Fig. 3
Download original image
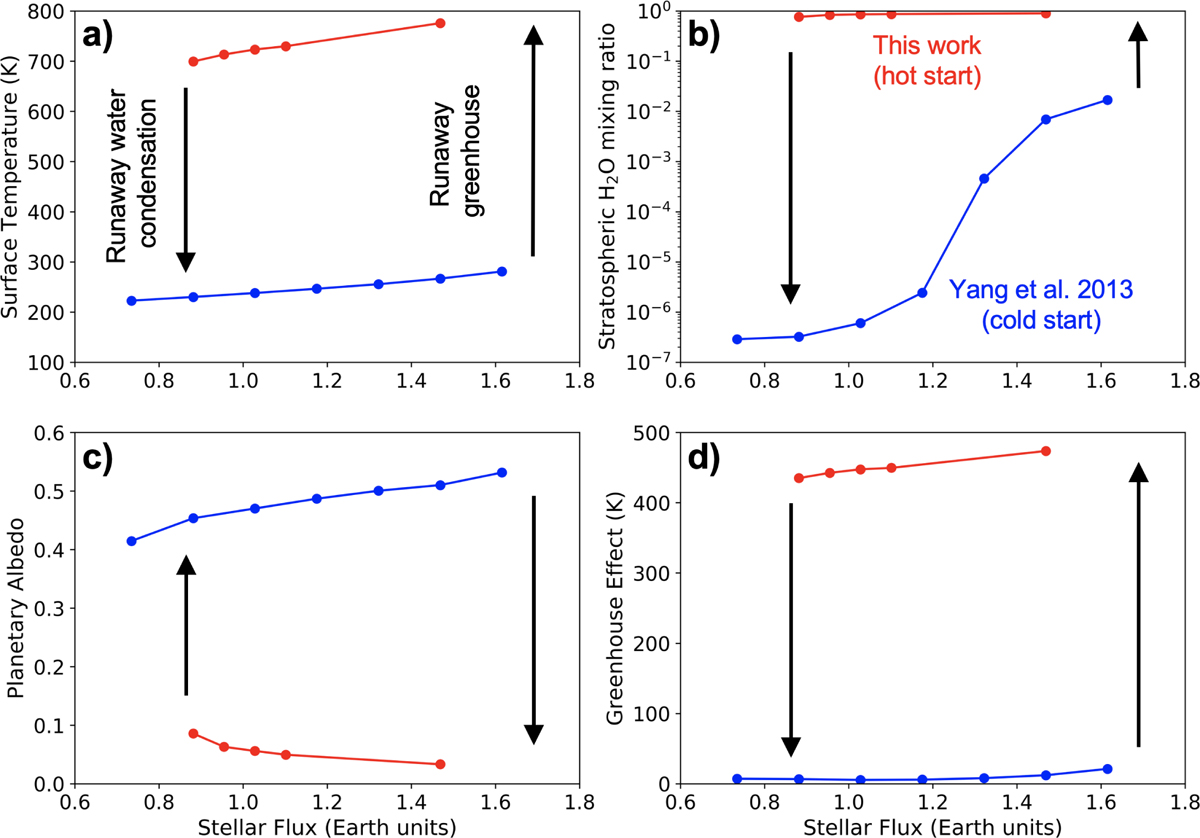
Hysteresis loops and conditions of ocean formation for an initially hot and steamy 2 R⊕ planet (with a 10 bar H2O + 1 bar N2 atmosphere) synchronously rotating (fixed rotation period of 60 Earth days) around an M3 star (simulation M3-YANG-1). The figure depicts the evolution of surface temperature (top left), stratospheric water mixing ratio (top right), bond albedo (bottom left), and greenhouse effect (bottom right) as a function of the incoming stellar flux. The blue branches correspond to simulation results (Yang et al. 2013) that assume water is initially condensed on the surface. The red branches (this study) correspond to initially hot and steamy simulation results that assume water is initially in vapor form in the atmosphere.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


