| Issue |
A&A
Volume 428, Number 2, December III 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 545 - 554 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20040325 | |
| Published online | 26 November 2004 | |
The influence of rotation in radiation driven winds from hot stars
II. CAK topological analysis
1
Departamento de Física y Meteorología, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Valparaíso, Valparaíso, Chile e-mail: michel.cure@uv.cl
2
Departamento de Matemáticas, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Argentina e-mail: drial@dm.uba.ar
Received:
24
February
2004
Accepted:
26
August
2004
The topological analysis from Bjorkman ([CITE]) for the standard model that describes the winds from hot stars by Castor et al. ([CITE]) has been extended to include the effect of stellar rotation and changes in the ionization of the wind.
The differential equation for the momentum of the wind is non-linear and transcendental for the velocity gradient. Due to this non-linearity the number of solutions that this equation possess is not known. After a change of variables and the introduction of a new physically meaningless independent variable, we manage to replace the non-linear momentum differential equation by a system of differential equations where all the derivatives are explicitely given. We then use this system of equations to study the topology of the rotating-CAK model. For the particular case when the wind is frozen in ionization (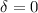 ) only one physical solution is found, the standard CAK solution, with a X-type singular point. For the more general case (
) only one physical solution is found, the standard CAK solution, with a X-type singular point. For the more general case (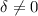 ), besides the standard CAK singular point, we find a second singular point which is focal-type (or attractor). We find also, that the wind does not adopt the maximal mass-loss rate but almost the minimal.
), besides the standard CAK singular point, we find a second singular point which is focal-type (or attractor). We find also, that the wind does not adopt the maximal mass-loss rate but almost the minimal.
Key words: hydrodynamics / methods: analytical / stars: early-type / stars: mass-loss / stars: rotation / stars: winds, outflows
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


