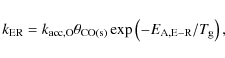| Issue |
A&A
Volume 515, June 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A66 | |
| Number of page(s) | 8 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200913896 | |
| Published online | 10 June 2010 | |
Beyond the pseudo-time-dependent approach: chemical models of dense core precursors
G. E. Hassel1 - E. Herbst1,2 - E. A. Bergin3
1 - Department of Physics, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210, USA
2 -
Departments of Astronomy and Chemistry, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210, USA
3 -
Department of Astronomy, University of Michigan, 825 Dennison Building, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA
Received 17 December 2009 / Accepted 10 March 2010
Abstract
Context. Chemical models of dense cloud cores often utilize
the so-called pseudo-time-dependent approximation, in which the
physical conditions are held fixed and uniform as the chemistry occurs.
In this approximation, the initial abundances chosen, which are totally
atomic in nature except for molecular hydrogen, are artificial. A more
detailed approach to the chemistry of dense cold cores should include
the physical evolution during their early stages of formation.
Aims. Our major goal is to investigate the initial synthesis of
molecular ices and gas-phase molecules as cold molecular gas begins to
form behind a shock in the diffuse interstellar medium. The abundances
calculated as the conditions evolve can then be utilized as reasonable
initial conditions for a theory of the chemistry of dense cores.
Methods. Hydrodynamic shock-wave simulations of the early stages
of cold core formation are used to determine the time-dependent
physical conditions for a gas-grain chemical network. We follow the
cold post-shock molecular evolution of ices and gas-phase molecules as
the visual extinction increases with time to
![]() .
(Note that instead of an equal sign, the approximately equal sign
should remain.) At higher extinction, self-gravity becomes important.
.
(Note that instead of an equal sign, the approximately equal sign
should remain.) At higher extinction, self-gravity becomes important.
Results. As the newly condensed gas enters its cool post-shock
phase, a large amount of CO is produced in the gas. As the CO forms,
water ice is produced on grains, while accretion of CO produces CO ice.
The production of CO2 ice from CO occurs via several surface mechanisms, while the production of CH4 ice is slowed by gas-phase conversion of C into CO.
Key words: ISM: clouds - evolution - ISM: molecules - shock waves - stars: formation
1 Introduction
The formation of molecular clouds from the diffuse atomic interstellar medium has been the subject of much interest. Proposed mechanisms have been reviewed in the recent literature (Bergin & Tafalla 2007; McKee & Ostriker 2007; André et al. 2008). Despite this interest, most chemical models of cold dense interstellar clouds utilize the simple pseudo-time-dependent approximation, in which the physical conditions are homogeneous and fixed, beginning from an already dense, cold, and darkened state with all H in H2. Moreover, the initial abundances for heavy elements are assumed to be atomic. Yet, the high abundance of molecular hydrogen in diffuse clouds suggests that molecules can be synthesized as clouds form as well as during their existence. One approach to dense cloud formation, that of hydrodynamic shock waves, has been studied by Bergin et al. (2004, hereafter B04), who showed that the gas-phase molecules H2 and CO are produced early in the formation of the cloud. In this paper, we revisit the approach of B04, and include a more complex treatment of the gas-grain chemistry that evolves in tandem with the post-shock physical conditions. We focus on the initial production of major solid phase and gaseous molecules in the post-shock material as the extinction gradually increases.
Prior investigations have considered some aspects of the problem we discuss here. Early dynamic models of dense and diffuse clouds were reviewed by Williams (1988). Cyclic models involving shocks were studied by Nejad & Williams (1992). Our approach is similar to the constant-pressure collapse model of Pineau des Forêts et al. (1991), although that paper did not include grain surface chemistry. Such chemistry was included by Ruffle & Herbst (2001) in a pseudo-time-dependent model of the formation of mantle ices using an earlier version of our gas-grain network. These authors were mainly interested in explaining the formation of CO2 ice, which had been under-produced in their previous models. A pseudo-time-dependent approach with surface chemistry was also used to study the water ice distribution at various conditions throughout the Taurus dark cloud (Nguyen et al. 2002).
Table 1: Shock models.
2 Hydrodynamical model
We have used four shock models based on the results presented in B04; the shock speed, initial total hydrogen density, and fractional abundance of gaseous H2 if any are listed in Table 1. Of these four models, the first three were taken directly from B04 whereas the fourth model, starting with the densest gas, was run using unpublished B04 model results, the motivation being to explore greater initial densities.
The shock initially heats the low density gas, which cools via atomic
fine structure emission. At the cooling timescale, the gas-phase
temperature drops to the equilibrium of C+
cooling and photoelectric heating, while the density rises. It is
important to note that the chemistry modeled in this work is not shock chemistry, such as the evolution during the hot phase of hydrodynamic shocks studied by Mitchell & Watt (1985)
and associated papers. Rather, all of the relevant chemical evolution
occurs in the post-shock phase where the initially atomic gas has
become dense (
![]() cm-3) and cold (
cm-3) and cold (
![]() K),
but critically is still at low extinction. We present the conditions at
the onset time of this stage when gas temperature and density reach
near-constant conditions and identify it as the ``discontinuity time'',
K),
but critically is still at low extinction. We present the conditions at
the onset time of this stage when gas temperature and density reach
near-constant conditions and identify it as the ``discontinuity time'',
![]() ,
in Table 1.
As time proceeds in our models, the major change in the physical state
is increasing dust extinction, which is key for the growth of molecular
abundances. Table 1 also contains information concerning the conditions of the post-shock cold and dense gas later when
,
in Table 1.
As time proceeds in our models, the major change in the physical state
is increasing dust extinction, which is key for the growth of molecular
abundances. Table 1 also contains information concerning the conditions of the post-shock cold and dense gas later when ![]() has reached 2.0.
has reached 2.0.
Some physical results for models 3 and 4, which possess the lowest and
highest density, respectively, in the post-shock gas, are displayed in
Fig. 1 starting at a time of 104
yr after the shock. Similar plots for models 1 and 2 previously
appeared in Fig. 2 of B04. As the gas temperature cools and the
density increases, the visual extinction and column slowly build up
over time. The results of B04 follow the time dependence of ![]() until it reaches a value of a few, which can take upwards of 10 Myr, as shown in Fig. 1 and Table 1. To extend this increase to slightly greater times, one can estimate
until it reaches a value of a few, which can take upwards of 10 Myr, as shown in Fig. 1 and Table 1. To extend this increase to slightly greater times, one can estimate ![]() by Eq. (4) in B04. The density and gas temperature are assumed not
to change from their final state during this extension. It is likely
that beyond
by Eq. (4) in B04. The density and gas temperature are assumed not
to change from their final state during this extension. It is likely
that beyond
![]() mag our simulations are strongly affected by self-gravity (Hartmann et al. 2001).
