Fig. D.1
Download original image
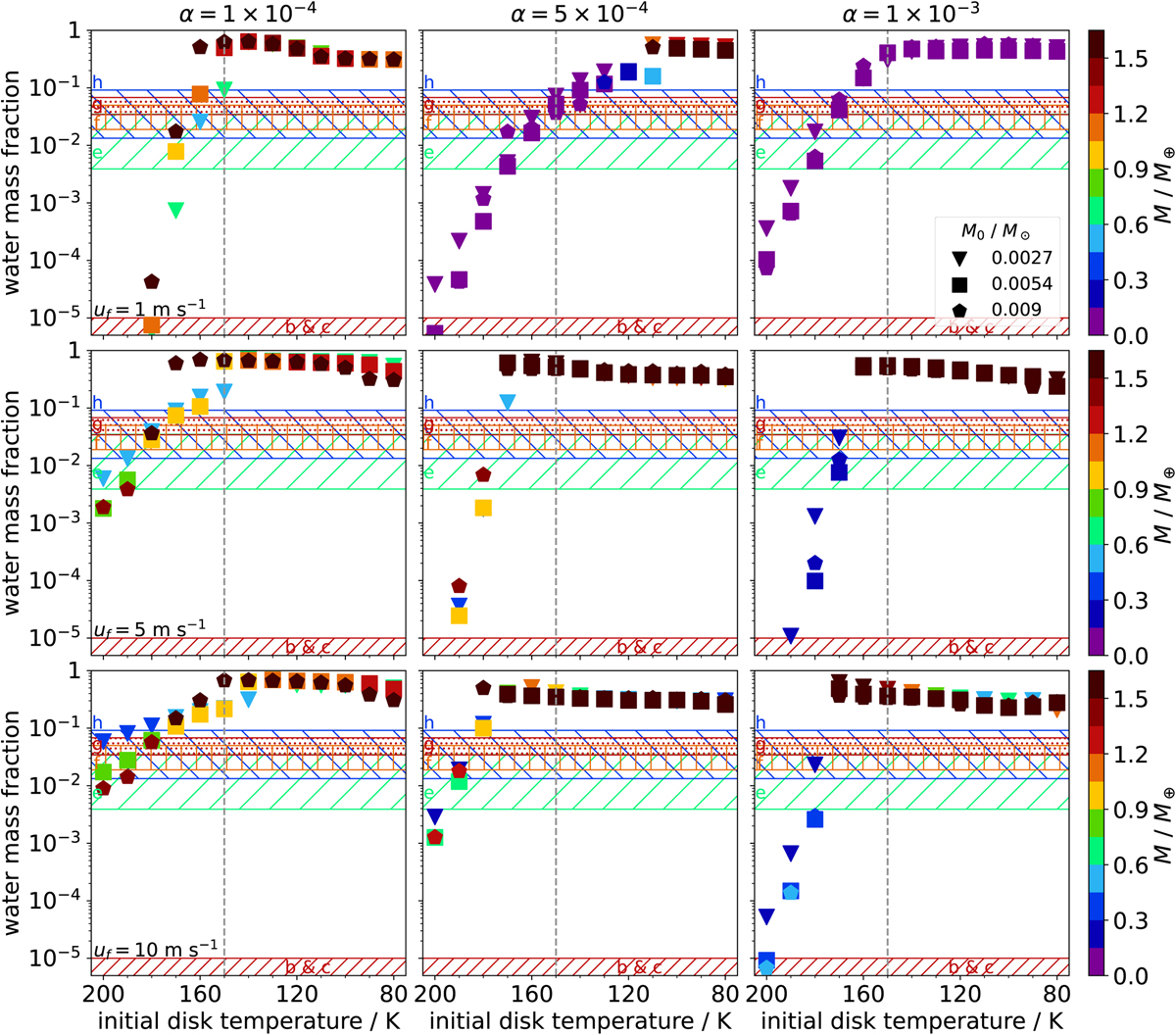
Same as Fig. 5, but neglecting the recycling of volatiles in the planetary envelope. The water mass fractions of the planets can exceed the initial maximum water content of the solids in our disk model (i.e., ~35%) if they accrete significant amounts of their final mass near the water-evaporation line. At that location, the water content of the solids is much higher due to local recondensation of water vapor (e.g., Drążkowska & Alibert 2017; Ros et al. 2019), see also Schneider & Bitsch (2021). This is similar to the effect for iron grains in the inner disk, which can explain the formation of super-Mercuries (Mah & Bitsch 2023).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


