| Issue |
A&A
Volume 404, Number 2, June III 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 405 - 421 | |
| Section | Astrophysical processes | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20030547 | |
| Published online | 02 June 2003 | |
Relativistic particle transport in extragalactic jets
I. Coupling MHD and kinetic theory
1
FOM-Institute for Plasma physics “Rijnhuizen”, PO Box 1207, 3430 BE Nieuwegein, The Netherlands e-mail: fcasse@rijnh.nl
2
CESR, 9 avenue du colonel Roche, BP 4346, 31028 Toulouse, France
Corresponding author: A. Marcowith, Alexandre.Marcowith@cesr.fr
Received:
26
December
2002
Accepted:
25
March
2003
Multidimensional magneto-hydrodynamical (MHD) simulations coupled
with stochastic differential equations (SDEs) adapted to test particle
acceleration and transport in complex astrophysical flows are
presented. The numerical scheme allows the investigation of shock
acceleration, adiabatic and radiative losses as well as diffusive spatial
transport in various diffusion regimes. The applicability of SDEs to
astrophysics is first discussed with regard to the different regimes and the
MHD code spatial resolution. The procedure is then applied to 2.5D
MHD-SDE simulations of kilo-parsec scale extragalactic jets. The ability of
SDE to reproduce analytical solutions of the diffusion-convection equation
for electrons is tested through the incorporation of an increasing number
of effects: shock acceleration, spatially dependent diffusion coefficients
and synchrotron losses. The SDEs prove to be efficient in various shock
configurations occurring in the inner jet during the development of the
Kelvin-Helmholtz instability. The particle acceleration in snapshots of
strong single and multiple shock acceleration including realistic spatial
transport is treated. In the chaotic magnetic diffusion regime, turbulence
levels 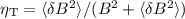 around
around 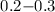 are found
to be the most efficient to enable particles to reach the highest
energies. The spectrum, extending from 100 MeV to few TeV (or even 100 TeV
for fast flows), does not exhibit a power-law shape due to transverse
momentum dependent escapes. Out of this range, the confinement is not as
efficient and the spectrum cuts-off above few hundreds of GeV, questioning
the Chandra observations of X-ray knots as being synchrotron radiation.
The extension to full time dependent simulations to X-ray extragalactic
jets is discussed.
are found
to be the most efficient to enable particles to reach the highest
energies. The spectrum, extending from 100 MeV to few TeV (or even 100 TeV
for fast flows), does not exhibit a power-law shape due to transverse
momentum dependent escapes. Out of this range, the confinement is not as
efficient and the spectrum cuts-off above few hundreds of GeV, questioning
the Chandra observations of X-ray knots as being synchrotron radiation.
The extension to full time dependent simulations to X-ray extragalactic
jets is discussed.
Key words: galaxies: jets / acceleration of particles / magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) / instabilities / radiation mechanisms: general
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