The same chemical-dynamical treatment cannot therefore be used
realistically to reach fully formed cloud cores of higher extinction
(e.g., TMC-1). However, the model results, especially for the ices, can
be compared with observations of cores of low extinction in assemblies
such as the Taurus cloud (Whittet et al. 2007,
and references therein). In addition, results for CO(g) can be compared
with observed values in diffuse and translucent regions. Perhaps most
importantly, the results can also be used as more realistic initial
abundances for normal dense core chemistry than the gaseous mainly
atomic abundances used in the pseudo-time-dependent treatments. It is
also possible to follow the dynamics and chemistry until cold dense
cores form at high extinction with a more detailed hydrodynamical model
(Aikawa et al. 2005).
mag our simulations are strongly affected by self-gravity (Hartmann et al. 2001).
The same chemical-dynamical treatment cannot therefore be used
realistically to reach fully formed cloud cores of higher extinction
(e.g., TMC-1). However, the model results, especially for the ices, can
be compared with observations of cores of low extinction in assemblies
such as the Taurus cloud (Whittet et al. 2007,
and references therein). In addition, results for CO(g) can be compared
with observed values in diffuse and translucent regions. Perhaps most
importantly, the results can also be used as more realistic initial
abundances for normal dense core chemistry than the gaseous mainly
atomic abundances used in the pseudo-time-dependent treatments. It is
also possible to follow the dynamics and chemistry until cold dense
cores form at high extinction with a more detailed hydrodynamical model
(Aikawa et al. 2005).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.2cm,clip]{13896f1nH.eps}\par {\hspace*{2mm}\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{13896f1T.eps}\hspace*{2mm}}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/07/aa13896-09/Timg23.png)
|
Figure 1:
Hydrodynamic results for models 3 & 4 with dust
temperature calculations. Model 3 parameters are represented by solid
lines (density, dust temperature with
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
To include surface chemistry during the post-shock cooling, we
determined the evolution of the dust temperature by equating the rate
of heating by interstellar radiation,
![]() (Cuppen et al. 2006; Zucconi et al. 2001; Bohren & Huffman 1983; Draine & Bertoldi 1996; Whittet 2003), and by collisions with gas molecules,
(Cuppen et al. 2006; Zucconi et al. 2001; Bohren & Huffman 1983; Draine & Bertoldi 1996; Whittet 2003), and by collisions with gas molecules,
![]() ,
with the rate of cooling by thermal emission,
,
with the rate of cooling by thermal emission,
![]() (Draine & Lee 1984), and by evaporation
(Draine & Lee 1984), and by evaporation
![]() .
The computed dust temperature profiles, included in Fig. 1, begin with
.
The computed dust temperature profiles, included in Fig. 1, begin with
![]() K regardless of the properties of the gas, and are thus labeled as
K regardless of the properties of the gas, and are thus labeled as
![]() K throughout this paper. However, this temperature falls slightly below the range measured by COBE for the diffuse ISM (
K throughout this paper. However, this temperature falls slightly below the range measured by COBE for the diffuse ISM (
![]() K; Reach et al. 1995), so we also calculate an increased dust temperature profile with an increased radiation field, starting at
K; Reach et al. 1995), so we also calculate an increased dust temperature profile with an increased radiation field, starting at
![]() K. The dust temperature evolution is dominated by the radiative
processes within the density range of these simulations, and gradually
decreases from the initial
K. The dust temperature evolution is dominated by the radiative
processes within the density range of these simulations, and gradually
decreases from the initial
![]() value as
value as ![]() increases. For all the models considered here, the value of
increases. For all the models considered here, the value of ![]() consistently evolves from 15.5 K at the discontinuity to 11.0 K at
consistently evolves from 15.5 K at the discontinuity to 11.0 K at
![]() for the cooler profile and from 20.2 K to 14.4 K for the warmer profile.
for the cooler profile and from 20.2 K to 14.4 K for the warmer profile.
3 Chemical model and modifications
We have used the Ohio State (OSU) gas-grain reaction network (Garrod et al. 2006; Hasegawa et al. 1992; Garrod & Herbst 2006; Garrod et al. 2007).
This network includes 6323 reactions involving 655 species in an
expanded form including two new types of processes. We adopt a single
grain size of
![]() m and a Rice-Ramsperger-Kessel (RRK) parameter for reactive desorption of 0.01 (Garrod et al. 2006). As in B04, we use a slightly enhanced interstellar radiation field of G0 =1.7, in units of the Habing field (Draine 1978). The cosmic ray ionization rate
m and a Rice-Ramsperger-Kessel (RRK) parameter for reactive desorption of 0.01 (Garrod et al. 2006). As in B04, we use a slightly enhanced interstellar radiation field of G0 =1.7, in units of the Habing field (Draine 1978). The cosmic ray ionization rate
![]() is set at
is set at
![]() s-1. The elemental abundances used are high in metals; these consist of the
s-1. The elemental abundances used are high in metals; these consist of the ![]() Oph abundances used by B04 with the exception of Ne, Ar, Ca, and Ni,
which are not in our network. We have included the elements P, Na, and
Cl, which do appear in the OSU networks but not in B04, at their
so-called ``high-metal'' values (Garrod & Herbst 2006).
The term ``high'' is used to distinguish the initial estimate from
those used to estimate depletions in initially dense models (Garrod et al. 2007).
Oph abundances used by B04 with the exception of Ne, Ar, Ca, and Ni,
which are not in our network. We have included the elements P, Na, and
Cl, which do appear in the OSU networks but not in B04, at their
so-called ``high-metal'' values (Garrod & Herbst 2006).
The term ``high'' is used to distinguish the initial estimate from
those used to estimate depletions in initially dense models (Garrod et al. 2007).
The self-shielding of H2 is treated in the present models using the formalism of Lee et al. (1996) as in the previously mentioned networks. To treat the self shielding of CO(g) in our model at low ![]() more properly, we have adopted photodissociation rates based on the results of the Meudon PDR code (Le Petit et al. 2006). Specifically, we obtain individual photodissociation rates at representative conditions spanning the range of
more properly, we have adopted photodissociation rates based on the results of the Meudon PDR code (Le Petit et al. 2006). Specifically, we obtain individual photodissociation rates at representative conditions spanning the range of ![]() and
and ![]() variation for each of the four models, and determine a unique exponential fit to the form
variation for each of the four models, and determine a unique exponential fit to the form
![]() for each model from those results. Our shielding results are in reasonable agreement with those of B04, whose H2 shielding is based on Draine & Bertoldi (1996).
