence their element
abundances were derived using the direct method. We found that younger
bursts have larger ionization budgets and are therefore capable to heat
the ionized gas to higher electron temperatures. Both c(H
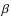 )
and
)
and 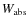 increase with increasing metallicity, as predicted by galaxy evolution
models.
increase with increasing metallicity, as predicted by galaxy evolution
models.
- 3.
- We compiled the oxygen abundance and N/O, S/O, Ne/O, Ar/O,
and Fe/O ratios in our WR galaxy sample. They generally agree well with
previous observations. The N/O ratio is found to be rather constant for
objects with
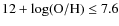 ,
has an important dispersion in galaxies with
,
has an important dispersion in galaxies with 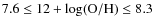 ,
and increases with the metallicity in objects with
,
and increases with the metallicity in objects with 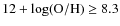 .
This behaviour is explained assuming the very different star-formation
histories that each individual system has experienced.
.
This behaviour is explained assuming the very different star-formation
histories that each individual system has experienced.
- 4.
- We detected a high N/O ratio in objects showing clear WR features (HCG 31 AC, UM 420, IRAS 0828+2816, III Zw 107, ESO 566-8 and NGC 5253). The ejecta of the WR stars may be the origin of the N enrichment in these galaxies, but further detailed data comparing the chemical properties of a larger sample of both WR and non-WR galaxies, as well as careful analyses of galaxies showing a localized high N/O ratio, are needed.
- 5.
- The relative abundance ratios of the
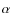 -elements to oxygen are
approximately constant, which is expected because all four elements are
mainly produced by massive stars. We found indications of a moderate
depletion of oxygen and iron onto grains in the most metal-rich
galaxies.
-elements to oxygen are
approximately constant, which is expected because all four elements are
mainly produced by massive stars. We found indications of a moderate
depletion of oxygen and iron onto grains in the most metal-rich
galaxies. - 6.
- We compared the abundances provided by the direct method
with those obtained using the most common empirical calibrations:
- the Pilyugin-method of Pilyugin (2001a,b), which considers the R23 and the P parameters and is updated by Pilyugin & Thuan (2005), is nowadays the best suitable empirical calibration to derive the oxygen abundance of star-forming galaxies. The cubic fit to R23 provided by Nagao et al. (2006) is not valid for analysing these star-forming galaxies;
- the relations between the oxygen abundance and the N2
or the O3N2 parameters
provided by Pettini & Pagel (2004) give
acceptable results for objects with
 ;
;
- the results provided by empirical calibrations based on photoionization models (McGaugh 1991; Kewley & Dopita 2002; Kobulnicky & Kewley 2004) are systematically 0.2-0.3 dex higher than the values derived from the direct method. These differences are of the same order as the abundance discrepancy found between abundances determined from recombination and collisionally excited lines of heavy-element ions. This may suggest temperature fluctuations in the ionized gas, as they exist in Galactic and other extragalactic H II regions.
- 7.
- We studied the optical/NIR
luminosity-metallicity relations for our sample galaxies. We found that
our data generally disagree with previous relations, perhaps because
the objects analysed here host strong starbursts, but maybe also
because we used the direct method and not the empirical calibrations to
derive the oxygen abundances. The L-Z
relations tend to be tighter when using NIR
luminosities, TDG candidates are indeed easier detected using the
 -Z
relation.
-Z
relation. - 8.
- The nitrogen abundance also has a strong correlation with the luminosity, but normal and dwarf non-starbursting galaxies show a higher N/O ratio than strong starbursting galaxies.
- 9.
- We found that galaxies with redder colours tend to have a higher oxygen abundance. The N/O ratio also increases with redder colours. Both results agree with galaxy evolution models. The colours of the underlying component seem to be metallicity-independent, but more data are still needed to confirm this trend.
Á.R. L.-S. thanks C.E. (his formal PhD supervisor) for the help and very valuable explanations, talks and discussions during these years. He also acknowledges the help and support given by the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (Spain) while doing his PhD. Á.R. L.-S. deeply thanks the Universidad de La Laguna (Tenerife, Spain) for force him to translate his PhD thesis from English to Spanish; he had to translate it from Spanish to English to complete this publication. This was the main reason of the delay of the publication of this research, because the main results shown here were already included in the PhD dissertation (in Spanish) which the first author finished in 2006 (López-Sánchez 2006). Á.R. L.-S. also thanks the people at the CSIRO/Australia Telescope National Facility, especially Bärbel Koribalski, for their support and friendship while translating his PhD. We are grateful to Janine van Eymeren for her comments about this manuscript, and to Mercedes Mollá for very fruitful discussions about the chemical evolution of the galaxies. We are also grateful for the comments provided by an anonymous referee, which improved the quality of this research. The authors also thank the language editor, A. Peter. This work has been partially funded by the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología (MCyT) under project AYA2004-07466. This research has made use of the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED) which is operated by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. This research has made extensive use of the SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System Bibliographic Services (ADS).
