| Issue |
A&A
Volume 479, Number 3, March I 2008
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 735 - 740 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20077791 | |
| Published online | 09 January 2008 | |
Can photo-ionisation explain the decreasing fraction of X-ray obscured AGN with luminosity?
Institute of Astronomy & Astrophysics, National Observatory of Athens, I.Metaxa & B. Pavlou, Penteli, 15236 Athens, Greece e-mail: aakylas@astro.noa.gr
Received:
4
May
2007
Accepted:
21
December
2007
Chandra and XMM-Newton surveys show that the fraction of obscured
AGN decreases rapidly with increasing luminosity. Although this
is usually explained by assuming that the covering factor of
the central engine is much smaller at luminous QSOs, the exact
origin of this effect remains unknown. We perform toy
simulations to test whether photo-ionisation of the obscuring screen
in the presence of a strong radiation field can reproduce this effect.
In particular, we create X-ray spectral simulations using a warm
absorber model assuming a range of input column densities and
ionisation parameters. We fit instead the simulated spectra with a
simple cold
absorption power-law model that is the standard practice in X-ray surveys.
We find that the fraction of absorbed AGN should fall with luminosity as
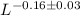 in rough agreement with the observations.
Furthermore, this apparent decrease in the obscuring material is
consistent with the dependence of the FeKα narrow-line equivalent
width on luminosity, i.e. the X-ray Baldwin effect.
in rough agreement with the observations.
Furthermore, this apparent decrease in the obscuring material is
consistent with the dependence of the FeKα narrow-line equivalent
width on luminosity, i.e. the X-ray Baldwin effect.
Key words: surveys / X-rays: galaxies / X-rays: general
© ESO, 2008
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


