Fig. 1
Download original image
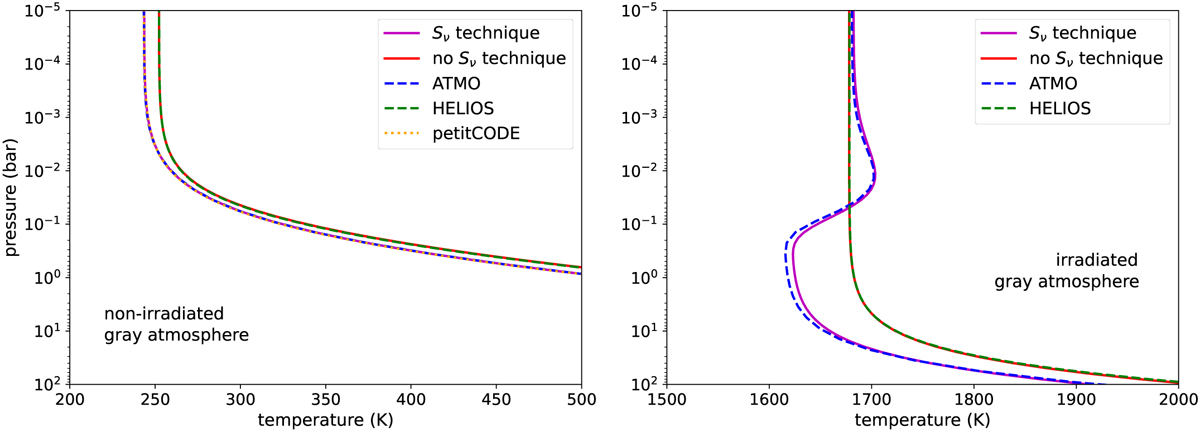
Pressure-temperature profiles calculated with our radiative-convective module with and without the source function (S ν) technique (see text) are compared to those obtained with other codes in the literature: ATMO (Tremblin et al. 2015), HELIOS (Malik et al. 2017, 2019), and petitCODE (Mollière et al. 2015, 2017). We consider two cases with parameters typical of HD 209458b. The first one is a non-irradiated gray atmosphere (left panel) with an absorption coefficient of 0.01 cm2 g−1, an internal planet temperature of 300 K, a mean atmosphere molecular weight of 2.3 amu, a planet mass of 219.3 M⊕, and a planet radius of 15.468 R⊕. The second case is an irradiated gray atmosphere (right panel) with the same parameters as the previous non-irradiated case and a zenith angle of 60°, a surface albedo of 0, a heat redistribution factor of 1 (i.e., no day-night heat redistribution), and a star with a radius of 1.118 R⊙ radiating as a blackbody at a temperature of 6000 K and located at a distance of 0.047 AU from the planet. In the non-irradiated case, our “S ν” result cannot be visually distinguished from those by ATMO and petitCODE, while the same happens between our “no S ν” result and that from HELIOS. In the irradiated case, our “no S ν” result overlaps with the HELIOS one.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