On the grain surfaces, photodesorption via external UV photons is an
important process to include. We have included photodesorption
processes for the four species studied in the laboratory by Öberg et al. (2009a,2007,2009b): CO(s), N2(s), H2O(s), and CO2(s), where (s) refers to the solid phase.
for each model from those results. Our shielding results are in reasonable agreement with those of B04, whose H2 shielding is based on Draine & Bertoldi (1996).
On the grain surfaces, photodesorption via external UV photons is an
important process to include. We have included photodesorption
processes for the four species studied in the laboratory by Öberg et al. (2009a,2007,2009b): CO(s), N2(s), H2O(s), and CO2(s), where (s) refers to the solid phase.
The surface reactions used in the gas-grain chemical network normally
involve the diffusion of one or more reaction partners across surface
sites via thermal hopping, a process known as the Langmuir-Hinshelwood
mechanism. At low temperatures, H atoms are a most important surface
reactant, and are responsible for the hydrogenation of heavy atoms
landing on grains into their saturated forms (e.g. O into H2O, C into CH4). Of the major ice species in our model (H2O, CO, CO2), CO2 has proven to be the most difficult to produce on surfaces via such processes (e.g. Ruffle & Herbst 2001). We have adopted an activation energy
![]() K, as measured by Roser et al. (2001), for the important CO2(s) formation reaction between CO(s) and O(s) (Nummelin et al. 2001). Following the approach of Ruffle & Herbst (2001), we also consider a decreased activation energy
K, as measured by Roser et al. (2001), for the important CO2(s) formation reaction between CO(s) and O(s) (Nummelin et al. 2001). Following the approach of Ruffle & Herbst (2001), we also consider a decreased activation energy ![]() of 130 K (see, for example, Fournier et al. 1979; Grim & D'Hendecourt 1986; Tielens & Hagen 1982).
of 130 K (see, for example, Fournier et al. 1979; Grim & D'Hendecourt 1986; Tielens & Hagen 1982).
Gas-phase species can also react directly with surface species via the Eley-Rideal mechanism (Ruffle & Herbst 2001).
To be efficient, such a mechanism requires a reactant with reasonably
high surface coverage, and CO(s) meets this criterion once CO(g) starts
to accrete. To possibly enhance the rate of CO2 formation, the Eley-Rideal reaction
![]() was added to the network, with a rate coefficient
was added to the network, with a rate coefficient
![]() given by
given by
where
To consider a reasonable portion of parameter space, we have run a
considerable number of models. The ones chosen for discussion comprise
all four shock models listed in Table 1, each with two different evolutions of granular temperature and two different barriers for the diffusive O + CO reaction.
Models that contain
![]() K and
K and ![]() = 290 K are labeled the A set, while models that contain
= 290 K are labeled the A set, while models that contain
![]() K and
K and ![]() = 130 K are labeled the B set. With the shock models 1-4, we label
the chemical models 1-A, 1-B, etc. Models with other sets of
varied parameters were also considered, but our choices for A and B
parameters span the range of variability of results.
= 130 K are labeled the B set. With the shock models 1-4, we label
the chemical models 1-A, 1-B, etc. Models with other sets of
varied parameters were also considered, but our choices for A and B
parameters span the range of variability of results.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=90,width=8.1cm,clip]{13896f2a.eps}\inc...
...96f2e.eps}\includegraphics[angle=90,width=8.1cm,clip]{13896f2f.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/07/aa13896-09/Timg47.png)
|
Figure 2: Column densities of
selected molecules vs. visual extinction, for shock models 1 (green), 2
(red), 3 (blue), and 4 (black). The solid lines represent models using
the (A) parameters of
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=90,width=8.1cm,clip]{13896f3a.eps}\inc...
...udegraphics[angle=90,width=8.1cm,clip]{13896f3d.eps}\vspace*{2.5mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/07/aa13896-09/Timg48.png)
|
Figure 3:
Column densities of CO(g) vs. H2(g) for shock models 1 (panel a), 2 (panel b), 3 (panel c), and 4 (panel d). The solid lines represent models using the (A) parameters of
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
4 Results
We report our principal results as column densities rather than
fractional abundances to facilitate comparison with the available
observations (see next section). The column densities are obtained from
the calculated fractional abundances at a given visual extinction by
using a relation between the visual extinction and the total column
density for hydrogen,
![]() cm-2 mag-1 (Whittet 2003), although there is some variation in the adopted value of this conversion factor in the literature.
cm-2 mag-1 (Whittet 2003), although there is some variation in the adopted value of this conversion factor in the literature.
As in B04, the gaseous species H2 and CO form after an enhanced density
![]() at low temperatures even though the extinction is very low. A variety
of other species start to form, both in the ice phase and in the gas.
After H2 and CO, the most abundant gas-phase species by
at low temperatures even though the extinction is very low. A variety
of other species start to form, both in the ice phase and in the gas.
After H2 and CO, the most abundant gas-phase species by
![]() include N2, CN, H2O, and CH4, although the last three possess columns of
include N2, CN, H2O, and CH4, although the last three possess columns of
![]() cm-2
or less, nearly three orders of magnitude smaller than the first three.
The high-metal elemental abundances maintain a high electron fractional
abundance exceeding 10-6, which diminishes the power of the
ion-molecule chemistry to produce larger molecules. There are no
molecular ions among the top 50 species of any model considered at this
time, nor does the largest abundance of a molecular ion come within six
orders of magnitude of the CO(g) abundance.
cm-2
or less, nearly three orders of magnitude smaller than the first three.
The high-metal elemental abundances maintain a high electron fractional
abundance exceeding 10-6, which diminishes the power of the
ion-molecule chemistry to produce larger molecules. There are no
molecular ions among the top 50 species of any model considered at this
time, nor does the largest abundance of a molecular ion come within six
orders of magnitude of the CO(g) abundance.
Our principal results are contained in two figures, in which we plot assorted column densities vs. ![]() and
and
![]() ,
respectively; the latter is more commonly used in studies of CO(g). The column densities of CO(g), N[CO(g)], and an assortment of ices are plotted against
,
respectively; the latter is more commonly used in studies of CO(g). The column densities of CO(g), N[CO(g)], and an assortment of ices are plotted against ![]() in Fig. 2 for the A and B parameter sets and all four shock models. The column densities are shown for visual extinction through
in Fig. 2 for the A and B parameter sets and all four shock models. The column densities are shown for visual extinction through
![]() ,
as further extensions of the evolution are definitely beyond the scope
of the shock hydrodynamics (see discussion in B04 regarding the
importance of gravity). The extinction used in Fig. 2
is considered to be ``edge-to-center'' for a line of sight into dense
or translucent material. Thus an observed extinction of 2 mag would
correspond to 1 mag in the edge-to-center model frame. The column
density for CO(g) is plotted against N[H2] in Fig. 3 along with column densities for the other major forms of carbon in the gas - C+ and C. In both figures, solid lines represent models with the A parameter set, while dashed lines represent the B set.
