Fig. 1.
Download original image
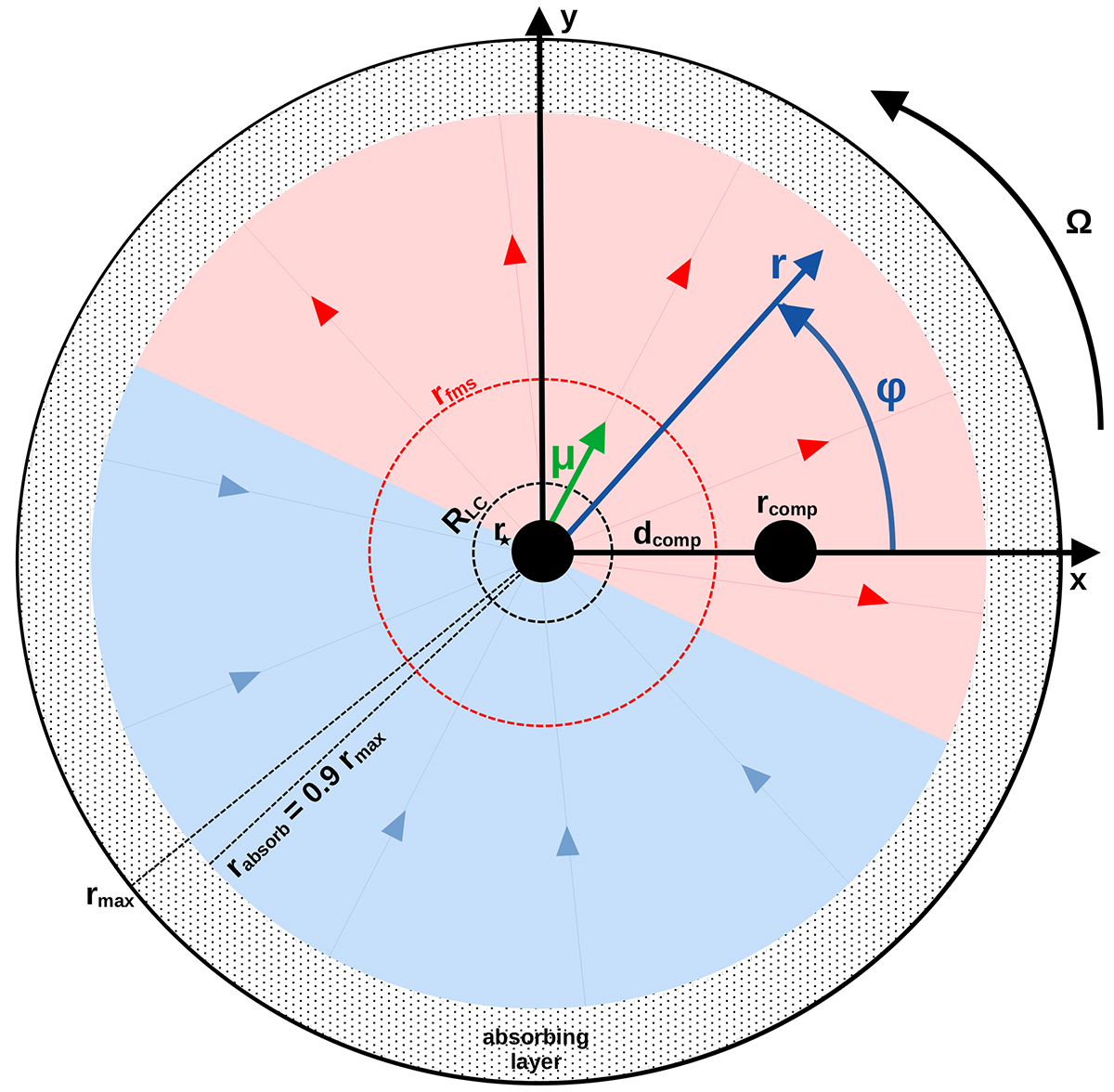
Initial numerical setup. The pulsar, of a radius, r⋆ and angular velocity, Ω, lies at the center of the spherical box of coordinates (r,ϕ) and radius rmax. The companion, of radius rcomp, is settled at a fixed distance dcomp along the ϕ = 0 direction. Initially, the box is empty of particles. Magnetic field lines (blue and red arrows) are radial, directed outwards on one hemisphere and inwards on the other hemisphere, according to the split-monopole configuration. The plane inclination in between both hemispheres is perpendicular to the magnetic moment μ shown in green. An absorbing layer is implemented at rabsorb = 0.9rmax. The light-cylinder radius RLC is represented by the black dashed circle and the fast magnetosonic radius rfms is given by the red dashed circle.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


