| Issue |
A&A
Volume 431, Number 2, February IV 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 423 - 431 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20041630 | |
| Published online | 04 February 2005 | |
Lower limits on the Hubble constant from models of type Ia supernovae
1
Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 1, 85741 Garching bei München, Germany e-mail: stritzin@mpa-garching.mpg.de
2
European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, 85748 Garching bei München, Germany e-mail: bleibundgut@eso.org
Received:
9
July
2004
Accepted:
23
October
2004
By coupling observations of type Ia supernovae with results
obtained from the best available numerical models we constrain the Hubble
constant, independently of any external calibrators. We find an absolute
lower limit of H0 > 50 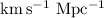 . In addition, we construct a Hubble
diagram with UVOIR light curves of 12 type Ia supernovae located in the
Hubble flow, and when adopting the most likely values (obtained from 1-D
and 3-D deflagration simulations) of the amount of
. In addition, we construct a Hubble
diagram with UVOIR light curves of 12 type Ia supernovae located in the
Hubble flow, and when adopting the most likely values (obtained from 1-D
and 3-D deflagration simulations) of the amount of 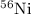 produced
in a typical event, we find values of H0 ≥ 66 ± 8
and ≥78 ± 9
produced
in a typical event, we find values of H0 ≥ 66 ± 8
and ≥78 ± 9 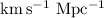 , respectively.
Our result may be difficult to reconcile with recent discussions in
the literature as it seems that an Einstein-de Sitter universe
requires H0
, respectively.
Our result may be difficult to reconcile with recent discussions in
the literature as it seems that an Einstein-de Sitter universe
requires H0  46
46 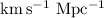 in order to fit the
temperature power spectrum of the cosmic microwave background
and maintain the age constraints of the oldest stars.
in order to fit the
temperature power spectrum of the cosmic microwave background
and maintain the age constraints of the oldest stars.
Key words: cosmology: cosmological parameters / stars: supernovae: general
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