,
as further extensions of the evolution are definitely beyond the scope
of the shock hydrodynamics (see discussion in B04 regarding the
importance of gravity). The extinction used in Fig. 2
is considered to be ``edge-to-center'' for a line of sight into dense
or translucent material. Thus an observed extinction of 2 mag would
correspond to 1 mag in the edge-to-center model frame. The column
density for CO(g) is plotted against N[H2] in Fig. 3 along with column densities for the other major forms of carbon in the gas - C+ and C. In both figures, solid lines represent models with the A parameter set, while dashed lines represent the B set.
In each figure, it can be seen that the difference in N[CO(g)] between the A and B parameter sets decreases as the extinction or H2 column increases. At low H2 column, the amount of CO(g) produced in the B models apparently exceeds that in the A models by up to 2 orders of magnitude.
This effect occurs primarily because the warmer grains produce less H2(g) at a given ![]() with our simple ``smooth'' grain model; there is much less of a temperature dependence in the ``rough'' grain model of Chang et al. (2007), which utilizes a microscopic Monte Carlo approach. If the abscissa in Fig. 3 were the column of total hydrogen rather than of just H2, the B and A model results for CO(g) would appear to be more similar. Note also that the two plots with N[CO(g)] emphasize its growth with time in different ranges. In particular, the range of labeled
with our simple ``smooth'' grain model; there is much less of a temperature dependence in the ``rough'' grain model of Chang et al. (2007), which utilizes a microscopic Monte Carlo approach. If the abscissa in Fig. 3 were the column of total hydrogen rather than of just H2, the B and A model results for CO(g) would appear to be more similar. Note also that the two plots with N[CO(g)] emphasize its growth with time in different ranges. In particular, the range of labeled ![]() values in Fig. 2 of 0.5-3.0 corresponds to only a small portion of the H2 column density range in Fig. 3.
values in Fig. 2 of 0.5-3.0 corresponds to only a small portion of the H2 column density range in Fig. 3.
Despite these complications, a salient feature of both figures is that
CO(g) becomes the most abundant of the three major forms of carbon as
![]() cm-2 (corresponding to an edge-to-center
cm-2 (corresponding to an edge-to-center
![]() ). Thus, long before a cold core with
). Thus, long before a cold core with
![]() forms, the carbon inventory in the gas phase contains large amounts of
CO(g). Our results, obtained with a gas-grain model, are not identical
with those of B04. Nevertheless, they confirm how artificial the
initial carbon inventory is for pseudo-time-dependent models, in which
carbon is assumed to be totally in its atomic ionic form while the
density and visual extinction are already at their final values.
Moreover, at a visual extinction
of 2, the [C+ + C]/[CO] abundance ratio is the same as we obtain at
steady-state with a gas-phase model at roughly the same density. Thus, the
system has already evolved into a translucent cloud.
forms, the carbon inventory in the gas phase contains large amounts of
CO(g). Our results, obtained with a gas-grain model, are not identical
with those of B04. Nevertheless, they confirm how artificial the
initial carbon inventory is for pseudo-time-dependent models, in which
carbon is assumed to be totally in its atomic ionic form while the
density and visual extinction are already at their final values.
Moreover, at a visual extinction
of 2, the [C+ + C]/[CO] abundance ratio is the same as we obtain at
steady-state with a gas-phase model at roughly the same density. Thus, the
system has already evolved into a translucent cloud.
In addition to CO(g), calculated column densities for the major ice species H2O(s), CO(s), and CO2(s), along with the somewhat less abundant ices CH4(s) and CH3OH(s), are shown in Fig. 2. As illustrated in panel (b), the amount of H2O(s) grows relatively quickly to column densities in excess of 1016 cm-2 between
![]() and 2.1 for the various models. As with CO(g), the results illustrate
that this occurs most efficiently for shock models with greater total
density.
The evolution of CO(s), as shown in panel (c), tends to lag behind
CO(g), and the plot of its column vs.
and 2.1 for the various models. As with CO(g), the results illustrate
that this occurs most efficiently for shock models with greater total
density.
The evolution of CO(s), as shown in panel (c), tends to lag behind
CO(g), and the plot of its column vs. ![]() shows a sharp threshold at intermediate visual extinction, which is
correlated with a decrease in the rate of synthesis of methanol (see
below). The molecule forms more efficiently at lower extinction and
earlier times for models with greater density, similar to the trend
seen for H2O(s).
shows a sharp threshold at intermediate visual extinction, which is
correlated with a decrease in the rate of synthesis of methanol (see
below). The molecule forms more efficiently at lower extinction and
earlier times for models with greater density, similar to the trend
seen for H2O(s).
There is a large distinction between models with the A and B parameters at low and intermediate visual extinction. For some molecular ices, specifically CO(s) and H2O(s), as the visual extinction grows, the calculated column densities converge towards one another, while others show order of magnitude agreement (CH4, CH3OH). No convergence occurs for CO2(s), as shown in panel (d), which requires the adoption of the B parameter set to achieve a significant column density, mainly because the warmer grains allow faster diffusive reaction processes for heavy species. Although the effects of individually varying the CO2(s) formation barrier and turning off the Eley-Rideal mechanism on the abundance of CO2(s) were considered, the grain temperature is the most influential parameter for CO2(s) formation.
The formation of CO(g) and CO(s) also affects the evolution of methane ice (CH4(s)) and methanol ice (CH3OH(s)), shown in panels (e) and (f) of Fig. 2,
respectively. Methane on grain surfaces is formed via sequential
hydrogenation of C atoms, which accrete from the gas. The less carbon
and the more CO in the gas, the less efficient the surface formation of
methane and the more CO(s) accretes onto grains. Even at an extinction
of 3.0, the CH4(s) column densities for individual models
tend to lie below those of CO(s), especially for B parameter (warm
grain) models. As regards methanol, its only formation is via
sequential hydrogenation of CO(s) by reactions involving H atoms on
grain surfaces:
| (2) |
so that the abundances of CO(s) and CH3OH(s) should be intimately tied together. Nevertheless, the extinction dependence of the column densities of methane and methanol is far more complex than that of CO(s), especially with the B parameters, where extra peaks are seen. For both CH4(s) and CH3OH(s) formation, warmer temperatures lead to more desorption of H atoms from the grains and would appear to slow down the hydrogenation of C(s) and CO(s). This factor clearly affects the formation of methane at most times, but runs counter to the view that higher surface temperatures aid methanol formation and CO(s) depletion. Presumably this latter effect occurs because two of the reactions in the hydrogenation of methanol (H + CO and H + H2CO) require overcoming a chemical reaction barrier.
