Fig. 4
Download original image
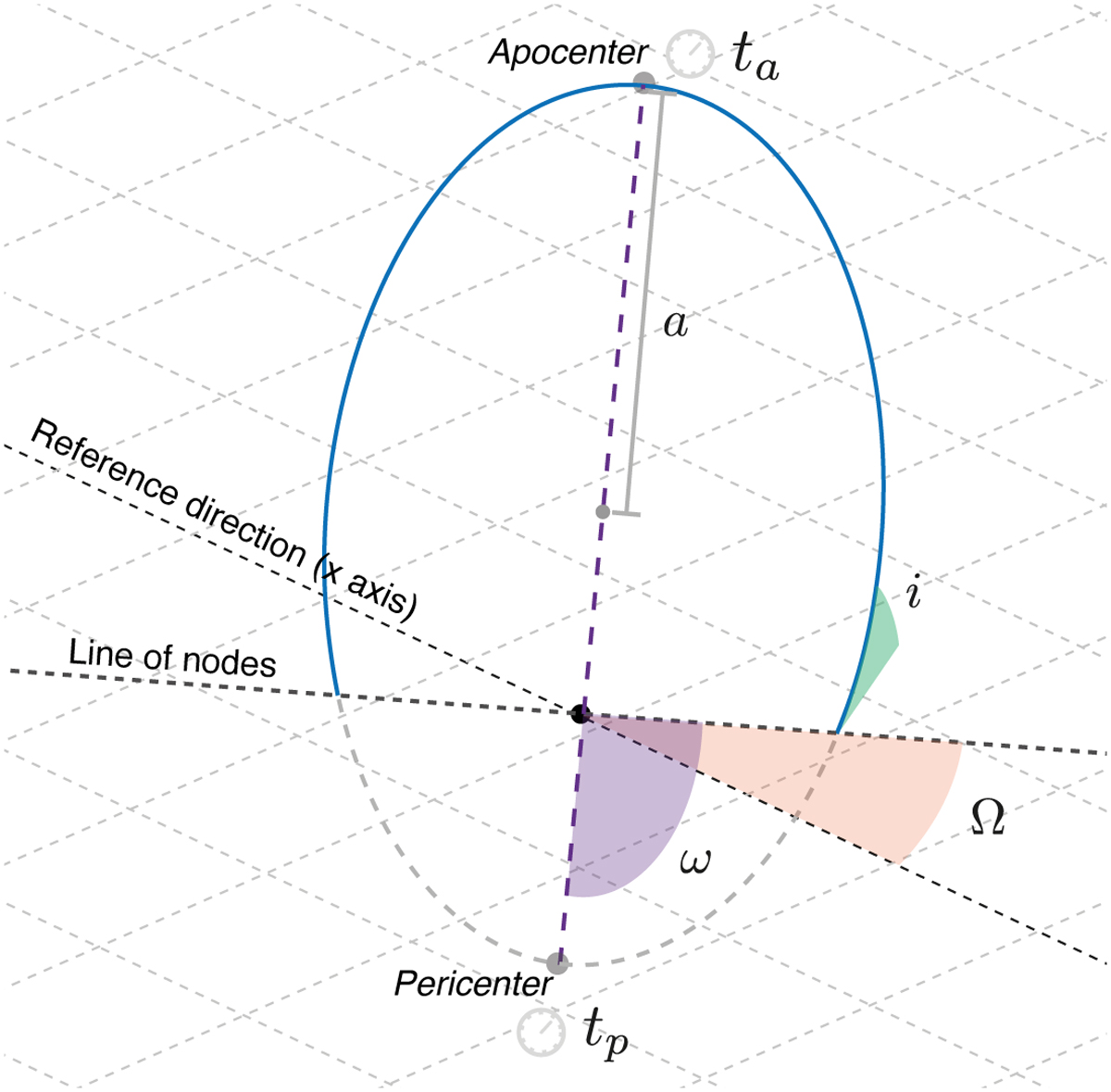
Illustration of the angular orbital elements for a Keplerian orbit. The orbital inclination, i, represents the inclination of the orbital plane with respect to a reference plane (e.g., the plane of sky for a distant observer), and the longitude of the ascending node, Ω, corresponds to the angle between a reference direction (in our case the ϕ = 0 line on the equatorial plane) and the line of nodes, namely, the line in which the orbital plane intersects the reference plane. The argument of the pericenter, ω, is the angle along the orbital plane between the line of nodes and the orbit’s pericenter.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


