Fig. 3.
Download original image
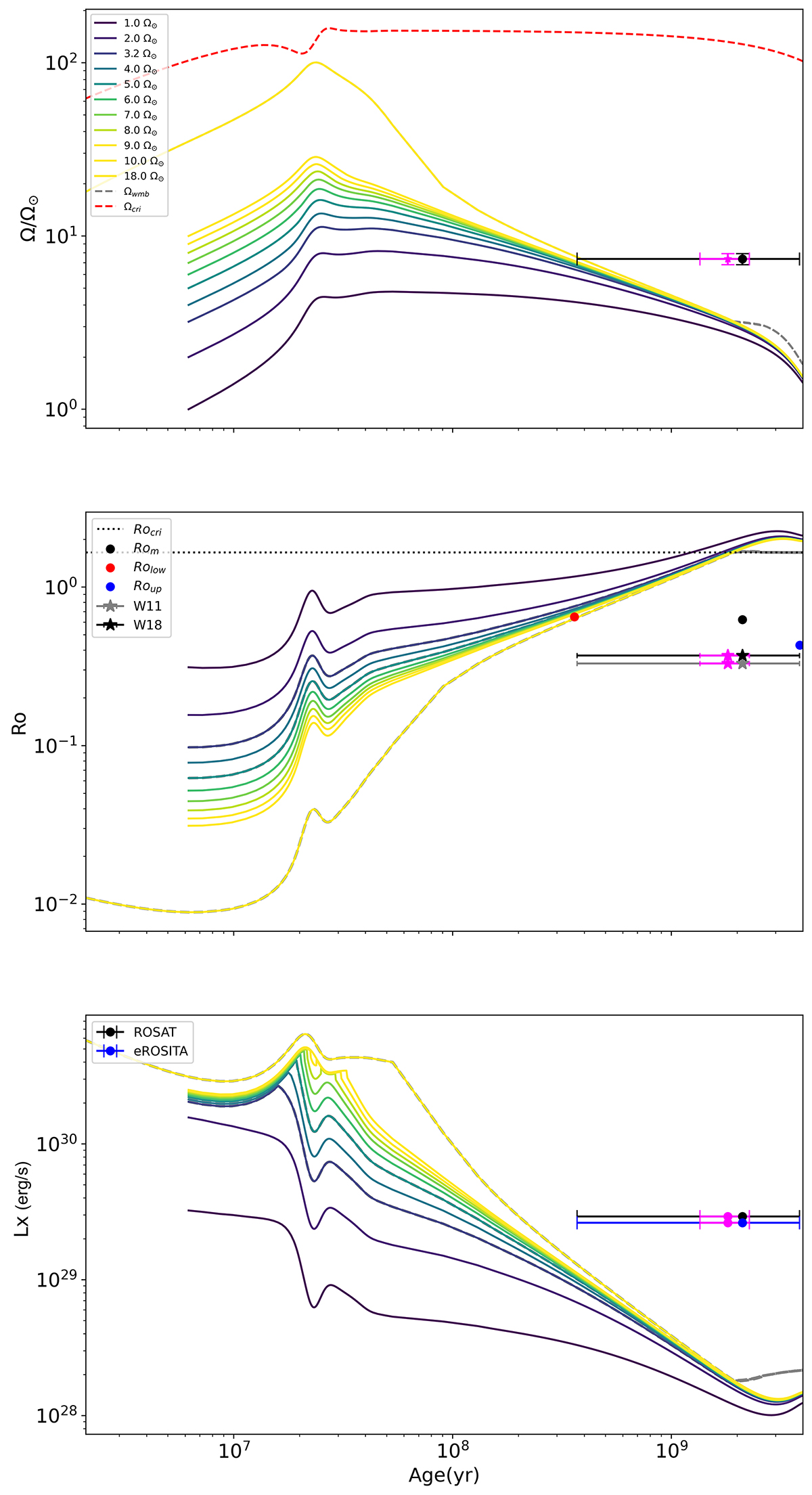
Host star’s evolutionary tracks in the SwoP scenario. Top panel: Surface-rotation-rate evolution versus age for our optimal stellar model, with Ωin = 1, 2, 3.2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 18 Ω⊙. The dashed red line shows the evolution of the critical rotation velocity (Ωcrit), defined as the velocity at which the centrifugal acceleration at the equator equals the gravity. The magenta and black markers show GJ 504’s surface rotation rate, with age uncertainties derived from the global and local minimisation modelling, respectively. Middle panel: Evolution of stellar Rossby number (RO). RO for GJ 504 is indicated by the red, black, and blue circles corresponding to the lower, mean, and upper values of the largest age uncertainty, respectively. The grey and black stars represent the values obtained from τconv as in Wright et al. (2011) and Wright et al. (2018). Analogously, the magenta markers represent the same quantities for the smallest age uncertainty. Bottom panel: Evolution of X-ray luminosity for each of the considered rotators. The black and blue markers show the X-ray luminosities from Voges et al. (1999), Wright et al. (2011) (ROSAT) and in this work (eROSITA), respectively. Analogously, the magenta markers represent the same quantities for the smallest age uncertainty. In all panels, the starting point of the tracks corresponds to the dissipation of the protoplanetary disc (2 Myr for Ωin = 18 Ω⊙; 6 Myr for the other ones).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