In addition to the results shown in Figs. 2 and 3, we report additional results for major species at ![]() = 3. Specifically, Table 2
contains the fractional abundances of the major gaseous and solid
species for the A and B variants of models 3 and 4. These
models span the range of physical conditions considered, and the table
illustrates the differences in composition that arise as a result. This
table provides a range of input abundances for subsequent dense core
models.
= 3. Specifically, Table 2
contains the fractional abundances of the major gaseous and solid
species for the A and B variants of models 3 and 4. These
models span the range of physical conditions considered, and the table
illustrates the differences in composition that arise as a result. This
table provides a range of input abundances for subsequent dense core
models.
Table 2:
Fractional abundances of major species at
![]() .
.
Our results are obtained with a model that ignores grain growth. But,
as grains accumulate icy mantles, the cross sections grow likewise,
potentially by substantial factors. This effect is often omitted from
gas-grain chemistry models. In the single grain-size model considered
in this paper, the cross section gradually doubles following
![]() .
In some preliminary simulations with mantle growth, we found that the onset of CO(s) and CO2(s) growth occurs at slightly lower
.
In some preliminary simulations with mantle growth, we found that the onset of CO(s) and CO2(s) growth occurs at slightly lower ![]() ,
and that these ices reach abundances slightly different from those of Fig. 2,
while CO(g) and water ice decrease. Our overall results and conclusions
are not changed significantly by consideration of this effect. The
inclusion of mantle growth in a chemical model with a distribution of
grain sizes is currently being undertaken by Acharyya and Herbst. In
addition to mantle growth, the effect of grain-grain collisions can
lead to size distributions with considerably larger grains at time
scales such as those considered here, according to detailed
calculations by Ormel et al. (2009, see, in particular, their Table 3). Inclusion of this effect is beyond the scope of this paper.
,
and that these ices reach abundances slightly different from those of Fig. 2,
while CO(g) and water ice decrease. Our overall results and conclusions
are not changed significantly by consideration of this effect. The
inclusion of mantle growth in a chemical model with a distribution of
grain sizes is currently being undertaken by Acharyya and Herbst. In
addition to mantle growth, the effect of grain-grain collisions can
lead to size distributions with considerably larger grains at time
scales such as those considered here, according to detailed
calculations by Ormel et al. (2009, see, in particular, their Table 3). Inclusion of this effect is beyond the scope of this paper.
5 Comparison with observations
Although the density of the post-shock models can be as high as
![]() cm-3,
these do not simulate fully-formed dense cores given their low
extinction, but rather the cloud material such as that from which dense
cores form. Can relevant comparison be made with existing observational
data, or are our results best used as initial conditions for models of
normal dense cold cores? The dark cloud in Taurus is perhaps the best
region to explore this question for measurements of ices, while a large
sample of CO(g) observations exists for diffuse and translucent clouds,
as well as some lines of sight in Taurus. One must also remember that
our results represent cold material in the act of forming larger
structures via a specific post-shock process, whereas there is no
guarantee that the observed sources are transitional in this sense.
Indeed, at low visual extinction and/or H2 column densities, our objects tend to be denser, smaller, and colder than well-studied diffuse clouds.
cm-3,
these do not simulate fully-formed dense cores given their low
extinction, but rather the cloud material such as that from which dense
cores form. Can relevant comparison be made with existing observational
data, or are our results best used as initial conditions for models of
normal dense cold cores? The dark cloud in Taurus is perhaps the best
region to explore this question for measurements of ices, while a large
sample of CO(g) observations exists for diffuse and translucent clouds,
as well as some lines of sight in Taurus. One must also remember that
our results represent cold material in the act of forming larger
structures via a specific post-shock process, whereas there is no
guarantee that the observed sources are transitional in this sense.
Indeed, at low visual extinction and/or H2 column densities, our objects tend to be denser, smaller, and colder than well-studied diffuse clouds.
5.1 CO(g) observations
Estimates of N[CO(g)] along darker lines of sight in the Taurus dark cloud were presented by Whittet et al. (1989) based on observations of Frerking et al. (1982) and Crutcher (1985). Observations of N[CO(g)] in more translucent and diffuse clouds have been reported by Sonnentrucker et al. (2007); Liszt (2008); Sheffer et al. (2007); Gredel et al. (1994); Burgh et al. (2007), and references therein. The value of ![]() was reported for some of these sources by Rachford et al. (2009), while for the majority only N[H2(g)] was reported.
was reported for some of these sources by Rachford et al. (2009), while for the majority only N[H2(g)] was reported.
The
![]() vs.
vs. ![]() data appear in Fig. 2a
as circles for the darker lines of sight, seen in the Taurus cloud, and
asterisks for the translucent lines of sight except for one upper
limit, shown as an inverted triangle. It is apparent from this figure
that many of the data points fall within the model curves in the lower
data appear in Fig. 2a
as circles for the darker lines of sight, seen in the Taurus cloud, and
asterisks for the translucent lines of sight except for one upper
limit, shown as an inverted triangle. It is apparent from this figure
that many of the data points fall within the model curves in the lower ![]() range, and that all four shock models with A and B parameter sets fit
three of the darker line of sight observations to within a factor of 3
or better.
range, and that all four shock models with A and B parameter sets fit
three of the darker line of sight observations to within a factor of 3
or better.
The N[CO(g)] vs. N[H2(g)] data appear in Fig. 3 as either circles or inverted triangles for upper limits. The data, which are more numerous than those plotted against ![]() and
tend to contain lower CO(g) columns from diffuse and translucent cloud
data, are fit best by model 2-A. The B-models tend to be somewhat worse
than the A-models. Although the density, gas temperature, and size of
the post-shock objects for the lower H2
columns may not correspond with these parameters for actual observed
clouds, the CO(g) columns we calculate are dependent mainly on the
visual extinction, so observation and theory are in reasonable
agreement anyway. In addition, the calculated CO(g) columns agree well
with steady-state values for gas-phase models, if not quite as well as
in Fig. 2.
and
tend to contain lower CO(g) columns from diffuse and translucent cloud
data, are fit best by model 2-A. The B-models tend to be somewhat worse
than the A-models. Although the density, gas temperature, and size of
the post-shock objects for the lower H2
columns may not correspond with these parameters for actual observed
clouds, the CO(g) columns we calculate are dependent mainly on the
visual extinction, so observation and theory are in reasonable
agreement anyway. In addition, the calculated CO(g) columns agree well
with steady-state values for gas-phase models, if not quite as well as
in Fig. 2.
