| Issue |
A&A
Volume 432, Number 1, March II 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 69 - 81 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20041468 | |
| Published online | 22 February 2005 | |
XMM-Newton observations of Extremely Red Objects and the link with luminous, X-ray obscured quasars*
1
Dipartimento di Astronomia Universita' di Bologna, via Ranzani 1, 40127 Bologna, Italy e-mail: marcella@mpe.mpg.de
2
INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, via Ranzani 1, 40127 Bologna, Italy
3
European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Strasse 2, 85748 Garching bei Muenchen, Germany
4
INAF - Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Largo E. Fermi 5, 50125 Firenze, Italy
5
INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, via Frascati 33, 00040 Monteporzio, Italy
6
Sterrewacht Leiden, PO Box 9513, 2300 RA, Leiden, The Netherlands
Received:
14
June
2004
Accepted:
28
October
2004
We present the results of a deep (about 80 ks) XMM-Newton
survey of the largest sample of near-infrared selected Extremely Red
Objects (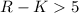 ) available to date to
) available to date to 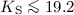 .
At the relatively bright X-ray fluxes (
.
At the relatively bright X-ray fluxes (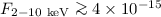 erg cm-2 s-1) and near-infrared magnitude probed by the
present observations, the fraction of AGN (i.e. X-ray detected)
among the ERO population is small (~3.5%);
conversely, the fraction of EROs among
hard X-ray selected sources is much higher (~20%).
The X-ray properties of EROs detected in our XMM-Newton observation indicate absorption in excess of 1022 cm-2
in a large fraction of them.
We have also
considered additional samples of X-ray detected EROs available in the
literature.
X-ray spectral analysis of the highest S/N sources unambiguously indicates
that large columns of cold gas (even >1023 cm-2) are the
rule rather than the exception.
The X-ray, optical and near-infrared properties of those X-ray
selected EROs with a spectroscopic or photometric redshift
nicely match those expected for type 2 quasars, the
high-luminosity, high-redshift obscured AGNs predicted in baseline
XRB synthesis models.
A close correlation is detected between X- and K-band fluxes. For the
AGN EROs this is consistent, under reasonable assumptions, with the
relation established locally between the host galaxies and their central
black holes. This suggests that
the majority of EROs are powered by massive black holes accreting, on average,
at about 0.03-0.1 of the Eddington limit.
erg cm-2 s-1) and near-infrared magnitude probed by the
present observations, the fraction of AGN (i.e. X-ray detected)
among the ERO population is small (~3.5%);
conversely, the fraction of EROs among
hard X-ray selected sources is much higher (~20%).
The X-ray properties of EROs detected in our XMM-Newton observation indicate absorption in excess of 1022 cm-2
in a large fraction of them.
We have also
considered additional samples of X-ray detected EROs available in the
literature.
X-ray spectral analysis of the highest S/N sources unambiguously indicates
that large columns of cold gas (even >1023 cm-2) are the
rule rather than the exception.
The X-ray, optical and near-infrared properties of those X-ray
selected EROs with a spectroscopic or photometric redshift
nicely match those expected for type 2 quasars, the
high-luminosity, high-redshift obscured AGNs predicted in baseline
XRB synthesis models.
A close correlation is detected between X- and K-band fluxes. For the
AGN EROs this is consistent, under reasonable assumptions, with the
relation established locally between the host galaxies and their central
black holes. This suggests that
the majority of EROs are powered by massive black holes accreting, on average,
at about 0.03-0.1 of the Eddington limit.
Key words: X-rays: general / galaxies: active / galaxies: high-redshift / cosmology: observations / X-rays: galaxies
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


