| Issue |
A&A
Volume 475, Number 2, November IV 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | L15 - L18 | |
| Section | Letters | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20078693 | |
| Published online | 02 October 2007 | |
Letter to the Editor
Low energy H+CO scattering revisited
CO rotational excitation with new potential surfaces
1
Department of Chemistry and Cherry L. Emerson Center for Scientific Computation, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30322, USA e-mail: [bcshepl;jmbowman]@emory.edu
2
Department of Physics and Astronomy and the Center for Simulational Physics, The University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602-2451, USA e-mail: [yang;stancil]@physast.uga.edu
3
Department of Chemistry, University of Nevada Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV 89154, USA e-mail: dhilip.thogluva@unlv.edu; naduvala@unlv.nevada.edu
4
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St., Cambridge, MA 02138, USA e-mail: [pezhang;adalgarno]@cfa.harvard.edu
5
Department of Chemistry and CNISM, University of Rome “Sapienza”, Piazzale, A. Moro, 00185 Rome, Italy e-mail: e.bodo@caspur.it
Received:
17
September
2007
Accepted:
25
September
2007
Context.A recent modeling study of brightness ratios for CO rotational transitions in
gas typical of the diffuse ISM by Liszt found the role of H collisions to
be more important than previously assumed. This conclusion
was based on recent quantum scattering calculations using the so-called WKS
potential energy surface (PES) which reported a large cross section for
the important 0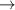 1 rotational transition. This result is in contradiction to
one obtained using the earlier BBH PES for which the cross section is quite
small and which is consistent with an expected homonuclear-like
propensity for even
1 rotational transition. This result is in contradiction to
one obtained using the earlier BBH PES for which the cross section is quite
small and which is consistent with an expected homonuclear-like
propensity for even 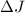 transitions.
transitions.
Aims.We revisit this contradiction with new scattering
calculations using two new ab initio PESs
that focus on the important long-range behavior and explore the
validity of the apparent departure from the expected
even 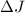 propensity
in H-CO rotational excitation obtained with the WKS PES.
propensity
in H-CO rotational excitation obtained with the WKS PES.
Methods.Close-coupling (CC) rigid-rotor calculations for CO(v = 0, J = 0) excitation by H are performed on four different PESs. Two of the PESs are obtained in this work using state-of-the-art quantum chemistry techniques at the CCSD(T) and MRCI levels of theory.
Results.Cross sections for the J = 0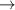 1, as well as other odd
1, as well as other odd 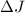 ,
transitions are significantly suppressed compared to even
,
transitions are significantly suppressed compared to even 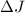 transitions in thermal energy CC calculations using the CCSD(T) and MRCI
surfaces. This is consistent with the expected even
transitions in thermal energy CC calculations using the CCSD(T) and MRCI
surfaces. This is consistent with the expected even 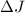 propensity
and in contrast to CC calculations using the WKS PES which predict a
dominating 0
propensity
and in contrast to CC calculations using the WKS PES which predict a
dominating 0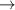 1 transition.
1 transition.
Conclusions.Inelastic collision cross section calculations are sensitive to fine details in the anisotropic components of the PES and its long-range behavior. The current results obtained with new surfaces for H-CO scattering suggest that the original astrophysical assumption that excitation of CO by H2 dominates the kinetics of CO in diffuse ISM gas is likely to remain valid.
Key words: molecular processes / ISM: molecules
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


