| Issue |
A&A
Volume 367, Number 1, February III 2001
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 371 - 380 | |
| Section | Numerical methods and codes | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20000342 | |
| Published online | 15 February 2001 | |
Dark-speckle coronagraphic detection of binary stars in the near-IR*
1
GPS - CalTech Pasadena, CA, USA e-mail: boccalet@gps.caltech.edu
2
ESO Santiago, Chile e-mail: cmoutou@eso.org
3
LAOG, Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Grenoble, France e-mail: mouillet@obs.ujf-grenoble.fr; lagrange@obs.ujf-grenoble.fr; augereau@obs.ujf-grenoble.fr
A. Boccaletti
Received:
13
June
2000
Accepted:
28
November
2000
In this paper, we present the first attempt to obtain images of binary stars in the near IR using the dark-speckle method on the 3.6 m telescope at La Silla. Promising results are presented, despite the effect of the detector high read-out noise affecting the efficiency of speckle observations. We give some comparisons with the long exposure method.
We derive in these data a reliable limit of detection for binary star companions, around 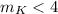 stars, which is about
stars, which is about 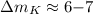 for angular separations ranging from
for angular separations ranging from 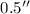 to
to 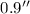 .
.
Key words: methods: data analysis / techniques: interferometric / instrumentation: adaptives optics / binaries: close / planetary systems
© ESO, 2001
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


