| Issue |
A&A
Volume 514, May 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A64 | |
| Number of page(s) | 12 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200913425 | |
| Published online | 20 May 2010 | |
Physical and morphological properties of z ~ 3 Lyman break galaxies: dependence on Lyα line emission
1
INAF – Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, via Frascati 33, 00040 Monte Porzio Catone, Italy
e-mail: penteric@oa-roma.inaf.it
2
Spitzer Science Center, Pasadena, CA, USA
3
INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste, via G. B. Tiepolo 11, 40131 Trieste, Italy
Received:
8
October
2009
Accepted:
10
February
2010
Aims. We investigate the physical and morphological properties of Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) at redshift ~2.5 to ~3.5, to determine if and how they depend on the nature and strength of the Lyα emission.
Methods. We selected U-dropout galaxies from the z-detected GOODS-MUSIC catalog by adapting the classical Lyman break criteria on the GOODS filter set. We kept only those galaxies with spectroscopic confirmation, mainly from VIMOS and FORS public observations. Using the full multi-wavelength 14-bands information (U to IRAC), we determined the physical properties of the galaxies through a standard spectral energy distribution fitting procedure with the updated Charlot & Bruzual (2009) templates. We also added other relevant observations of the GOODS field, i.e. the 24 μm observations from Spitzer/MIPS and the 2 MSec Chandra X-ray observations. Finally, using non parametric diagnostics (Gini, Concentration, Asymmetry, M20 and ellipticity), we characterized the rest-frame UV morphologies of the galaxies. We then analyzed how these physical and morphological properties correlate with the presence of the Lyα emission line in the optical spectra.
Results. We find that unlike at higher redshift, the dependence of physical
properties on the Lyα line is milder: galaxies without Lyα in emission tend to be more massive and dustier than the
rest of the sample, but all other parameters, ages, star formation rates (SFR), X-ray emission and UV morphology do not depend strongly
on the presence of the Lyα emission. A simple scenario where all LBGs have intrinsically high Lyα emission, but where the dust
and neutral hydrogen content (which shapes the final appearance of the Lyα) depend on the mass of the galaxies, is able to
reproduce the majority of the observed properties at 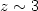 . Some modification might be needed to account for the observed evolution
of these properties with cosmic epoch, which is also discussed.
. Some modification might be needed to account for the observed evolution
of these properties with cosmic epoch, which is also discussed.
Key words: galaxies: starburst / galaxies: evolution / galaxies: high-redshift / galaxies: fundamental parameters
© ESO, 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


