| Issue |
A&A
Volume 475, Number 2, November IV 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 401 - 407 | |
| Section | Astrophysical processes | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20066808 | |
| Published online | 17 September 2007 | |
Generation of potential/surface density pairs in flat disks
Power law distributions
1
Université Bordeaux 1/CNRS/OASU/UMR 5804/LAB, 2 rue de l'Observatoire, BP 89, 33270 Floirac, France e-mail: jean-marc.hure@obs.u-bordeaux1.fr
2
LUTh/Observatoire de Paris-Meudon-Nancay, Place Jules Janssen, 92195 Meudon Cedex, France e-mail: didier.pelat@obspm.fr
3
Astronomy Unit, Queen Mary, University of London, Mile end Road, London E1 4NS, UK e-mail: a.pierens@qmul.ac.uk
Received:
24
November
2006
Accepted:
5
June
2007
Aims.We report a simple method to generate potential/surface density pairs in flat axially symmetric finite size disks.
Methods.Potential/surface density pairs consist of a “homogeneous” pair (a closed form expression) corresponding to a uniform disk, and a “residual” pair. This residual component is converted into an infinite series of integrals over the radial extent of the disk. For a certain class of surface density distributions (like power laws of the radius), this series is fully analytical.
Results.The extraction of the homogeneous pair is equivalent to a convergence acceleration technique, in a matematical sense. In the case of power law distributions (i.e. surface densities of the form 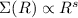 ), the convergence rate of the residual series is shown to be cubic inside the source. As a consequence, very accurate potential values are obtained by low order truncation of the series. At zero order, relative errors on potential values do not exceed a few percent typically, and scale with the order N of truncation as
), the convergence rate of the residual series is shown to be cubic inside the source. As a consequence, very accurate potential values are obtained by low order truncation of the series. At zero order, relative errors on potential values do not exceed a few percent typically, and scale with the order N of truncation as  . This method is superior to the classical multipole expansion whose very slow convergence is often critical for most practical applications.
. This method is superior to the classical multipole expansion whose very slow convergence is often critical for most practical applications.
Key words: gravitation / methods: analytical / accretion, accretion disks / methods: numerical
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


