| Issue |
A&A
Volume 411, Number 1, November III 2003
Special letters issue on: first science with integral
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | L331 - L342 | |
| Section | Letters | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20031440 | |
| Published online | 17 November 2003 | |
Letter to the Editor
Gamma-ray bursts observed by the INTEGRAL-SPI anticoincidence shield: A study of individual pulses and temporal variability*
1
Stockholm Observatory, AlbaNova University Center, 106 91 Stockholm, Sweden
2
Danish Space Research Institute, Juliane Maries vej 30, 2100 Copenhagen O, Denmark
3
Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, 85741 Garching bei München, Germany
Corresponding author: F. Ryde, felix@astro.su.se
Received:
16
July
2003
Accepted:
16
September
2003
We study a set of 28 GRB light-curves detected between 15 December
2002 and 9 June 2003 by the anti-coincidence shield of the
spectrometer (SPI) of INTEGRAL. During this period it has detected
50 bursts, that have been confirmed by other instruments, with a
time resolution of 50 ms. First, we derive the basic
characteristics of the bursts: various duration measures, the
count peak flux and the count fluence. Second, a sub-sample of 11 bursts with 12 individual, well-separated pulses is studied. We
fit the pulse shape with a model by Kocevski et al. (2003)
and find that the pulses are quite self-similar in shape. There is
also a weak tendency for the pulses with steep power-law decays to
be more asymmetric. Third, the variability of the complex
light-curves is studied by analyzing their power-density-spectra
(PDS) and their RMS variability.
The averaged PDS, of the whole sample, is a power-law with index
of 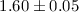 and a break between 1–2 Hz. Fourth, we also
discuss the background and noise levels. We found that the
background noise has a Gaussian distribution and its power is
independent of frequency, i.e., it is white noise. However, it
does not follow a Poisson statistic since on average the variance
is ~1.6 larger than the mean. We discuss our results in
context of the current theoretical picture in which GRBs are
created in an anisotropic, highly relativistic outflow from
collapsing massive stars. Finally, we note that the exact
behaviour of the instrument is not yet known and therefore the
above results should be treated as preliminary.
and a break between 1–2 Hz. Fourth, we also
discuss the background and noise levels. We found that the
background noise has a Gaussian distribution and its power is
independent of frequency, i.e., it is white noise. However, it
does not follow a Poisson statistic since on average the variance
is ~1.6 larger than the mean. We discuss our results in
context of the current theoretical picture in which GRBs are
created in an anisotropic, highly relativistic outflow from
collapsing massive stars. Finally, we note that the exact
behaviour of the instrument is not yet known and therefore the
above results should be treated as preliminary.
Key words: gamma-rays: bursts / methods: data analysis
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