5.2 Ice observations
Our predicted column densities for ices as functions of edge-to-center
visual extinction can be compared with at least some infrared
observational data along quiescent lines of sight in Taurus in our low
visual extinction regime. Shown in Fig. 2, the limited data available in the extinction range up to 3.3 come from Murakawa et al. (2000); Teixeira & Emerson (1999); Whittet et al. (2007), and references therein. Some of these data are merely upper limits, while for CH4(s) and CH3OH(s),
there are to the best of our knowledge not even upper limits in this
range. The question arises as to whether observations at our relatively
low extinction range belong to small cores or whether the material
being sampled is simply the diffuse background. That at least some of
the Taurus observations at low extinction pertain to small cores has
been shown by Whittet et al. (2004,2001), who concluded that the lines of sight to HD 29647 and HD 283809 sample dense gas with extinctions of
![]() and 2.85 (see their Fig. 1 in the 2004 paper). If representative
of expanding objects as treated by our shock model, the size of the
object with lower extinction, in the absence of self-gravity, would be
in the range 0.05 pc (model 4) to 0.5 pc (model 3) (see
Table 1).
and 2.85 (see their Fig. 1 in the 2004 paper). If representative
of expanding objects as treated by our shock model, the size of the
object with lower extinction, in the absence of self-gravity, would be
in the range 0.05 pc (model 4) to 0.5 pc (model 3) (see
Table 1).
The vertical line or lines in panels (b), (d) are empirically determined threshold extinctions,
![]() ,
and their uncertainty ranges for the Taurus dark cloud (the panel for
CO(s) only shows the lower limit of this range). The center lines
represent the lowest
,
and their uncertainty ranges for the Taurus dark cloud (the panel for
CO(s) only shows the lower limit of this range). The center lines
represent the lowest ![]() values above which the specific ices are detectable in a cloud and are
obtained by empirical fits to column density vs. visual extinction for
a wide range of dark quiescent lines of sight in Taurus towards
background stars at larger visual extinction (Whittet et al. 2007).
The specific edge-to-center thresholds for Taurus are
values above which the specific ices are detectable in a cloud and are
obtained by empirical fits to column density vs. visual extinction for
a wide range of dark quiescent lines of sight in Taurus towards
background stars at larger visual extinction (Whittet et al. 2007).
The specific edge-to-center thresholds for Taurus are
![]() for H2O(s),
for H2O(s),
![]() for CO(s), and
for CO(s), and
![]() mag for CO2(s).
These threshold values can be regarded as conservative compared with
some of the equivocal data at lower extinction from other groups (Murakawa et al. 2000; Teixeira & Emerson 1999),
which might represent the diffuse background. The thresholds are
thought to roughly correspond with the accumulation of the equivalent
of a few monolayers of a surface species, in a sudden onset above the
threshold extinction. To help interpret these thresholds, we have also
plotted minimum detectable columns for the major ices, which are shown
as horizontal lines. The estimates are made by substituting a minimal
discernible optical depth of
mag for CO2(s).
These threshold values can be regarded as conservative compared with
some of the equivocal data at lower extinction from other groups (Murakawa et al. 2000; Teixeira & Emerson 1999),
which might represent the diffuse background. The thresholds are
thought to roughly correspond with the accumulation of the equivalent
of a few monolayers of a surface species, in a sudden onset above the
threshold extinction. To help interpret these thresholds, we have also
plotted minimum detectable columns for the major ices, which are shown
as horizontal lines. The estimates are made by substituting a minimal
discernible optical depth of ![]() (Whittet, private communication) into equation (5.5) of Whittet (2003).
At the time when
(Whittet, private communication) into equation (5.5) of Whittet (2003).
At the time when
![]() ,
the horizontal lines in panels (b) and (d) represent the equivalent column density of about one or two monolayers of H2O(s) and CO2(s), while the line in panel (c) is closer to five layers of CO(s).
,
the horizontal lines in panels (b) and (d) represent the equivalent column density of about one or two monolayers of H2O(s) and CO2(s), while the line in panel (c) is closer to five layers of CO(s).
The observations of N[H2O(s)] appear in Fig. 2b. The Murakawa et al. detections were reported as optical depths, ![]() ,
and we note that several of these values are less than the observational uncertainty of
,
and we note that several of these values are less than the observational uncertainty of
![]() reported. If we instead count these points as upper limits, as shown in
the plot, the data below Whittet's threshold range are only limits,
while firm detections appear at greater
reported. If we instead count these points as upper limits, as shown in
the plot, the data below Whittet's threshold range are only limits,
while firm detections appear at greater ![]() than the threshold. Below the threshold, the models results lie below
these ``limits''. Above the threshold, the spread of data points and
upper limits falls within the range of our model results, although it
is difficult to determine which models are best. Regarding the
threshold itself, our calculated columns do not show a real threshold,
but rise gradually and reach the empirical threshold around the minimum
detectable column (the horizontal line). A proper interpretation may be
that there is not really a threshold, so much as a drop below
detectability masquerading as one.
Towards the highest extinction plotted, the assorted model results tend
to converge to a narrow range of values 3-10
than the threshold. Below the threshold, the models results lie below
these ``limits''. Above the threshold, the spread of data points and
upper limits falls within the range of our model results, although it
is difficult to determine which models are best. Regarding the
threshold itself, our calculated columns do not show a real threshold,
but rise gradually and reach the empirical threshold around the minimum
detectable column (the horizontal line). A proper interpretation may be
that there is not really a threshold, so much as a drop below
detectability masquerading as one.
Towards the highest extinction plotted, the assorted model results tend
to converge to a narrow range of values 3-10 ![]() larger than the observed columns. In some sense this is due to the
chemistry readily hydrogenating oxygen atoms on grain surfaces. At cold
temperatures it is difficult to stop this process. The difference
between model and observations could be related to our assumed oxygen
atom abundance being too high, perhaps through the presence of another
reservoir of oxygen (see, e.g. Whittet et al. 2007).
larger than the observed columns. In some sense this is due to the
chemistry readily hydrogenating oxygen atoms on grain surfaces. At cold
temperatures it is difficult to stop this process. The difference
between model and observations could be related to our assumed oxygen
atom abundance being too high, perhaps through the presence of another
reservoir of oxygen (see, e.g. Whittet et al. 2007).
For the other major ices, CO(s) and CO2(s), there are only upper limits in the extinction range ![]() through
through ![]() 3, except for one detection of CO2(s) toward Tamura 2 (Whittet et al. 1989,2007). The observational N[CO(s)]
upper limits are not very constraining except perhaps at the highest
visual extinction plotted where two upper limits are in better
agreement with shock models 1 and 3. For the case of CO2(s),
the B parameter models are required to bring the column density to
near-detectable abundances. The one firmly detected observational data
point is fit best by models 4-B and 2-B.