References
- Alloin, D., Collin-Souffrin, S., Joly, M., & Vigroux, L. 1979, A&A, 78, 200 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Amorín, R. O., Muñoz-Tuñón, C., Aguerri, J.A.L., Cairós, L.M., & Caon, N. 2007, A&A, 467, 541 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Amorín, R., Aguerri, J. A. L., Muñoz-Tuñón, C., & Cairós, L. M. 2009, A&A, 501, 75 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Bell, E. F., & de Jong, R. S. 2000, MNRAS, 312, 497 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bergvall, N., & Östlin, G. 2002, A&A, 390, 891 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Bomans, D. J., van Eymeren, J., Dettmar, R.-J., Weis, K., & Hopp, U. 2007, NewAR, 51, 141 [Google Scholar]
- Boselli, A., Gavazzi, G., Donas., J., & Scodeggio, M. 2001, AJ, 121, 753 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bothun, G. D., Romanishin, W., Strom, S. E., & Strom, K. M. 1984, AJ, 89, 1300 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Brinchmann, J., Kunth, D., & Durret, F. 2008, A&A, 485, 657 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzual, G., & Charlot, S. 2003, MNRAS, 344, 1000, BC03 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Cairós, L.M., Vílchez, J.M., González Pérez, J.N., Iglesias-Páramo, J., & Caon, N. 2001a, ApJS, 133, 321 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Cairós, L. M., Caon, N., Vílchez, J. M., González-Pérez, J. N., & Muñoz-Tuñón, C. 2001b, ApJS, 136, 393 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Aguilar, A., Moles, M., & Masegosa, J. 1993, AJ, 106 1784 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton, D. D., & Pantelaki, I. 1993, PhR, 227, 293 [Google Scholar]
- Crowther, P. A. 2007, ARAA, 45, 177 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther, P. A., & Hadfield, L. J., 2006, A&A, 449, 711 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Davé, R., & Oppenheimer, B. D. 2007, MNRAS, 374, 427 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- De Lucia, G., Kauffmann, G., & White, S. D. M. 2004, MNRAS, 374, 323 [Google Scholar]
- Denicoló, G., Terlevich, R., & Terlevich, E. 2002, MNRAS, 330, 69 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- de Naray, R. K., McGaugh S. S., & de Blok W. J. G., 2004, MNRAS, 355, 887 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- De Rossi, M. E., Tissera, P. B., & Scannapieco, C. 2006, MNRAS, 374, 323 [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, A. I., & Pérez-Montero, E. 2000, MNRAS, 312, 130 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Dopita, M. A., & Evans, I. N. 1986, ApJ, 307, 431 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Dopita, M. A., Kewley, L. J., Heisler, C. A., & Sutherland, R. S. 2000, ApJ, 542, 224 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, Y., & Teyssier, R. 2007, EAS, 24, 95 [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Duc, P.-A., & Mirabel, I. F. 1998, A&A 338, 813 [Google Scholar]
- Duc, P. A., Brinks, E., Springel, V., Pichardo, B., Weilbacher, P., & Mirabel, I.F. 2000, AJ, 120, 1238 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Edmunds, M. G., & Pagel, B. E. J. 1978, MNRAS, 185, 77 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Edmunds, M. G., & Pagel, B. E. J. 1984, MNRAS, 211, 507 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Erb, D. K., Shapley, A. E., Steidel, C. C., et al. 2003, ApJ, 591, 101 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Erb, D. K., Shapley, A. E., Pettini, M., et al. 2006, ApJ, 644, 813 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, C., & Peimbert, M. 1995, A&A, 300, 78 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, C., Bresolin, F., Peimbert, M., et al. 2009, ApJ, 700, 654 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Ferland G. J., Korista K. T., Verner D. A., et al. 1998, PASP, 110, 761 [Google Scholar]
- Fioc, M., & Rocca-Volmerange, B. 1997, A&A 326, 950 [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, S. C., Durrell, P. R., Elmegreen, D. M., et al. 2010, AJ, 139, 545 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- García-Rojas, J., & Esteban, C., 2007, ApJ, 670, 457 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett, D. R. 1992, AJ, 103, 1330 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett, D. R. 2002, ApJ, 581, 1019 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- Hägele, G. F., Díez, Á. I., Terlevich, E., et al. 2008. MNRAS, 383, 209 [Google Scholar]
- Henry, R. B. C., Edmunds, M. G., & Köppen, J. 2000, ApJ, 541, 660 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo-Gámez, A. M., & Olofsson, K. 1998, A&A, 334, 45 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashita, H., Inoue, A. K., Kamaya, H., & Shibai, H. 2001, A&A, 366, 83 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Izotov, Y. I., & Thuan, T. X. 1998, ApJ, 500, 188 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Izotov, Y. I., & Thuan, T. X. 1999, ApJ, 511, 639 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Izotov, Y. I., & Thuan, T. X. 2004, ApJ, 616, 768 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Izotov, Y. I., Papaderos, P., Guseva, N. G., Fricke, K. J., & Thuan, T. X. 2004, A&A 421, 539 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Izotov, Y. I., Stasinska, G., Meynet, G., Guseva, N. G., & Thuan, T. X. 2006, A&A, 448, 955 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- James, B. L., Tsamis, Y. G., & Barlow, M. J. 2010, MNRAS, 401, 759 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, R. A., Franx, M., Fabricant, D., & Caldwell, N. 2000, ApJS, 126, 271 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. B., Strom K. M., & Strom S. E. 1976, ApJ, 209, 748 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann, G., & White, S. D. M. 1993, MNRAS, 261, 921 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann, G., Heckman, T. M., Tremonti, C., et al. 2003, MNRAS, 346 1055 [Google Scholar]
