Fig. 12
Download original image
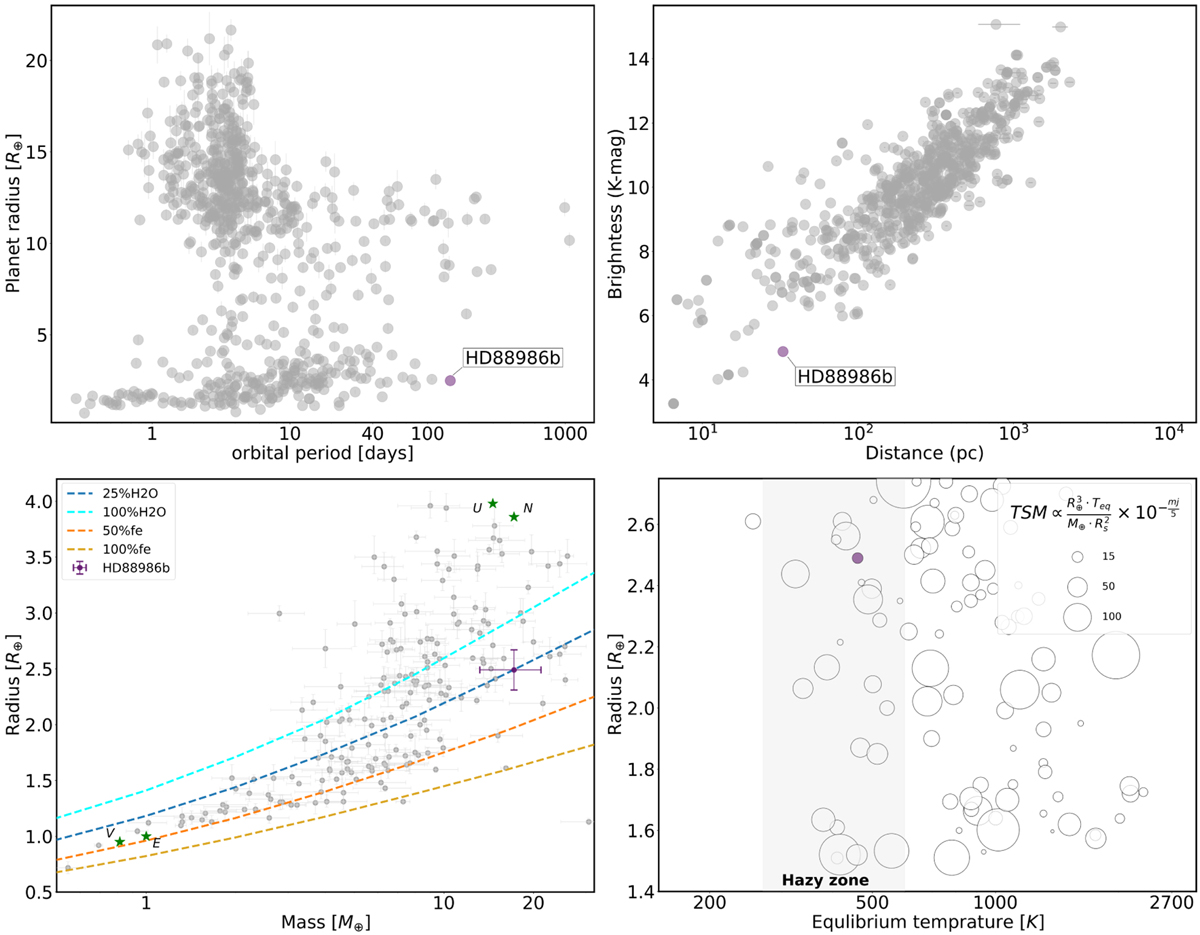
Position of HD 88986 b and its host star among known transiting exoplanetary systems, with precise planet mass and radius measurements (σ-M/M = 25% and σR/R = 8%, Otegi et al. 2020) from the NASA Exoplanet Data Archive (June 7, 2023). Top left: radius-period diagram of exoplanets. Top right: brightness in the K band versus distance of the exoplanet host star for the same planets. Bottom left: mass-radius diagrams of small planets (Rp < 4 R⊕). The colored curves are the two-layer theoretical composition models of Zeng et al. (2016). Bottom right: equilibrium temperature-radius diagram of planets within the radius range of 1.5 R⊕ to 2.75 R⊕ with each planet’s size scaled according to the propositional TSM introduced by Kempton et al. (2018). The gray area is the proposed hazy atmosphere zone by Yu et al. (2021). The purple mark indicates HD 88986 b. These planets possess either a known equilibrium temperature or information about the radius and temperature of their host star to estimate their temperature (![]() , Méndez & Rivera-Valentín 2017). These figures highlight the unique position of the HD 88986 system.
, Méndez & Rivera-Valentín 2017). These figures highlight the unique position of the HD 88986 system.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