3, except for one detection of CO2(s) toward Tamura 2 (Whittet et al. 1989,2007). The observational N[CO(s)]
upper limits are not very constraining except perhaps at the highest
visual extinction plotted where two upper limits are in better
agreement with shock models 1 and 3. For the case of CO2(s),
the B parameter models are required to bring the column density to
near-detectable abundances. The one firmly detected observational data
point is fit best by models 4-B and 2-B.
Figure 2 shows very sharp thresholds for the onset of column densities of CO(s) and CO2(s), but only for the latter are the calculated thresholds even in rough agreement with the empirical range of Whittet et al. (2007).
For CO(s), we reach the minimum detectable column at visual extinction
much smaller than the empirical threshold, which needs to be checked by
data at lower extinction, where there are currently only high upper
limits to the CO(s) column. It should be noted that, in the absence of
photodesorption, minimum detectable columns for H2O(s) and CO(s) are reached at lower visual extinction (
![]() ), worsening the agreement with the threshold observations.
), worsening the agreement with the threshold observations.
6 Discussion
The chemistry of cold dense cores has typically been treated by pseudo-time-dependent methods, in which physical conditions are homogeneous and time-independent. Also, the initial chemical abundances are artificially assumed to take the form of atoms except for molecular hydrogen. Although such gas-phase and gas-grain models of the chemistry are often in reasonable agreement with observations and even predictive in nature for the gas-phase species, the assumption of time-independent physical conditions ignores the formation of the core, a process that cannot be totally distinct from the chemistry that occurs. For these reasons, we have started a program to determine how the chemistry is altered by consideration of the physical evolution of dense cores.
In this paper, we have reported our study of the chemistry that
occurs during shock-induced formation of dark cloud material from the
more diffuse background, with an emphasis on the composition of icy
grain mantles and gaseous CO. In this picture, gas-phase and
grain-mantle molecular species form after the post-shock material cools
and becomes dense, and as the visual extinction increases, in contrast
with the assumption of constant physical conditions. This stage can be
considered as preliminary to the stage in which cold pre-stellar cores
form. Since our approach does not extend to the phase in which the
self-gravity governs the evolution of these cooled objects, we cannot
continue to increase their size and visual extinction beyond an
extinction of ![]() 2-3.
Although our calculated column densities cannot then be compared with
those of ordinary cold dense, or prestellar, cores, we have compared
them with the observed abundances of diverse low-
2-3.
Although our calculated column densities cannot then be compared with
those of ordinary cold dense, or prestellar, cores, we have compared
them with the observed abundances of diverse low-![]() sources within the Taurus dark cloud, and a variety of other diffuse-to-translucent sources.
sources within the Taurus dark cloud, and a variety of other diffuse-to-translucent sources.
There are several key results of our calculations:
- 1.
- Despite some divergence at lower extinction, all model results
for CO(g) tend to converge as the edge-to-center extinction reaches
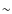 2.0 (an H2 column of
2.0 (an H2 column of
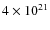 cm-2)
where CO(g) becomes the dominant form of gaseous carbon. We conclude
that homogeneous gas-grain dense core models should not use atomic
carbon as an initial abundance, but would be more realistic with
initial abundances from the low-extinction results reported here. In
particular, the calculated CO(g) columns and [C+ + C]/CO
ratios for the different models are not drastically different from the
values obtained from gas-phase models at steady-state as a function of
visual extinction or molecular hydrogen column density.
Our suggestion concerning the proper initial abundances to use has also
appeared in a recent paper by Liszt (2009),
who advocated that ``mechanisms for the chemical evolution from diffuse
to dark gas should be included in model calculations'', a view that is
the basis for our paper.
cm-2)
where CO(g) becomes the dominant form of gaseous carbon. We conclude
that homogeneous gas-grain dense core models should not use atomic
carbon as an initial abundance, but would be more realistic with
initial abundances from the low-extinction results reported here. In
particular, the calculated CO(g) columns and [C+ + C]/CO
ratios for the different models are not drastically different from the
values obtained from gas-phase models at steady-state as a function of
visual extinction or molecular hydrogen column density.
Our suggestion concerning the proper initial abundances to use has also
appeared in a recent paper by Liszt (2009),
who advocated that ``mechanisms for the chemical evolution from diffuse
to dark gas should be included in model calculations'', a view that is
the basis for our paper. - 2.
- By
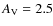 ,
all models show that H2O(s) and CO(s) have grown above their minimum observable abundances. Models that form denser gas grow these ices at lower
,
all models show that H2O(s) and CO(s) have grown above their minimum observable abundances. Models that form denser gas grow these ices at lower 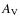 .
These ices thus become abundant before a full-fledged dense core can be produced.
.
These ices thus become abundant before a full-fledged dense core can be produced.
- 3.
- The growth of CO(s) slows down the rate of synthesis of CH4(s) because there is less of its precursor, neutral C, available. By an extinction of 3.0, the methane column densities for individual models tend to lie below those of CO(s), especially for the B parameter set, in which the dust temperature is higher.
- 4.
- The formation of CO2(s) occurs efficiently only with the B parameter models, especially with the higher density models, 2-B and 4-B. The grain temperature is the most critical parameter for efficient CO2(s) formation, with or without the Eley-Rideal mechanism.
- 5.
- Models excluding photodesorption rates would form multiple layers of H2O(s) and CO(s) at lower
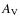 than either thresholds or the lowest reported firm detections (Whittet et al. 2007). This result indicates that the inclusion of measured photodesorption rates is critical for realistic models.
than either thresholds or the lowest reported firm detections (Whittet et al. 2007). This result indicates that the inclusion of measured photodesorption rates is critical for realistic models.
We thank the referee for some interesting points. We are very thankful for helpful discussions with K. I. Öberg and H. M. Cuppen regarding photodesorption experiments and D. C. B. Whittet and S. S. Shenoy regarding observational data. We wish to thank P. Rimmer for assistance with the use of the Meudon PDR code. We gratefully acknowledge the support of NASA through Spitzer data analysis contract 30331. E.H. would like to thank the National Science Foundation for support of his research program in astrochemistry via grant AST-0702876 and through the NSF Center for the Chemistry of the Universe (GA10750-131847).