- Kennicutt, R. C. Jr., Bresolin, F., & Garnett, D. R. 2003, ApJ, 591, 801 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kewley, L. J., & Dopita, M. A. 2002, ApJS, 142, 35 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kewley, L. J., & Ellison, S. E. 2008, ApJ, 681, 1183 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kewley, L. J., Dopita, M. A., Sutherland, R. S., Heisler, C. A., & Trevena, J. 2001, ApJS, 556, 121 [Google Scholar]
- Kinman, T. D., & Davidson, K. 1981, ApJ, 243, 127 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kobulnicky, H. A., & Kewley, L. J. 2004, ApJ, 617, 240 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kobulnicky, H. A., & Skillman, E. D. 1998, ApJ, 497, 601 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kobulnicky, H. A., Skillman, E. D., Roy, J.-R., Walsh, J. R., & Rosa, M. R., 1997, ApJ, 277, 679 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kobulnicky, H. A., Kennicutt, R. C.Jr., & Pizagno, J. L. 1999, ApJ, 514, 544 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kobulnicky, H. A., Willmer, C. N. A., Phillips, A. C., et al. 2003, ApJ, 599, 1006 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J. C., Salzer J. J., & Melbourne, J. 2004, ApJ, 616, 752 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Leitherer, C., Schaerer, D., Goldader, J. D., et al. 1999, ApJS, 123, 3 (STARBURST 99) [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Lequeux, J., Peimbert, M., Rayo, J. F., Serrano, A., & Torres-Peimbert, S. 1979, A&A, 80, 155 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y. C., Yin, S. Y., Hammer, F., et al. 2006, ApJ, 652, 257 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly, S. J., Carollo, C. M., & Stockton, A. N. 2003, ApJ, 597, 730 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- López-Sánchez, Á. R. 2006, Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de la Laguna, Tenerife, Spain [Google Scholar]
- López-Sánchez, Á. R., & Esteban, C. 2008, A&A, 491, 131, Paper I [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- López-Sánchez, Á. R., & Esteban, C. 2009, A&A, 508, 615, Paper II [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- López-Sánchez, Á. R., & Esteban, C. 2010, A&A, 516, 104, Paper III [Google Scholar]
- López-Sánchez, Á. R., Esteban, C., & Rodríguez, M. 2004a, ApJS, 153, 243 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- López-Sánchez, Á. R., Esteban, C., & Rodríguez, M. 2004b, A&A, 428, 445 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- López-Sánchez, Á. R., Esteban, C., & García-Rojas, J. 2006, A&A, 449, 997 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- López-Sánchez, Á. R., Esteban, C., García-Rojas, J., Peimbert, M., & Rodríguez, M. 2007, ApJ, 656, 168 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Mac Low, M., & Ferrara, A. 1999, ApJ, 513, 142 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Marlowe, A. T., Heckman, T. M., Wyse, R. F. G., & Schommer, R. 1995, ApJ, 438, 563 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Manjón, M. L., Mollá, M., Díaz, A. I., & Terlevich, R. 2008, MNRAS, 385, 854 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- McCall, M. L., Rybski, P. M., & Shields, G. A. 1985, ApJS 57, 1 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh, S. S. 1991, ApJ, 380, 140 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh, S. S. 1994, ApJ, 426, 135 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh, S. S., & de Blok, W. J. G. 1997, ApJ, 481, 689 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Mendes de Oliveira, C. L., Temporin, S., Cypriano, E. S., et al. 2006, AJ, 132, 570 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Méndez, D. I., & Esteban, C. 1997, ApJ, 488, 652 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Meynet, G., & Maeder, A. 2005, A&A, 429, 581 [Google Scholar]
- Mollá, M., Vílchez, J. M., Gavilán, M., & Díaz, A. I. 2006, MNRAS, 372, 1069 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao, T., Maiolino, R., & Marconi, A. 2006, A&A, 459, 85 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Oey M. S., & Shields J. C. 2000, ApJ, 539, 687 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Pagel, B. E. J., Edmunds, M. G., Blackwell, D. E., Chun, M. S., Smith, G. 1979, MNRAS, 189, 95 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Papaderos, P., Guseva, N. G., Izotov, Y. I., et al. 2006, A&A, 457, 45 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Peimbert, M. 1967, ApJ, 150, 825 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Peimbert, M., Peimbert, A., Esteban, C., et al. 2007, RMxAC, 29, 72 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Peña, M., & Ayala, S. 1993, Rev. Mex. Astron. Astrofis., 27, 171 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Montero, E., & Díaz, A. I. 2005, MNRAS, 361, 1063 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Pettini, M., & Pagel, B. E. J. 2004, MNRAS, 348, 59 [Google Scholar]
