| Issue |
A&A
Volume 454, Number 2, August I 2006
APEX Special Booklet
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 473 - 480 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20054776 | |
| Published online | 11 July 2006 | |
Multifractality in a ring of star formation: the case of Arp 220
Suffolk University Madrid Campus, C/ Viña 3, 28003 Madrid, Spain e-mail: raul@galaxy.suffolk.es
Received:
26
December
2005
Accepted:
21
March
2006
Context.Formation of super star-clusters can be triggered during the final stages of galaxy mergers or galactic interactions, when significant numbers of massive stars are formed out of large gas-cloud systems. Giant cloud complexes show a fractal structure due to turbulence and/or self-gravitation; therefore, super clusters formed out of these complexes are expected to show a multifractal spectrum.
Aims.Here we investigate the projected spatial distribution of young massive clusters in the ultraluminous infrared galaxy Arp 220 and its underlying fractal geometry.
Methods.The projected radial distribution of super clusters is dominated by a prominent ring of star formation. Taking the presence of this annulus into account, the fractal spectrum is determined by using the Minkowski-sausage method to compute the Minkowski-Bouligand dimension as a function of the parameter q.
Results.The ring appears to extend from a radial distance of 2.0 to
4.5 kpc. The Arp 220 annulus of star formation could be an
outer ring associated with the outer Lindblad resonance/radius
of corotation. The average projected fractal dimension in the
ring of star formation is found to be 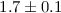 , which is
consistent with values found for non-starburst, star-forming
regions in spiral galaxies. However, the fractal dimension
appears to be lower in the outer regions of the ring and, for
Arp 220, this implies an actual decrease in the fractal
dimension over time probably induced by star cluster
destruction. This trend is not observed under quiescent star
formation.
, which is
consistent with values found for non-starburst, star-forming
regions in spiral galaxies. However, the fractal dimension
appears to be lower in the outer regions of the ring and, for
Arp 220, this implies an actual decrease in the fractal
dimension over time probably induced by star cluster
destruction. This trend is not observed under quiescent star
formation.
Conclusions.The projected distribution of super clusters in Arp 220 can be described using an annular model, and it exhibits multifractal behaviour. The properties of its fractal geometry are similar to those found in quiescent star-forming regions in disk galaxies although the average fractal dimension evolves differently over time, decreasing instead of increasing. This result implies that, for the short-term evolution of super cluster populations, destruction may be far more important than diffusion-like processes.
Key words: galaxies: starburst / galaxies: star clusters / galaxies: individual Arp 220 / stars: formation / galaxies: interactions / galaxies: peculiar
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


