| Issue |
A&A
Volume 503, Number 2, August IV 2009
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 357 - 371 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200911788 | |
| Published online | 22 June 2009 | |
Internal dynamics of Abell 1240: a galaxy cluster with symmetric double radio relics
1
Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, C/Vía Láctea s/n, 38205 La Laguna (Tenerife), Canary Islands, Spain e-mail: rbarrena@iac.es
2
Dipartimento di Astronomia of the Università degli Studi di Trieste, via Tiepolo 11, 34143 Trieste, Italy
3
INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste, via Tiepolo 11, 34143 Trieste, Italy
4
Fundación Galileo Galilei - INAF, Rambla José Ana Fernández Perez 7, 38712 Breña Baja (La Palma), Canary Islands, Spain
5
Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung, Max-Planck-Str. 2, 37191 Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany
Received:
4
February
2009
Accepted:
12
May
2009
Context. The mechanisms giving rise to diffuse radio emission in galaxy clusters, and in particular their connection with cluster mergers, are still debated.
Aims. We aim to obtain new insights into the
internal dynamics of the cluster Abell 1240, which appears to contain
two roughly symmetric radio relics, separated by ~2 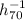 Mpc.
Mpc.
Methods. Our analysis is based mainly on redshift data for 145 galaxies mostly acquired at the Telescopio Nazionale Galileo and on new photometric data acquired at the Isaac Newton Telescope. We also use X-ray data from the Chandra archive and photometric data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (Data Release 7). We combine galaxy velocities and positions to select 89 cluster galaxies and analyze the internal dynamics of the Abell 1237 + Abell 1240 cluster complex, Abell 1237 being a close companion of Abell 1240 in its southern direction.
Results. We estimate similar redshifts for Abell
1237 and Abell 1240,  = 0.1935 and
= 0.1935 and
 = 0.1948, respectively. For Abell 1237, we estimate a
line-of-sight (LOS) velocity dispersion of
= 0.1948, respectively. For Abell 1237, we estimate a
line-of-sight (LOS) velocity dispersion of  ~ 740 km s-1and a mass of M ~ 6
~ 740 km s-1and a mass of M ~ 6  1014
1014 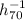
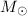 . For Abell 1240, we estimate a LOS
. For Abell 1240, we estimate a LOS  ~ 870 km s-1and a mass in the range M ~ 0.9-1.9
~ 870 km s-1and a mass in the range M ~ 0.9-1.9  1015
1015 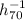
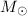 , which takes account of its complex dynamics. Abell 1240 is
shown to have a bimodal structure with two galaxy clumps roughly
aligned along its N–S direction, the same as defined by the elongation
of its X-ray surface brightness and the axis of symmetry of the
relics. The two brightest galaxies of Abell 1240, associated with the
northern and southern clumps, are separated by a LOS rest-frame
velocity difference
, which takes account of its complex dynamics. Abell 1240 is
shown to have a bimodal structure with two galaxy clumps roughly
aligned along its N–S direction, the same as defined by the elongation
of its X-ray surface brightness and the axis of symmetry of the
relics. The two brightest galaxies of Abell 1240, associated with the
northern and southern clumps, are separated by a LOS rest-frame
velocity difference 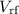 ~ 400 km s-1and a projected
distance D ~ 1.2
~ 400 km s-1and a projected
distance D ~ 1.2 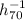 Mpc. The two-body model agrees with the
hypothesis that we are looking at a cluster merger that occurred largely
in the plane of the sky, the two galaxy clumps being separated by a
rest-frame velocity difference
Mpc. The two-body model agrees with the
hypothesis that we are looking at a cluster merger that occurred largely
in the plane of the sky, the two galaxy clumps being separated by a
rest-frame velocity difference 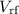 ~ 2000 km s-1at a time
of 0.3 Gyr after the crossing core, while Abell 1237 is still
infalling onto Abell 1240. Chandra archive data confirm the complex
structure of Abell 1240 and allow us to estimate a global X-ray
temperature of
~ 2000 km s-1at a time
of 0.3 Gyr after the crossing core, while Abell 1237 is still
infalling onto Abell 1240. Chandra archive data confirm the complex
structure of Abell 1240 and allow us to estimate a global X-ray
temperature of 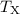 = 6.0±0.5 keV.
= 6.0±0.5 keV.
Conclusions. In agreement with the findings from radio data, our results for Abell 1240 strongly support the “outgoing merger shocks” model to explain the presence of the relics.
Key words: galaxies: clusters: individual: Abell 1240 / galaxies: clusters: individual: Abell 1237 / galaxies: clusters: general / galaxies: distances and redshifts
© ESO, 2009
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