- Pettini, M., Shapley, A. E., Steidel, C. C., et al. 2001, ApJ, 554, 981 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Pilyugin, L. S. 2000, A&A, 362, 325 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Pilyugin, L. S. 2001a, A&A, 369, 594 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Pilyugin, L. S. 2001b, A&A, 374, 412 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Pilyugin, L. S., & Thuan, T. X. 2005, ApJ, 631, 231 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- Pilyugin, L. S., Thuan, T. X., & Vílchez, J. M. 2003, A&A, 397, 487 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Pilyugin, L. S., Vílchez, J. M., & Contini, T. 2004, A&A, 425, 849 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Piovan, L., Tantalo, R., & Chiosi, C. 2006, MNRAS, 366, 923 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Pustilnik, S., Kniazev, A., Pramskij, A., et al. 2004, A&A, 419, 469 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Richer, M. G., & McCall, M. L. 1995, ApJ, 445, 642 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, V. C., Ford, W. K., Jr., & Whitmore, B. C. 1984, ApJ, 281, L21 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Salzer, J. J., Lee, J. C., Melbourne, J., et al. 2005, ApJ, 624, 661 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Schaerer, D., & Vacca, W. D. 1998, ApJ, 497, 618 (SV98) [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Schaerer, D., Contini, T., & Pindao, M. 1999, A&AS, 136, 35 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Skillman, E. D., Kennicutt, R. C., & Hodge, P. W. 1989, ApJ, 347, 875 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Springel, V., & Hernquist, L. 2003, MNRAS, 339, 312 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Springel, V., White, S., Jenkins, A., et al. 2005, Nature, 435, 629 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasinska, G. 2002, RMxAC, 12, 62 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Stasinska, G. 2005, A&A, 434, 507 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Stasinska, G. 2006, A&A, 454, 127 [Google Scholar]
- Stasinska, G. 2010, Stellar Populations - planning for the next decade, ed. Bruzual, & Charlot, Proc. IAU Symp., 262, 93 [Google Scholar]
- Stasinska, G., Schaerer, D., & Leitherer, C. 2001, A&A, 370, 1 [Google Scholar]
- Steidel, C. C., Shapley A. E., Pettini M., et al. 2004, ApJ, 604, 534 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Storchi-Bergmann, T., Calzetti, D., & Kinney, A. L. 1994, ApJ, 429, 572 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, R. S., & Dopita, M. A. 1993, ApJS, 88, 253 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Tenorio-Tagle, G., Muñoz-Tuñón, C., Pérez, E. Silich, S., & Telles, E. 2006, ApJ, 643, 186 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Teplitz, H. I., Malkan, M. A., Steidel, C. C., et al. 2000, ApJ, 542, 18 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Tissera, P. B., De Rossi, M. E., & Scannapieco, C. 2005, MNRAS, 364, L38 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Peimbert, S., Peimbert, M., & Fierro, J. 1989, ApJ, 345, 186 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Tremonti, C. A., Heckman, T. M., Kauffmann, G., et al. 2004, ApJ, 613, 898 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- van Eymeren, J., Bomans, D. J., Weis, K., & Dettmar, R.-J. 2007, A&A, 474, 67 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- van Eymeren, J., Marcelin, M., Koribalski, B. S., et al. 2009, A&A, 505, 105 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- van Eymeren, J., Koribalski, B. S., López-Sánchez, Á. R., Dettmar, R.-J., & Bomans, D. J. 2010, MNRAS, accepted [Google Scholar]
- van Zee, L., Salzer, J. J., & Haynes, M. P. 1998, ApJ, 497, 1 [Google Scholar]
- van Zee, L., & Haynes, M.P. 2006, ApJ, 636, 214 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez, G. A., & Leitherer, C. 2005, ApJ, 621, 695 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A., Lutz, D., Sturm, E., et al. 2003, A&A, 403, 829 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Vila-Costas, M. B., & Edmunds, M. G. 1992, MNRAS, 259, 121 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Vila-Costas, M. B., & Edmunds, M. G. 1993, MNRAS, 265, 199 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Vílchez, J. M., & Esteban, C. 1996, MNRAS, 280, 720 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Weilbacher, P. M., Duc, P. A., & Fritze-von Alvensleben, U. 2003, A&A, 397, 545 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Woosley S. E., & Weaver, T. A. 1995, ApJS, 101, 181 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Wyse, R. F. G., & Silk, J. 1985, ApJ, 296, L1 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S. Y., Liang, Y. C., Hammer, F., et al. 2007, A&A, 462, 535 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- York, D. G., Adelman, J., Anderson, J. E., Jr., et al. 2000, AJ, 120, 1579 [Google Scholar]
- Zaritsky, D., Kennicutt, R. C. Jr., & Huchra, J. P. 1994, ApJ, 420, 87 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Online Material
Appendix A: Empirical calibrations of the oxygen abundance
When the spectrum of an extragalactic H II region
does not show the [O III] ![]() 4363
emission line or other auroral lines that can be used to derive
4363
emission line or other auroral lines that can be used to derive ![]() ,
the so-called empirical calibrations are applied
to get a rough estimation of its metallicity.
