Fig. 1
Download original image
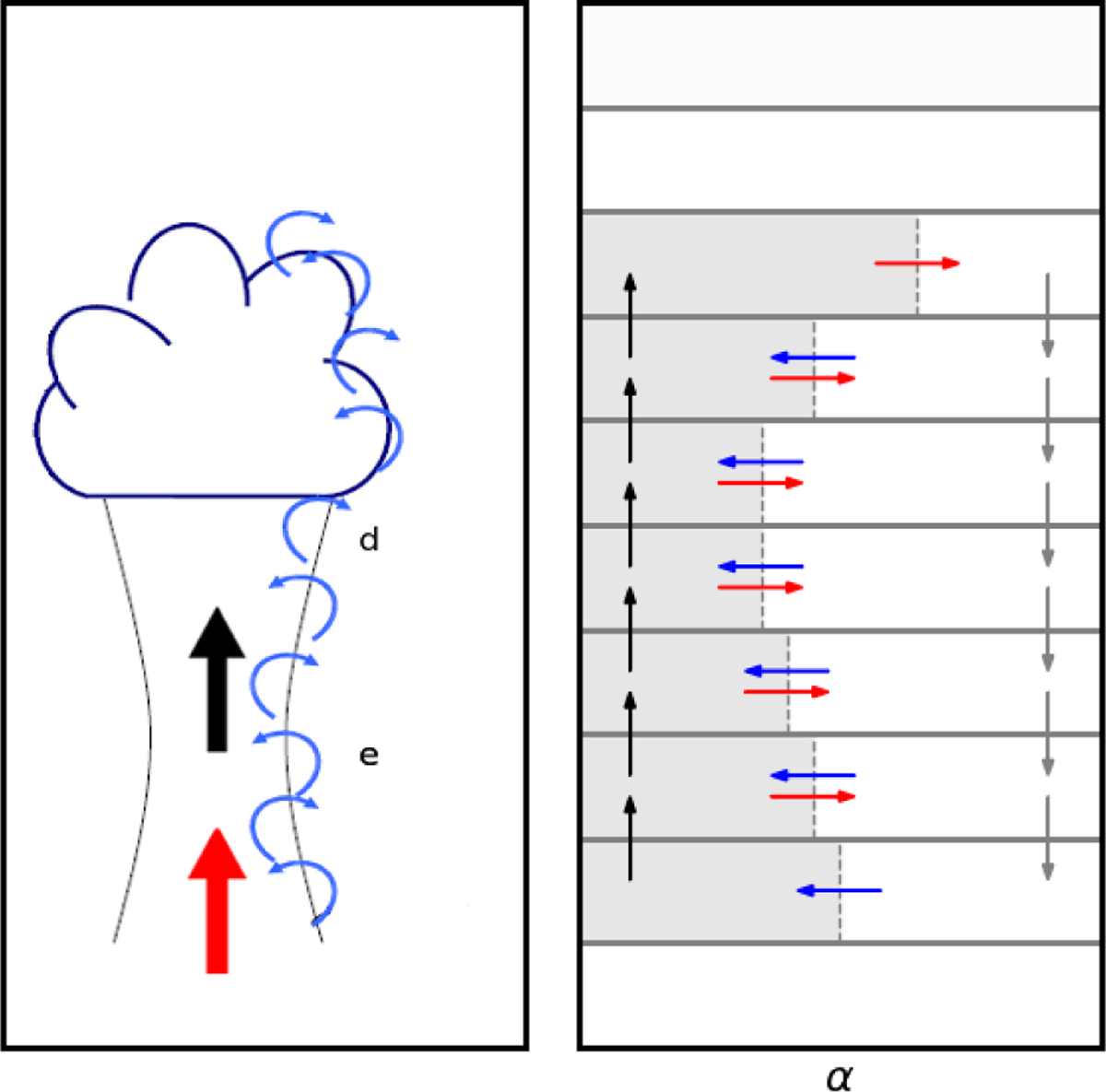
Principles of the thermal plume model. Left panel: schematics of a real convective plume. The bottleneck part is the bulk of the plume, and the puffy upper part is the overshoot. The black arrow represents vertical fluxes in the ascending plume (the red arrow is the bottom source of the plume). The rounded blue arrows represent exchanges between the ascending plume and the environment: entrain-ment e toward the plume, and detrainment d toward the environment. Right panel: schematics of the idealization adopted in the thermal plume model. The gray areas represent the ascending plume subcolumn (see text in Sect. 3.2). The mass fluxes are both vertical (black and gray arrows) and horizontal (entrainment e as blue arrows and detrainment d as red arrows). α is the fraction of the GCM grid mesh that is covered by ascending convective plumes. They are represented as the single plume in the thermal plume model.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


