| Issue |
A&A
Volume 450, Number 1, April IV 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | L5 - L8 | |
| Section | Letters | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:200600020 | |
| Published online | 03 April 2006 | |
Letter to the Editor
Chemical self-enrichment of HII regions by the Wolf-Rayet phase of an 85 M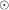 star
star
1
Institut für Theoretische Physik und Astrophysik der Universität Kiel, 24098 Kiel, Germany e-mail: danica@astrophysik.uni-kiel.de
2
Institute of Astronomy, University of Vienna, Türkenschanzstr. 17, 1180 Vienna, Austria e-mail: hensler@astro.univie.ac.at
Received:
12
December
2005
Accepted:
24
February
2006
It is clear from stellar evolution and from observations of
WR stars that massive stars are releasing metal-enriched gas through
their stellar winds in the Wolf-Rayet phase. Although Hii
region spectra serve as diagnostics to determine the present-day
chemical composition of the interstellar medium, it is far from
being understood to what extent the Hii gas is already
contaminated by chemically processed stellar wind. Therefore, we
analyzed our models of radiative and wind bubbles of an isolated
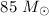 star with solar metallicity (Kröger et al. 2006, A&A, in preparation) with
respect to the chemical enrichment of the circumstellar Hii
region. Plausibly, the hot stellar wind bubble (SWB) is enriched
with
star with solar metallicity (Kröger et al. 2006, A&A, in preparation) with
respect to the chemical enrichment of the circumstellar Hii
region. Plausibly, the hot stellar wind bubble (SWB) is enriched
with  during the WN phase and even much higher with
during the WN phase and even much higher with
 and
and  during the WC phase of the star.
During the short period that the
during the WC phase of the star.
During the short period that the 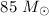 star spends in
the WC stage enriched SWB material mixes with warm Hii gas of
solar abundances and thus enhances the metallicity in the Hii
region. However, at the end of the stellar lifetime the mass ratios
of the traced elements N and O in the warm ionized gas are
insignificantly higher than solar, whereas an enrichment of
star spends in
the WC stage enriched SWB material mixes with warm Hii gas of
solar abundances and thus enhances the metallicity in the Hii
region. However, at the end of the stellar lifetime the mass ratios
of the traced elements N and O in the warm ionized gas are
insignificantly higher than solar, whereas an enrichment of 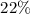 above solar is found for C. Important issues from the presented
study comprise a steeper radial gradient of C than O and a
decreasing effect of self-enrichment for metal-poor galaxies.
above solar is found for C. Important issues from the presented
study comprise a steeper radial gradient of C than O and a
decreasing effect of self-enrichment for metal-poor galaxies.
Key words: galaxies: evolution / Hii regions / hydrodynamics / instabilities / ISM: bubbles / ISM: structure
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


