| Issue |
A&A
Volume 511, February 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A37 | |
| Number of page(s) | 14 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200913376 | |
| Published online | 04 March 2010 | |
The detached dust and gas shells around the carbon star U Antliae
1
Department of Astronomy, Stockholm University, AlbaNova University Center, 106 91 Stockholm, Sweden e-mail: maercker@astro.su.se
2
Onsala Space Observatory, 439 92 Onsala, Sweden
3
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Uppsala University, 75120 Uppsala, Sweden
Received:
30
September
2009
Accepted:
10
December
2009
Context. Geometrically thin, detached shells of gas have been found around a handful of carbon stars. The current knowledge on these shells is mostly based on CO radio line data. However, imaging in scattered stellar light adds important new information as well as allows studies of the dust shells.
Aims. Previous observations of scattered stellar light in the circumstellar medium around the carbon star U Ant were taken through filters centred on the resonance lines of K and Na. These observations could not separate the scattering by dust and atoms. The aim of this paper is to remedy this situation.
Methods. We have obtained polarization data on stellar light scattered in the circumstellar medium around U Ant through filters which contain no strong lines, making it possible to differentiate between the two scattering agents. Kinematic, as well as spatial, information on the gas shells were obtained through high-resolution echelle spectrograph observations of the KI and NaD lines.
Results. We confirm the existence of two detached shells around U Ant. The inner shell (at a radius of ≈43´´ and a width of ≈2´´) consists mainly of gas, while the outer shell (at a radius of ≈50´´ and a width of ≈7´´) appears to consist exclusively of dust. Both shells appear to have an over-all spherical geometry. The gas shell mass is estimated to be 2 
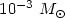 , while the mass of the dust shell is estimated to be 5
, while the mass of the dust shell is estimated to be 5 
 . The derived expansion velocity, from the KI and NaD lines, of the gas shell, 19.5
. The derived expansion velocity, from the KI and NaD lines, of the gas shell, 19.5 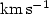 , agrees with that obtained from CO radio line data. The inferred shell age is 2700 years. There is structure, e.g. in the form of arcs, inside the gas shell, but it is not clear whether these are due to additional shells.
, agrees with that obtained from CO radio line data. The inferred shell age is 2700 years. There is structure, e.g. in the form of arcs, inside the gas shell, but it is not clear whether these are due to additional shells.
Conclusions. Our results support the hypothesis that the observed geometrically thin, detached shells around carbon stars are the results of brief periods of intense mass loss, probably associated with thermal pulses, and subsequent wind-wind interactions. The separation into a gas and a dust shell, with different widths, is most likely the effect of different dynamical evolutions of the two media after their ejection.
Key words: stars: abundances / stars: AGB and post-AGB / stars: evolution / stars: mass-loss
© ESO, 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


