Fig. 8
Download original image
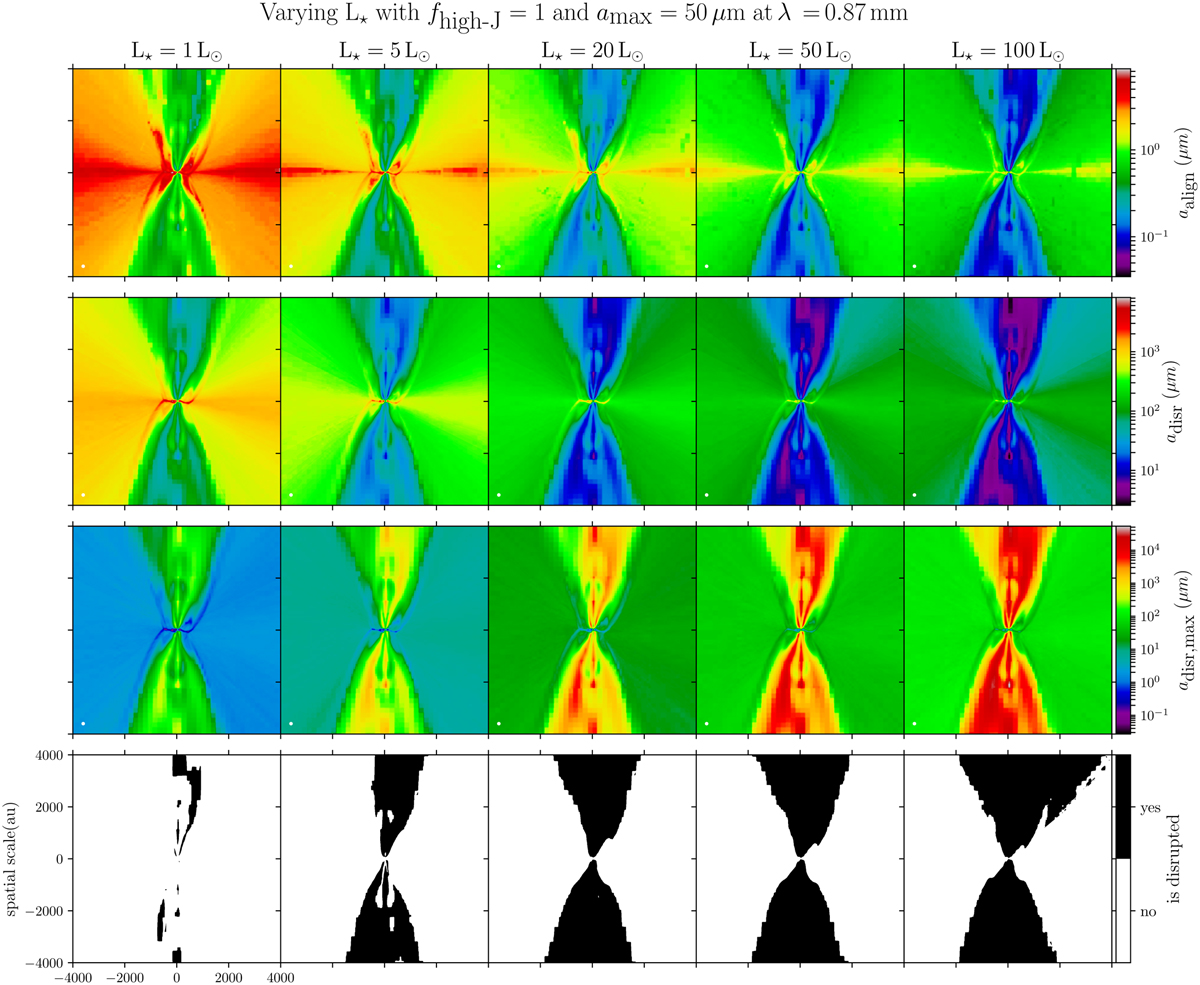
Effect of the central luminosity, L★, on the RATD of dust grains, at 0.87 mm, with the fixed parameters of amax = 50 µm and fhigh−J = 1. Each plot is a 2D slice taken at the center of the core in our radiative transfer results. Each column is one radiative transfer run of POLARIS, with L★ = 1, 5, 20, 50, and 100 L⊙. The first row is the aalign parameter, i.e., the dust grain size above which dust grains are considered aligned in our radiative transfer calculations. The second and third rows are the adisr and adisr,max parameters, respectively. In RATD theory, these two values correspond to the window in grain size, inside which dust grains are rotationally disrupted. The last row indicates whether dust grains are rotationally disrupted in our models for Smax = 105 erg cm−3, i.e., if the intervals [aalign; amax] and [adisr; adisr,max] overlap. For a given pixel, if there is an overlap, the pixel is black (i.e., grains are disrupted). If it is not the case, it is white (i.e., grains are not disrupted).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


