Fig. 8
Download original image
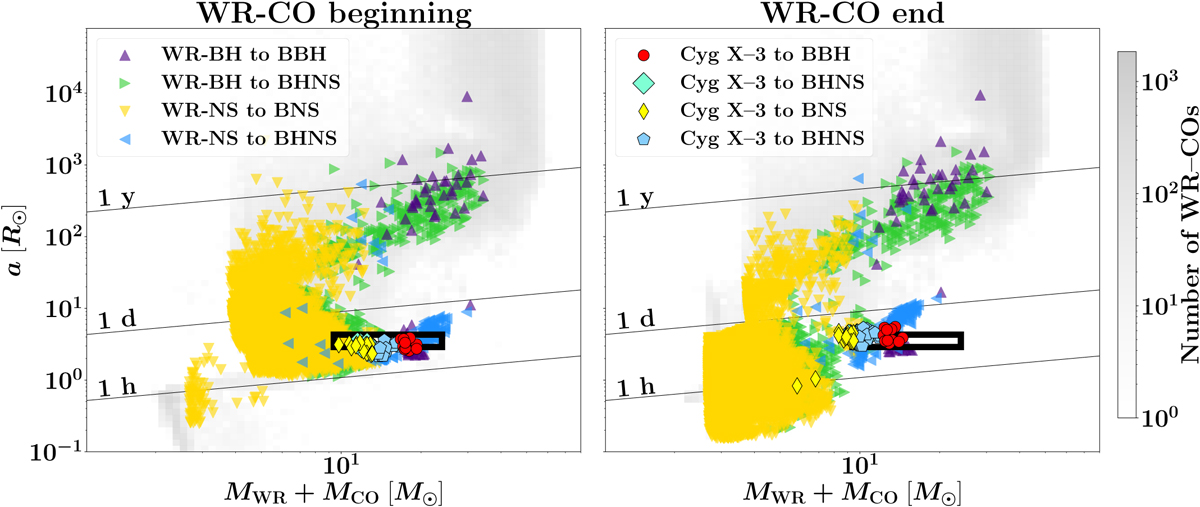
Orbital properties of WR–COs and Cyg X-3 at the beginning (left) or end (right) of the WR–CO configuration. We highlight the properties of WR–COs (triangular markers) and Cyg X-3-like binaries (non-triangular markers) that are BCO progenitors, comparing them to the properties of the whole sample of WR–CO (gray areas in the background). We distinguish binaries ending up as BBHs (purple upward triangles; red circles), as BNSs (gold downward triangles; yellow thin diamonds), or as BHNSs, either forming the BH first (green rightward triangles; thick turquoise diamonds) or the NS (blue leftward triangles; turquoise pentagons). The black rectangular box indicates the region of orbital parameters that we use to select Cyg X-3 candidates (Section 3.4). Black diagonal lines indicate orbital periods of 1 hour, 1 day or 1 year. Here we show the set evolved with αCE = 3, Z = 0.02, G20 natal kick model and delayed CCSN model. In Appendix B.2 we show other sets at αCE = 3 and Z = 0.02.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