References
- Aikawa, Y., Herbst, E., Roberts, H., & Caselli, P. 2005, ApJ, 620, 330 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- André, P., Basu, S., & Inutsuka, S. I. 2008, in Structure Formation in Astrophysics, ed. G. Chabrier (Cambridge University Press) [arXiv:0801.4210] [Google Scholar]
- Bergin, E. A., & Tafalla, M. 2007, ARA&A, 45, 339 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bergin, E. A., Hartmann, L. W., Raymond, J. C., & Ballesteros-Paredes, J. 2004, ApJ, 612, 921 (B04) [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bohren, C. F., & Huffman, D. R. 1983, Absorption and scattering of light by small particles (New York: Wiley) [Google Scholar]
- Burgh, E. B., France, K., & McCandliss, S. R. 2007, ApJ, 658, 446 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Q., Cuppen, H. M., & Herbst, E. 2007, A&A, 469, 973 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Crutcher, R. M. 1985, ApJ, 288, 604 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Cuppen, H. M., Morata, O., & Herbst, E. 2006, MNRAS, 367, 1757 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Draine, B. T. 1978, ApJS, 36, 595 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Draine, B. T., & Bertoldi, F. 1996, ApJ, 468, 269 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Draine, B. T., & Lee, H. M. 1984, ApJ, 285, 89 [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, J., Deson, J., Vermeil, C., & Pimentel, G. C. 1979, J. Chem. Phys., 70, 5726 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Frerking, M. A., Langer, W. D., & Wilson, R. W. 1982, ApJ, 262, 590 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod, R. T., & Herbst, E. 2006, A&A, 457, 927 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod, R. T., Park, I. H., Caselli, P., & Herbst, E. 2006, Faraday Discuss., 133, 51 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod, R. T., Wakelam, V., & Herbst, E. 2007, A&A, 467, 1103 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Gredel, R., van Dishoeck, E. F., & Black, J. H. 1994, A&A, 285, 300 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Grim, R. J. A., & D'Hendecourt, L. B. 1986, A&A, 167, 161 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, L., Ballesteros-Paredes, J., & Bergin, E. A. 2001, ApJ, 562, 852 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, T. I., Herbst, E., & Leung, C. M. 1992, ApJS, 82, 167 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Le Petit, F., Nehmé, C., Le Bourlot, J., & Roueff, E. 2006, ApJS, 164, 506 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H., Herbst, E., Pineau des Forets, G., Roueff, E., & Le Bourlot, J. 1996, A&A, 311, 690 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Liszt, H. S. 2008, A&A, 492, 743 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Liszt, H. S. 2009, A&A, 508, 783 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- McKee, C. F., & Ostriker, E. C. 2007, ARA&A, 45, 565 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, G. F., & Watt, G. D. 1985, A&A, 151, 121 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Murakawa, K., Tamura, M., & Nagata, T. 2000, ApJS, 128, 603 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Nejad, L. A. M., & Williams, D. A. 1992, MNRAS, 255, 441 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T. K., Ruffle, D. P., Herbst, E., & Williams, D. A. 2002, MNRAS, 329, 301 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Nummelin, A., Whittet, D. C. B., Gibb, E. L., Gerakines, P. A., & Chiar, J. E. 2001, ApJ, 558, 185 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Öberg, K. I., Fuchs, G. W., Awad, Z., et al. 2007, ApJ, 662, L23 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Öberg, K. I., Linnartz, H., Visser, R., & van Dishoeck, E. F. 2009a, ApJ, 693, 1209 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Öberg, K. I., van Dishoeck, E. F., & Linnartz, H. 2009b, A&A, 496, 281 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Ormel, C. W., Paszun, D., Dominik, C., & Tielens, A. G. G. M. 2009, A&A, 502, 845 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Pineau des Forêts, G., Flower, D. R., & Herbst, E. 1991, MNRAS, 253, 359 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Rachford, B. L., Snow, T. P., Destree, J. D., et al. 2009, ApJS, 180, 125 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Reach, W. T., Dwek, E., Fixsen, D. J., et al. 1995, ApJ, 451, 188 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Roser, J. E., Vidali, G., Manicò, G., & Pirronello, V. 2001, ApJ, 555, L61 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffle, D. P., & Herbst, E. 2001, MNRAS, 324, 1054 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffer, Y., Rogers, M., Federman, S. R., Lambert, D. L., & Gredel, R. 2007, ApJ, 667, 1002 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnentrucker, P., Welty, D. E., Thorburn, J. A., & York, D. G. 2007, ApJS, 168, 58 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, T. C., & Emerson, J. P. 1999, A&A, 351, 292 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Tielens, A. G. G. M., & Hagen, W. 1982, A&A, 114, 245 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Whittet, D. C. B. 2003, Dust in the galactic environment (Bristol: Institute of Physics Publishing) [Google Scholar]
- Whittet, D. C. B., Adamson, A. J., Duley, W. W., Geballe, T. R., & McFadzean, A. D. 1989, MNRAS, 241, 707 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Whittet, D. C. B., Gerakines, P. A., Hough, J. H., & Shenoy, S. S. 2001, ApJ, 547, 872 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Whittet, D. C. B., Shenoy, S. S., Clayton, G. C., & Gordon, K. D. 2004, ApJ, 602, 291 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Whittet, D. C. B., Shenoy, S. S., Bergin, E. A., et al. 2007, ApJ, 655, 332 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D. A. 1988, in Rate Coefficients in Astrochemistry, ed. T. J. Millar, & D. A. Williams (Dordrecht: Kluwer), 281 [Google Scholar]
- Zucconi, A., Walmsley, C. M., & Galli, D. 2001, A&A, 376, 650 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
All Tables
Table 1: Shock models.
Table 2:
Fractional abundances of major species at
![]() .
.
All Figures
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.2cm,clip]{13896f1nH.eps}\par {\hspace*{2mm}\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{13896f1T.eps}\hspace*{2mm}}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/07/aa13896-09/Timg23.png)
|
Figure 1:
Hydrodynamic results for models 3 & 4 with dust
temperature calculations. Model 3 parameters are represented by solid
lines (density, dust temperature with
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=90,width=8.1cm,clip]{13896f2a.eps}\inc...
...96f2e.eps}\includegraphics[angle=90,width=8.1cm,clip]{13896f2f.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/07/aa13896-09/Timg47.png)
|
Figure 2: Column densities of
selected molecules vs. visual extinction, for shock models 1 (green), 2
(red), 3 (blue), and 4 (black). The solid lines represent models using
the (A) parameters of
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=90,width=8.1cm,clip]{13896f3a.eps}\inc...
...udegraphics[angle=90,width=8.1cm,clip]{13896f3d.eps}\vspace*{2.5mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/07/aa13896-09/Timg48.png)
|
Figure 3:
Column densities of CO(g) vs. H2(g) for shock models 1 (panel a), 2 (panel b), 3 (panel c), and 4 (panel d). The solid lines represent models using the (A) parameters of
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
Copyright ESO 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.