| Issue |
A&A
Volume 424, Number 1, September II 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 13 - 22 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20035744 | |
| Published online | 17 August 2004 | |
Mass-sheet degeneracy: Fundamental limit on the cluster mass reconstruction from statistical (weak) lensing
1
Institut für Astrophysik und Extraterrestrische Forschung, Auf dem Hügel 71, 53121 Bonn, Germany e-mail: marusa@astro.uni-bonn.de
2
Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 53121 Bonn, Germany
3
European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, 85748 Garching bei München, Germany
Received:
25
November
2003
Accepted:
11
May
2004
Weak gravitational lensing is considered to be one of the
most powerful tools to study the mass and the mass distribution of
galaxy clusters. However, weak lensing mass reconstructions are
plagued by the so-called mass-sheet degeneracy – the surface mass
density κ of the cluster can be determined only up to a degeneracy
transformation 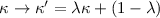 , where λ is an arbitrary
constant. This transformation fundamentally limits the accuracy of
cluster mass determinations if no further assumptions are made. We
describe here a method to break the mass-sheet degeneracy in weak
lensing mass maps using the distortion and redshift information of
background galaxies and illustrate this by two simple toy models.
Compared to other techniques proposed in the
past, it does not rely on any assumptions on cluster potential;
it can be easily applied to non-parametric mass-reconstructions and
no assumptions on boundary conditions have to be made. In addition it
does not make use of weakly constrained information (such as the
source number counts, used in the magnification effect).
Our simulations show that we are effectively able to break the
mass-sheet degeneracy for supercritical lenses, but
that for undercritical lenses the mass-sheet degeneracy is very
difficult to break, even under idealised conditions.
, where λ is an arbitrary
constant. This transformation fundamentally limits the accuracy of
cluster mass determinations if no further assumptions are made. We
describe here a method to break the mass-sheet degeneracy in weak
lensing mass maps using the distortion and redshift information of
background galaxies and illustrate this by two simple toy models.
Compared to other techniques proposed in the
past, it does not rely on any assumptions on cluster potential;
it can be easily applied to non-parametric mass-reconstructions and
no assumptions on boundary conditions have to be made. In addition it
does not make use of weakly constrained information (such as the
source number counts, used in the magnification effect).
Our simulations show that we are effectively able to break the
mass-sheet degeneracy for supercritical lenses, but
that for undercritical lenses the mass-sheet degeneracy is very
difficult to break, even under idealised conditions.
Key words: dark matter / galaxies: clusters: general / gravitational lensing
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


