| Issue |
A&A
Volume 578, June 2015
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A125 | |
| Number of page(s) | 26 | |
| Section | Stellar atmospheres | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201526229 | |
| Published online | 16 June 2015 | |
Search with UVES and X-Shooter for signatures of the low-mass secondary in the post common-envelope binary AA Doradus⋆,⋆⋆,⋆⋆⋆
1 Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Kepler Center for Astro and Particle Physics, Eberhard Karls University, Sand 1, 72076 Tübingen, Germany
e-mail: rauch@astro.uni-tuebingen.de
2 Hamburger Sternwarte, Gojenbergsweg 112, 21029 Hamburg, Germany
3 NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA
Received: 31 March 2015
Accepted: 25 April 2015
Context. AA Dor is a close, totally eclipsing, post common-envelope binary with an sdOB-type primary star and an extremely low-mass secondary star, located close to the mass limit of stable central hydrogen burning. Within error limits, it may either be a brown dwarf or a late M-type dwarf.
Aims. We aim to extract the secondary’s contribution to the phase-dependent composite spectra. The spectrum and identified lines of the secondary decide on its nature.
Methods. In January 2014, we measured the phase-dependent spectrum of AA Dor with X-Shooter over one complete orbital period. Since the secondary’s rotation is presumable synchronized with the orbital period, its surface strictly divides into a day and night side. Therefore, we may obtain the spectrum of its cool side during its transit and of its hot, irradiated side close to its occultation. We developed the Virtual Observatory (VO) tool TLISA to search for weak lines of a faint companion in a binary system. We successfully applied it to the observations of AA Dor.
Results. We identified 53 spectral lines of the secondary in the ultraviolet-blue, visual, and near-infrared X-Shooter spectra that are strongest close to its occultation. We identified 57 (20 additional) lines in available Ultraviolet and Visual Echelle Spectrograph (UVES) spectra from 2001. The lines are mostly from C ii-iii and O ii, typical for a low-mass star that is irradiated and heated by the primary. We verified the orbital period of P = 22 597.033201 ± 0.00007 s and determined the orbital velocity 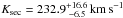 of the secondary. The mass of the secondary is
of the secondary. The mass of the secondary is 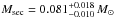 and, hence, it is not possible to reliably determine a brown dwarf or an M-type dwarf nature.
and, hence, it is not possible to reliably determine a brown dwarf or an M-type dwarf nature.
Conclusions. Although we identified many emission lines of the secondary’s irradiated surface, the resolution and signal-to-noise ratio of our UVES and X-Shooter spectra are not good enough to extract a good spectrum of the secondary’s nonirradiated hemisphere.
Key words: stars: abundances / binaries: eclipsing / stars: low-mass / stars: individual: AA Dor / virtual observatory tools
Based on observations collected at the European Southern Observatory, Chile, programs 066.D-1800 and 092.C-0692.
Figures 2–5, 9, and Appendices are available in electronic form at http://www.aanda.org
© ESO, 2015
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


