Fig. 1
Download original image
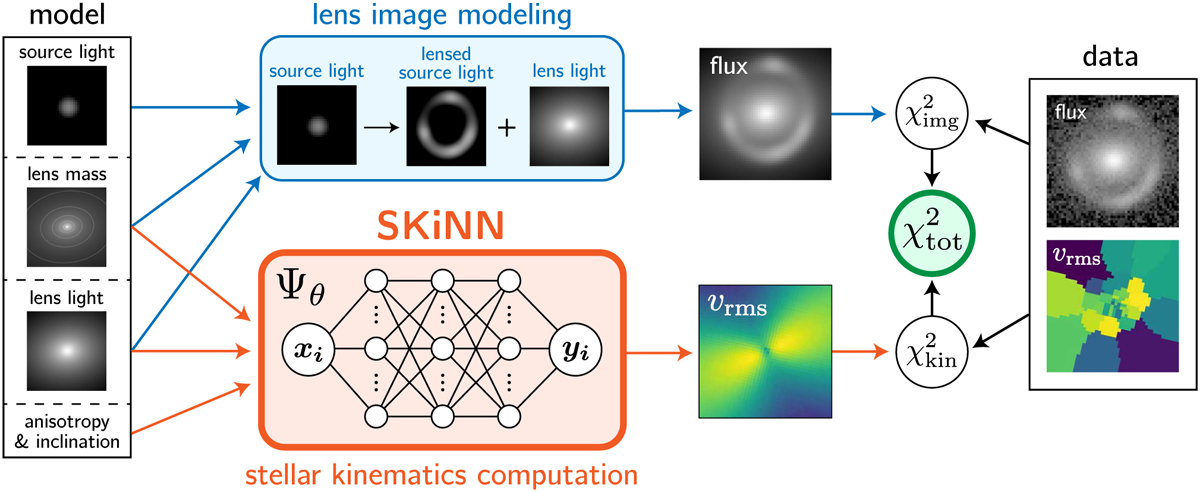
SKiNN’s role in a joint modeling framework. SKiNN takes, as input, a parametric description of the lens mass profile, lens light profile, anisotropy of the stellar orbits in the lens galaxy, and lens inclination and outputs a υrms map used to evaluate a kinematic likelihood (![]() ). This likelihood is then combined with the lensing likelihood (
). This likelihood is then combined with the lensing likelihood (![]() ) to give a total likelihood (
) to give a total likelihood (![]() ), which is then sampled. In the case of a variable lensed source with measured time delays, a time-delay likelihood (
), which is then sampled. In the case of a variable lensed source with measured time delays, a time-delay likelihood (![]() , not shown in the figure) can be added to the inference (see Sect. 5).
, not shown in the figure) can be added to the inference (see Sect. 5).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


