| Issue |
A&A
Volume 458, Number 2, November I 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 507 - 511 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20065802 | |
| Published online | 12 September 2006 | |
Rotational excitation of CO in a cool, mixed atomic and molecular hydrogen gas
National Radio Astronomy Observatory, 520 Edgemont Road, Charlottesville, VA 22903-2475, USA e-mail: hliszt@nrao.edu
Received:
11
June
2006
Accepted:
4
August
2006
Context.Rate constants for rotational excitation of CO by atomic hydrogen have recently been recalculated and found to be much larger than was previously believed, larger even than for excitation by H2.
Aims.To clarify the effect upon CO rotational excitation of an admixture of atomic hydrogen in diffuse molecule-bearing gas.
Methods.The equations of statistical equilibrium in the CO rotation ladder are solved under a variety of conditions typical of CO-bearing gas in the diffuse ISM.
Results. Atomic hydrogen, if present, substantiantially increases the brightness and
excitation temperatures of the CO rotational transitions, and
increases the 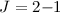 /
/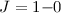 ,
, 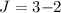 /
/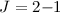 , etc. line brightness ratios.
A modest admixture of atomic hydrogen mimics a pure H2-gas of substantially
higher ambient thermal pressure.
, etc. line brightness ratios.
A modest admixture of atomic hydrogen mimics a pure H2-gas of substantially
higher ambient thermal pressure.
Conclusions.Rotational excitation of CO by atomic hydrogen is important if even a few percent of the hydrogen is in atomic form.
Key words: molecular processes / radio lines: ISM / ISM: atoms / ISM: molecules / ISM: clouds
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


