| Issue |
A&A
Volume 365, Number 1, January 2001
First Results from XMM-Newton
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | L146 - L151 | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20000083 | |
| Published online | 15 January 2001 | |
Detection of an X-ray periodicity in the Narrow-line Seyfert 1 Galaxy Mrk 766 with XMM-Newton*
1
Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Postfach 1312, 85741 Garching, Germany
2
X-Ray Astronomy Group, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Leicester University, Leicester LE1 7RH, UK
3
Mullard Space Science Laboratory, University College London, Holmbury St. Mary, Dorking, Surrey, RH5 6NT, UK
Corresponding author: Th. Boller, bol@mpe.mpg.de
Received:
2
October
2000
Accepted:
30
October
2000
We have analyzed the timing properties of the Narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxy
Mrk 766 observed with XMM-Newton during the PV phase. The source intensity changes by a factor of 1.3 over the 29 000 s observation. If the soft excess is modeled by a black body component, as indicated by the EPIC pn data, the luminosity of the black body component
scales with its temperature according to  . This requires a lower limit "black body size"of about
. This requires a lower limit "black body size"of about  . In addition, we report the detection of a strong periodic signal with
. In addition, we report the detection of a strong periodic signal with 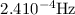 . Simulations of light curves with the observed time sequence and phase randomized for a red noise spectrum clearly indicate that the periodicity
peak is intrinsic to the distant AGN. Furthermore, its existence is confirmed by the EPIC MOS and RGS data. The spectral fitting results show that the black body temperature and the
absorption by neutral hydrogen remain constant during the periodic oscillations. This observational fact tends to rule out models in which the intensity changes are due to hot spots orbiting the central black hole. Precession according to the Bardeen-Petterson effect or instabilities in the inner accretion disk may provide explanations for the periodic signal.
. Simulations of light curves with the observed time sequence and phase randomized for a red noise spectrum clearly indicate that the periodicity
peak is intrinsic to the distant AGN. Furthermore, its existence is confirmed by the EPIC MOS and RGS data. The spectral fitting results show that the black body temperature and the
absorption by neutral hydrogen remain constant during the periodic oscillations. This observational fact tends to rule out models in which the intensity changes are due to hot spots orbiting the central black hole. Precession according to the Bardeen-Petterson effect or instabilities in the inner accretion disk may provide explanations for the periodic signal.
Key words: galaxies: active / galaxies: individual: Mrk 766 / X-rays: galaxies
© ESO, 2001
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


