Fig. 10
Download original image
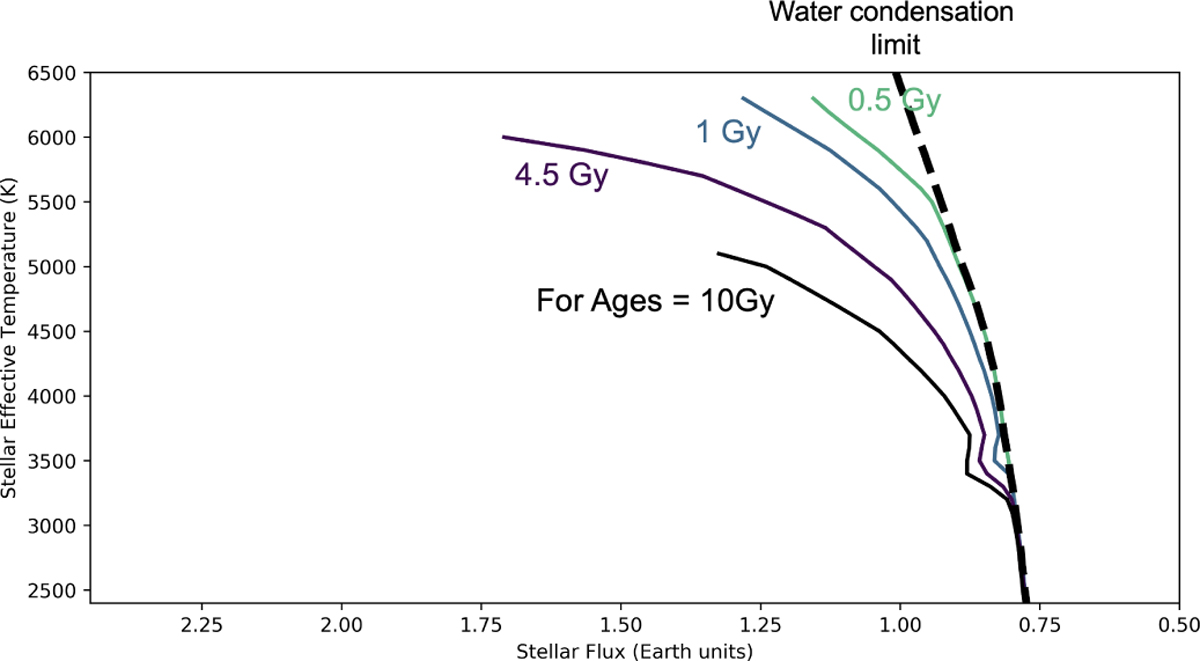
Various positions of the water condensation limit, depending on the age of the planetary system considered. The standard water condensation limit (black dashed line) is valid at the ZAMS. It can be used as is to evaluate the condensation of water on a planet, provided that the insolation of the planet is taken at the ZAMS (see, e.g., gray brackets in Fig. 8). The other water condensation limits (solid colored lines) indicate, for a planet of age X (here with X = 0.5, 1, 4.5, and 10 Gyr), that if that planet is to the left of the age X curve, then it has never been able, or never will be able, to condense its water at the surface. These curves were calculated from the standard water condensation curve (black dashed line), and shifted using the grid of stellar models of Baraffe et al. (2015). Numerical values of all the curves are provided in Table 2.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