Empirical calibrations are inspired partly by photo-ionization models
and partly by observational trends of line strengths with
galactocentric distance in gas-rich spirals, which are believed to be
due to a radial abundance gradient with abundances decreasing outwards.
In extragalactic objects, the usefulness of the empirical methods goes
beyond the derivation of abundance gradients in spirals (Pilyugin et
al. 2004),
as these methods find application in chemical abundance studies of a
variety of objects, including low-surface brightness galaxies (de Naray
et al. 2004)
and star-forming galaxies at intermediate and high redshift, where the
advent of 8-10 m class telescopes has made it possible to extend
observations (e.g., Teplitz et al. 2000; Pettini
et al. 2001;
Kobulnicky et al. 2003;
Lilly et al. 2003;
Steidel et al. 2004;
Kobulnicky & Kewley 2004;
Erb et al. 2006).
,
the so-called empirical calibrations are applied
to get a rough estimation of its metallicity.
Empirical calibrations are inspired partly by photo-ionization models
and partly by observational trends of line strengths with
galactocentric distance in gas-rich spirals, which are believed to be
due to a radial abundance gradient with abundances decreasing outwards.
In extragalactic objects, the usefulness of the empirical methods goes
beyond the derivation of abundance gradients in spirals (Pilyugin et
al. 2004),
as these methods find application in chemical abundance studies of a
variety of objects, including low-surface brightness galaxies (de Naray
et al. 2004)
and star-forming galaxies at intermediate and high redshift, where the
advent of 8-10 m class telescopes has made it possible to extend
observations (e.g., Teplitz et al. 2000; Pettini
et al. 2001;
Kobulnicky et al. 2003;
Lilly et al. 2003;
Steidel et al. 2004;
Kobulnicky & Kewley 2004;
Erb et al. 2006).
As the brightest metallic lines observed in spectra of
H II regions are those involving
oxygen, this element has been extensively used to get a suitable
empirical calibration. Oxygen abundance is important as one of the
fundamental characteristics of a galaxy: its radial distribution is
combined with radial distributions of gas and star surface mass
densities to constrain models of chemical evolution. Parameters defined
in empirical calibrations evolving bright oxygen lines are
| R3 | = | (A.1) | |
| R2 | = | (A.2) | |
| R23 | = | R3 + R2, | (A.3) |
| P | = | (A.4) | |
| y | = | (A.5) |
Jensen et al. (1976) presented the first exploration in this method considering the R3 index, which considers the [O III]
| Figure A.1:
Empirical calibrations of oxygen
abundance using the R23
parameter. Note that they are bi-valuated. The dashed zone indicates
the region with higher uncertainties in O/H. The empirical calibrations
plotted in the figure are: EP94: Edmunds & Pagel (1984); M91:
McGaugh (1991)
using y=0 (R2=R3);
P01: Pilyugin (2001)
using P=0.5 (R2=R3);
(KD02+KK04): Kewley & Dopita (2002) using the
formulation of Kobulnicky & Kewley (2004) assuming
|
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
The main problem associated with the use of R23
parameter is that it is bivaluated, i.e., a single value of R23
can be caused by two very different oxygen abundances. The reason of
this behaviour is that the intensity of oxygen lines does
not indefinitely increase with metallicity. Thus, there are
two branches for each empirical calibration (see
Fig. A.1):
the low-metallicity regime, with 12+log(O/H)![]() 8.1, and the
high-metallicity regime, with 12+log(O/H)
8.1, and the
high-metallicity regime, with 12+log(O/H)![]() 8.4. That
means that a very large fraction of the star-forming regions lie in the
ill-defined turning zone around 12+log(O/H
8.4. That
means that a very large fraction of the star-forming regions lie in the
ill-defined turning zone around 12+log(O/H
![]() ,
where regions with the same R23
value have oxygen abundances that differ by almost an order of
magnitude. Hence, additional information, such as the [N II]/H
,
where regions with the same R23
value have oxygen abundances that differ by almost an order of
magnitude. Hence, additional information, such as the [N II]/H![]() or the [O II]/[O III]
ratios, is needed to break the degeneracy between the high and low
branches (i.e., Kewley & Dopita, 2002). Besides,
the R23 method requires that
spectrophotometric data are corrected by reddening, which effect is
crucial because [O II] and [O III]
lines have a considerably separation in wavelength.
