| Issue |
A&A
Volume 471, Number 2, August IV 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 467 - 474 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20065908 | |
| Published online | 25 May 2007 | |
Keck spectroscopy and Spitzer space telescope analysis of the outer disk of the Triangulum spiral galaxy M 33
1
School of Computational and Applied Mathematics, University of Witwatersrand, Private Bag 3, WITS 2050, South Africa e-mail: block@cam.wits.ac.za
2
Mount Stromlo and Siding Spring Observatories, Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Australian National University, Australia
3
Observatoire de Paris, LERMA, 61 Av. de l'Observatoire, 75014 Paris, France
4
Instituto Nacional de Astrofísica, Optica y Electrónica, Calle Luis Enrique Erro 1, 72840 Tonantzintla, Puebla, México
5
Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii, 2680 Woodlawn Drive, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA
6
Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics and Department of Physics, University of California, Riverside, CA 92521, USA
7
Infrared Processing and Analysis Center, 100-22, CALTECH, 770 South Wilson Ave, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA
8
Washington State University, 1245 Webster Hall, Pullman, WA 99163-2814, USA
9
Department of Astronomy, University of Minnesota, 116 Church St. SE, Minneapolis MN 55455, USA
10
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St., Cambridge, MA 02138, USA
Received:
26
June
2006
Accepted:
15
May
2007
In an earlier study of the spiral galaxy M 33, we photometrically
identified arcs or outer spiral arms of intermediate
age (0.6-2 Gyr) carbon stars precisely at the commencement of the
HI-warp. Stars in the arcs were unresolved,
but were likely thermally-pulsing asymptotic giant branch carbon stars.
Here we present Keck I spectroscopy of seven intrinsically bright and red
target stars in the outer, northern arc in M 33. The target stars
have estimated visual magnitudes as faint as 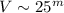 .
Absorption bands of CN are seen in all seven spectra
reported here, confirming their carbon star status. In addition, we
present Keck II spectra of a small area 0.5 degree away from the centre of
M 33; the target stars there are also identified as carbon
stars. We also study the non-stellar PAH dust morphology of M 33
secured using IRAC on board the Spitzer Space Telescope.
The Spitzer 8 μm image attests to a change of spiral phase at the start of
the HI warp. The Keck spectra confirm that carbon stars may safely be
identified on the basis of their red
.
Absorption bands of CN are seen in all seven spectra
reported here, confirming their carbon star status. In addition, we
present Keck II spectra of a small area 0.5 degree away from the centre of
M 33; the target stars there are also identified as carbon
stars. We also study the non-stellar PAH dust morphology of M 33
secured using IRAC on board the Spitzer Space Telescope.
The Spitzer 8 μm image attests to a change of spiral phase at the start of
the HI warp. The Keck spectra confirm that carbon stars may safely be
identified on the basis of their red 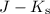 colours in the outer, low
metallicity disk of M 33. We propose that
the enhanced number of carbon stars in the outer arms are an indicator
of recent star formation, fueled by gas accretion from the HI-warp
reservoir.
colours in the outer, low
metallicity disk of M 33. We propose that
the enhanced number of carbon stars in the outer arms are an indicator
of recent star formation, fueled by gas accretion from the HI-warp
reservoir.
Key words: galaxies: evolution / galaxies: spiral / galaxies: individual: M 33 (NGC598) / galaxies: Local Group / galaxies: formation / galaxies: stellar content
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


