Fig. 18
Download original image
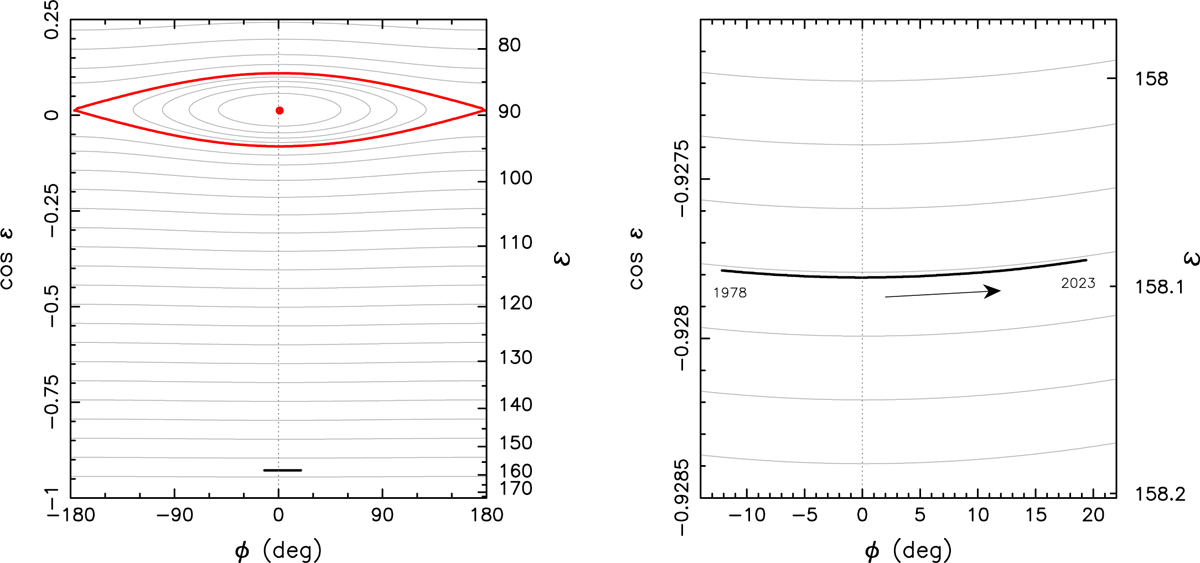
Rotation pole evolution of (2100) Ra-Shalom due to the solar torque and its comparison with the simple Colombo top model. The coordinates on the axes are defined in the orbital plane, namely (i) the obliquity є (or cos є) on the right and left ordinates, and (ii) the longitude ϕ reckoned from the direction 90° away from the orbital node (located at ϕ = −90°; e.g., Breiter et al. 2005). The numerically propagated evolution of the Ra-Shalom pole over the 44 yr time span is shown by the solid black line. The gray lines are solutions of the simple Colombo top model. For most of the obliquity values, they are basically simple straight lines of approximately constant є. The exception is the Cassini resonant zone at є ⋍ 90° (with the separatrix shown by the red curves, and the stationary Cassini state 2 shown by the red dot). Unlike the case of asteroid (433) Eros, whose spin axis librates in the resonant zone (Vokrouhlický et al. 2005a), the evolution of the Ra-Shalom pole is simpler and only consists of nearly regular precession. The zoom in the right panel shows that the change in obliquity is minimum, but conforms to the Colombo top solution.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


