Fig. 6
Download original image
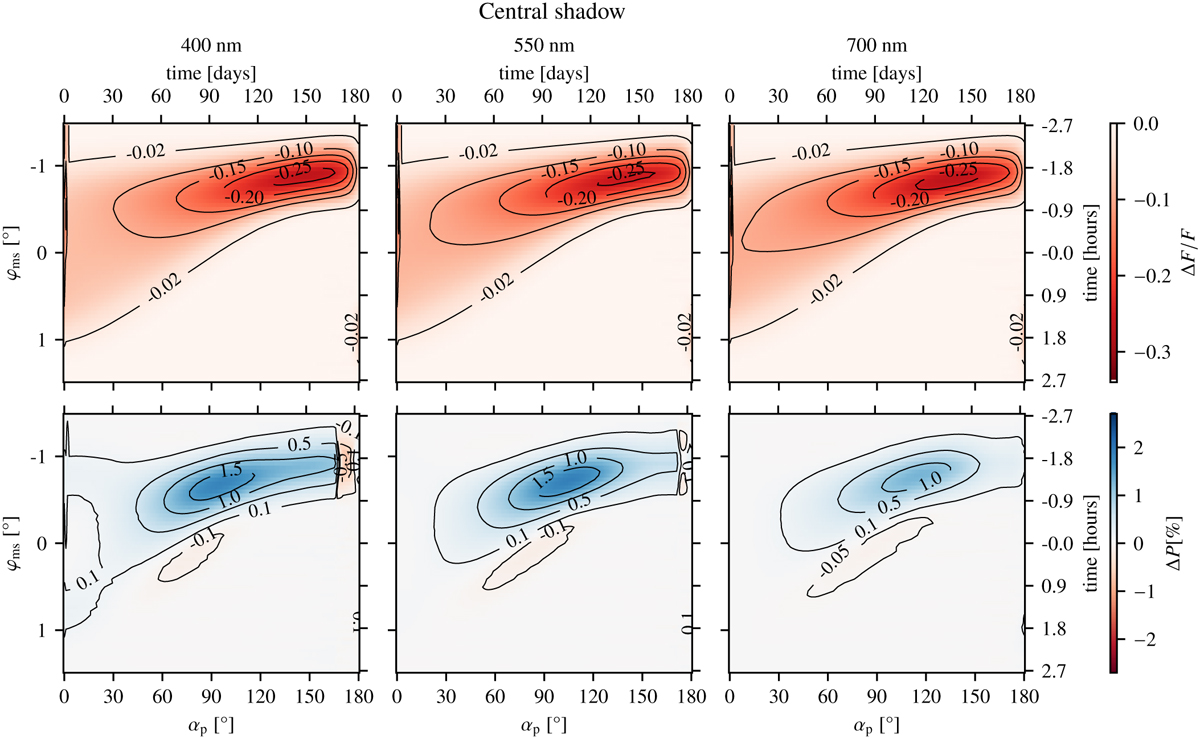
Similar to Fig. 4, but for phases during which the moon casts a shadow on the planet. The left ordinate now shows the angle φms, which specifies the lunar position. Again, this angle was transformed to a time in hours, as shown on the right ordinate, where a time of 0 corresponds to the time when the planet, moon, and star are perfectly aligned. A single run of the shadow of the moon across the planetary surface corresponds to a passage through the color maps perpendicular to the abscissa.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