or the [O II]/[O III]
ratios, is needed to break the degeneracy between the high and low
branches (i.e., Kewley & Dopita, 2002). Besides,
the R23 method requires that
spectrophotometric data are corrected by reddening, which effect is
crucial because [O II] and [O III]
lines have a considerably separation in wavelength.
Here we list all empirical calibrations that were considered in this work, compiling the equations needed to derive the oxygen abundance from bright emission line ratios following every method.
Edmunds & Pagel (1984):
Although the R23 parameter
was firstly proposed by Pagel et al. (1979), the first
empirical calibration was given by Edmunds & Pagel (1978),
| (A.6) |
with the limit between the lower and the upper branches at
Table A.1:
List of the parameters used to compute the oxygen abundance in all
regions with a direct estimation of ![]() using empirical calibrations.
using empirical calibrations.
Table A.2:
Results of the oxygen abundance, in the form ![]() ,
for objects with a direct estimation of the metallicity, considering
several empirical calibrations.
,
for objects with a direct estimation of the metallicity, considering
several empirical calibrations.
McCall et al. (1985)
presented an empirical calibration for oxygen abundance using the R23
parameter, only valid for 12+log(O/H)>8.15. However, they did
not give an analytic formulae but only listed it numerically (see their
Table 15). The four-order polynomical fit for their values
gives the following relation:
|
|
= | 9.32546 -0.360465x +0.203494x2 | |
| (A.7) |
with
Zaritsky et al. (1994)
provided a simple analytic relation between oxygen abundance and R23:
|
|
= | 9.265-0.33x -0.202x2 | |
| (A.8) |
Their formula is an average of three previous calibrations: Edmunds & Pagel (1978), McCall et al. (1985) and Dopita & Evans (1986). Following the authors, this calibration is only suitable for 12+log(O/H)>8.20, but perhaps a more realistic lower limit is 8.35.
McGaugh (1991) calibrated the relationship between the R23
ratio and gas-phase oxygen abundance using H II region
models derived from the photoionization code CLOUDY
(Ferland et al. 1998).
McGaugh's models include the effects of dust and variations in
ionization parameter, y. Kobulnicky et al.
(1999)
give analytical expressions for the McGaugh (1991) calibration
based on fits to photoionization models; the middle point between both
branches is ![]() :
:
|
|
= | 7.056+0.767x +0.602x2 | |
| (A.9) | |||
| = | 9.061 - 0.2x-0.237x2-0.305x3 | ||
| (A.10) |
Pilyugin (2000) found that the previous calibrations using the R23 parameter had a systematic error depending on the hardness of the ionizing radiation, suggesting that the excitation parameter, P, is a good indicator of it. In several papers, Pilyugin performed a detailed analysis of the observational data combined with photoionization models to obtain empirical calibrations for the oxygen abundance. Pilyugin (2000) confirmed the idea of McGaugh (1991) that the strong lines of [O II] and [O III] contain the necessary information for the determination of accurate abundances in low-metallicity (and may be also in high-metallicity) H II regions. He used new observational data to propose a linear fit involving only the R23 parameter,
| (A.11) | ||
| (A.12) |
assuming a limit of
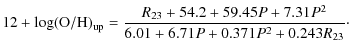
|
(A.13) |
This is the so-called P-method, which can be used in moderately high-metallicity H II regions (
| (A.14) |
Pilyugin estimates that the precision of oxygen abundance determination with this method is around 0.1 dex.
