| Issue |
A&A
Volume 451, Number 3, June I 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 859 - 864 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20053980 | |
| Published online | 04 May 2006 | |
An X-ray bright ERO hosting a type 2 QSO
1
INAF – Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera (OAB), via Brera 28, 20121 Milano, Italy e-mail: [paola;caccia;braito;rdc;tommaso;saracco]@brera.mi.astro.it
2
Exploration of the Universe Division, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt Road, Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA e-mail: vale@milkyway.gsfc.nasa.gov
3
Subaru Telescope, National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, 650 North A'ohoku Place, Hilo, HI 96720, USA e-mail: akiyama@subaru.naoj.org
4
Instituto de Fisica de Cantabria (CSIC-UC), Avenida de los Castros, 39005 Santander, Spain e-mail: [carreraf;ceballos]@ifca.unican.es
5
Mullard Space Science Laboratory, University College London, Holmbury St. Mary, Dorking, Surrey RH5 6NT, UK e-mail: mjp@mssl.ucl.ac.uk
6
X-ray Astronomy Group, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Leicester University, Leicester LE1 7RH, UK e-mail: mgw@star.le.ac.uk
Received:
29
July
2005
Accepted:
4
February
2006
We present the XMM-Newton and the optical-VLT spectra along with
the optical and the near-infrared photometric data of one of the brightest
X-ray (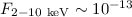 erg s-1 cm-2) extremely red
objects (
erg s-1 cm-2) extremely red
objects (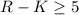 ) discovered so far. The source, XBS J0216-0435, belongs to
the XMM-Newton Bright Serendipitous Survey and it has extreme
X-ray-to-optical (~220) and X-ray-to-near-infrared (~60) flux
ratios. Thanks to its brightness, the X-ray statistics are good enough for an
accurate spectral analysis by which the presence of an X-ray obscured
(
) discovered so far. The source, XBS J0216-0435, belongs to
the XMM-Newton Bright Serendipitous Survey and it has extreme
X-ray-to-optical (~220) and X-ray-to-near-infrared (~60) flux
ratios. Thanks to its brightness, the X-ray statistics are good enough for an
accurate spectral analysis by which the presence of an X-ray obscured
(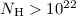 cm-2) QSO (
cm-2) QSO (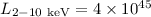 erg s-1) is determined. A statistically significant (~99%) excess
around 2 keV in the observed-frame suggests the presence of an emission line.
By assuming that this feature corresponds to the iron Kα line at 6.4 keV, a first estimate of the redshift of the source is
derived (
erg s-1) is determined. A statistically significant (~99%) excess
around 2 keV in the observed-frame suggests the presence of an emission line.
By assuming that this feature corresponds to the iron Kα line at 6.4 keV, a first estimate of the redshift of the source is
derived ( ). The presence of a high redshift QSO2 has been finally confirmed
through dedicated VLT optical spectroscopic observations
(
). The presence of a high redshift QSO2 has been finally confirmed
through dedicated VLT optical spectroscopic observations
(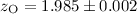 ). This result yields to an optical validation of a new
X-ray Line Emitting Object (XLEO) for which the redshift has
been firstly derived from the X-ray data. XBS J0216-0435 can be
considered one of the few examples of X-ray obscured QSO2 at high redshift
for which a detailed X-ray and optical spectral analysis has been possible.
The spectral energy distribution from radio to X-rays is also presented.
Finally from the near-infrared data the luminosity and the stellar mass of the
host galaxy has been estimated finding a new example of the coexistence at
high-z between massive galaxies and powerful QSOs.
). This result yields to an optical validation of a new
X-ray Line Emitting Object (XLEO) for which the redshift has
been firstly derived from the X-ray data. XBS J0216-0435 can be
considered one of the few examples of X-ray obscured QSO2 at high redshift
for which a detailed X-ray and optical spectral analysis has been possible.
The spectral energy distribution from radio to X-rays is also presented.
Finally from the near-infrared data the luminosity and the stellar mass of the
host galaxy has been estimated finding a new example of the coexistence at
high-z between massive galaxies and powerful QSOs.
Key words: galaxies: active / X-rays: galaxies / galaxies: individual: XBS J0216-0435
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