Pilyugin & Thuan (2005) revisited
these calibrations including more spectroscopic measurements of
H II regions in spiral and
irregular galaxies with a measured intensity of the [O III]
![]() 4363 line
and recalibrate the relation between the oxygen abundance and the R23
and P parameters, yielding to:
4363 line
and recalibrate the relation between the oxygen abundance and the R23
and P parameters, yielding to:
|
|
= | 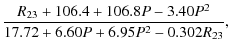
|
(A.15) |
| = | 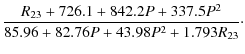
|
(A.16) |
Kewley & Dopita (2002) used a combination of stellar population synthesis and photoionization models to develop a set of ionization parameters and abundance diagnostic based only on the strong optical emission lines. Their optimal method uses ratios of [N II], [O II], [O III], [S II], [S III] and Balmer lines, which is the full complement of strong nebular lines accessible from the ground. They also recommend procedures for the derivation of abundances in cases where only a subset of these lines is available. Kewley & Dopita (2002) models start with the assumption that R23, and many of the other emission-line abundance diagnostics, also depends on the ionization parameter
Kobulnicky & Kewley (2004) gave a
parameterization of the Kewley & Dopita (2002) R23
method with a form similar to that given by McGaugh (1991)
calibration. Kobulnicky & Kewley (2004)
presented an iterative scheme to resolve for both the ionization
parameter q and the oxygen abundance using only [O III],
[O II] and H![]() lines. The parameterization they give for q is
lines. The parameterization they give for q is
|
|
= | ||
| (A.17) |
where
|
|
= | ||
| (A.18) | |||
| = | 9.40+4.65x-3.17x2 | ||
| (A.19) |
being
Nagao et al. (2006)
did not consider any ionization parameter. They merely used data of a
large sample of galaxies from the SDSS to derive a cubic fit to the
relation between R23 and the
oxygen abundance,
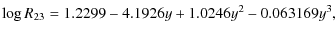
|
(A.20) |
with
Besides R23, additional
parameters have been used to derive metallicities in star-forming
galaxies. Without other emission lines, the N2
parameter, which is defined by
| (A.21) |
can be used as a crude estimator of metallicity. However, we note that the [N II]/H
| (A.22) |
which considerably improves the previous relations because of the inclusion of an extensible sample of nearby extragalactic H II regions. The uncertainty of this method is
Pettini & Pagel (2004)
revisited the relation between the N2 parameter
and the oxygen abundance including new data for the high- and
low-metallicity regimen. They only considered those extragalactic
H II regions where the oxygen
values are determined either via the ![]() method or with detailed photoionization modelling. Their linear fit to
their data is
method or with detailed photoionization modelling. Their linear fit to
their data is
| (A.23) |
which has both a lower slope and zero-point that the fit given by Denicoló et al. (2002). A somewhat better relation is provided by a third-order polynomical fit of the form
|
|
= | 9.37 + 2.032 N2 | |
| + 1.26 (N2)2 + 0.32 (N2)3, | (A.24) |
valid in the range -2.5 < N2 < -0.3. Nagao et al. (2006) also provided a relation between N2 and the oxygen abundance, their cubic fit to their SDSS data yields
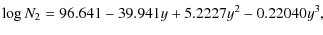
|
(A.25) |
with
Pettini & Pagel (2004)
revived the O3N2
parameter, previously introduced by Alloin et al. (1979) and defined
by
| (A.26) |
Pettini & Pagel (2004) derived the following least-square linear fit to their data:
| (A.27) |
Nagao et al. (2006) also revisited this calibration and derived a cubic fit between the O3N2 parameter and the oxygen abundance,
|
|
= | -232.18 + 84.423y -9.9330y2 | |
| (A.28) |
with
Other important empirical calibrations that were not used in this study involve the S23 parameter, introduced by Vílchez & Esteban (1996) and revisited by Díaz & Pérez-Montero (2000); Oey & Shields (2000) and Pérez-Montero & Díaz (2005). In the last years, bright emission line ratios such as [Ar III]/[O III] and [S III]/[O III] Stasinska (2006) or [Ne III]/[O III] and [O III]/[O II] (Nagao et al. 2006) have been explored as indicators of the oxygen abundance in H II regions and starburst galaxies. Peimbert et al. (2007) suggested to use the oxygen recombination lines to get a more precise estimation of the oxygen abundance. Nowadays, there is still a lot of observational and theoretical work to do involving empirical calibrations (see recent review by Kewley & Ellison 2008), but these methods should be used only for objects whose H II regions have the same structural properties as those of the calibrating samples (Stasinska 2010).
Footnotes
- ...
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
- Based on observations made with NOT (Nordic Optical Telescope), INT (Isaac Newton Telescope) and WHT (William Herschel Telescope) operated on the island of La Palma jointly by Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden (NOT) or the Isaac Newton Group (INT, WHT) in the Spanish Observatorio del Roque de Los Muchachos of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias. Based on observations made at the Centro Astronómico Hispano Alemán (CAHA) at Calar Alto, operated by the Max-Planck Institut für Astronomie and the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (CSIC).
- ...
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
- Appendices are only available in electronic form at http://www.aanda.org
All Tables
Table 1: Compilation of the broad-band photometric dataa for the individual galaxies analysed in this work.
Table 2: Physical properties of the ionized gas for the galaxies analysed in this work.
Table 3: Chemical properties of the ionized gas for the galaxies analysed in this work.
Table 4:
Results of the comparison between the oxygen abundance given by several
empirical calibrations and the oxygen abundance derived here following
the direct (![]() )
method.
)
method.
Table A.1:
List of the parameters used to compute the oxygen abundance in all
regions with a direct estimation of ![]() using empirical calibrations.
using empirical calibrations.
Table A.2:
Results of the oxygen abundance, in the form ![]() ,
for objects with a direct estimation of the metallicity, considering
several empirical calibrations.
,
for objects with a direct estimation of the metallicity, considering
several empirical calibrations.
All Figures
![\begin{figure}
\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f01.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg188.png)
|
Figure 1:
Comparison between the reddening-corrected absolute B-magnitudes
(MB) and
the uncorrected ones (
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=17cm,clip]{14156f02.eps}\vspace*{-1.5mm}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg192.png)
|
Figure 2:
Colour-colour diagrams comparing the predictions given
by evolutionary synthesis models (continous line: BC03, Bruzual
& Charlot 2003,
models; discontinuous line: PEGASE.2, Fioc & Rocca-Volmerange 1997, models; dotted
line: STARBURST 99, Leitherer et al. 1999,
assuming Z=0.4 |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f03.eps} %
\vspace*{-2.5mm}\vspace*{4mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg202.png)
|
Figure 3:
W(H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f04.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg617.png)
|
Figure 4: Comparison of some observational flux ratios obtained for all available regions analysed in this work with the diagnostic diagrams proposed by Dopita et al. (2000), blue continuous line (D00), and Kewley et al. (2001), red discontinuous line (K01). The left panel also shows the empirical relation provided by Kauffmann et al. (2003) with a dotted-dashed dark yellow line (Ka03). |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f05.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg618.png)
|
Figure 5:
High ionization electron temperature, |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f06.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg620.png)
|
Figure 6:
O++/O+ ratio vs. W(H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f07.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg621.png)
|
Figure 7:
Reddening coefficient, c(H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f08.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg622.png)
|
Figure 8:
Equivalent width of the underlying stellar absorption in the Balmer
H I lines, |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f09.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg625.png)
|
Figure 9:
H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f10.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg626.png)
|
Figure 10:
F([O III] |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f11.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg627.png)
|
Figure 11:
(Left) N/O ratio vs. oxygen abundance for all
objects with a direct estimate of |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f12.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg637.png)
|
Figure 12:
Observed nitrogen overabundance, |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{14156f13.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg642.png)
|
Figure 13:
H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f14.eps}
\vspace*{2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg643.png)
|
Figure 14: Ne/O, S/O, Ar/O ang Fe/O ratios vs the oxygen abundance for the galaxies analysed in this work. We compare with the results provided by the galaxy samples considered by Izotov & Thuan (1999) and Izotov et al. (2006). The dashed dark-blue lines indicate a fit to our data. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f15.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg651.png)
|
Figure 15:
Comparison between the oxygen abundances derived using the direct
method ( |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f16.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg652.png)
|
Figure 16:
Comparison between the oxygen abundances derived using the direct
method ( |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f17.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg662.png)
|
Figure 17:
Metallicity-luminosity diagrams for the objects analysed in this work.
The oxygen abundance is expressed in units of |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f18.eps}
\vspace{1.5mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg675.png)
|
Figure 18:
Nitrogen abundance vs. luminosity for the galaxies analysed in this
work. The nitrogen abundance is expressed in units of 12+log(N/H); the
luminosity is expressed as the absolute magnitude in B
( left) and |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f19.eps} %\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg681.png)
|
Figure 19: Metallicity-colour diagrams for the galaxies analysed in this work. A linear fit is shown with a continuous red line. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f20.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg686.png)
|
Figure 20:
N/O ratio vs. the reddening-corrected B-V
colour considering all the galaxy (left) or just the underlying stellar
population (right). A linear fit to our data is shown with a continuous
red line. The relationship found by van Zee & Haynes (2006) in their
analysis of dwarf irregular galaxies is plotted with a dashed green
line. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=18cm,clip]{14156f21.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/09/aa14156-10/Timg687.png)
|
Figure 21: N/O ratio vs. the reddening-corrected V-R ( left) and J-H ( right) colours. A linear fit to our data is shown with a continuous red line. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
| |
Figure A.1:
Empirical calibrations of oxygen
abundance using the R23
parameter. Note that they are bi-valuated. The dashed zone indicates
the region with higher uncertainties in O/H. The empirical calibrations
plotted in the figure are: EP94: Edmunds & Pagel (1984); M91:
McGaugh (1991)
using y=0 (R2=R3);
P01: Pilyugin (2001)
using P=0.5 (R2=R3);
(KD02+KK04): Kewley & Dopita (2002) using the
formulation of Kobulnicky & Kewley (2004) assuming
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
Copyright ESO 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


