Fig. 3
Download original image
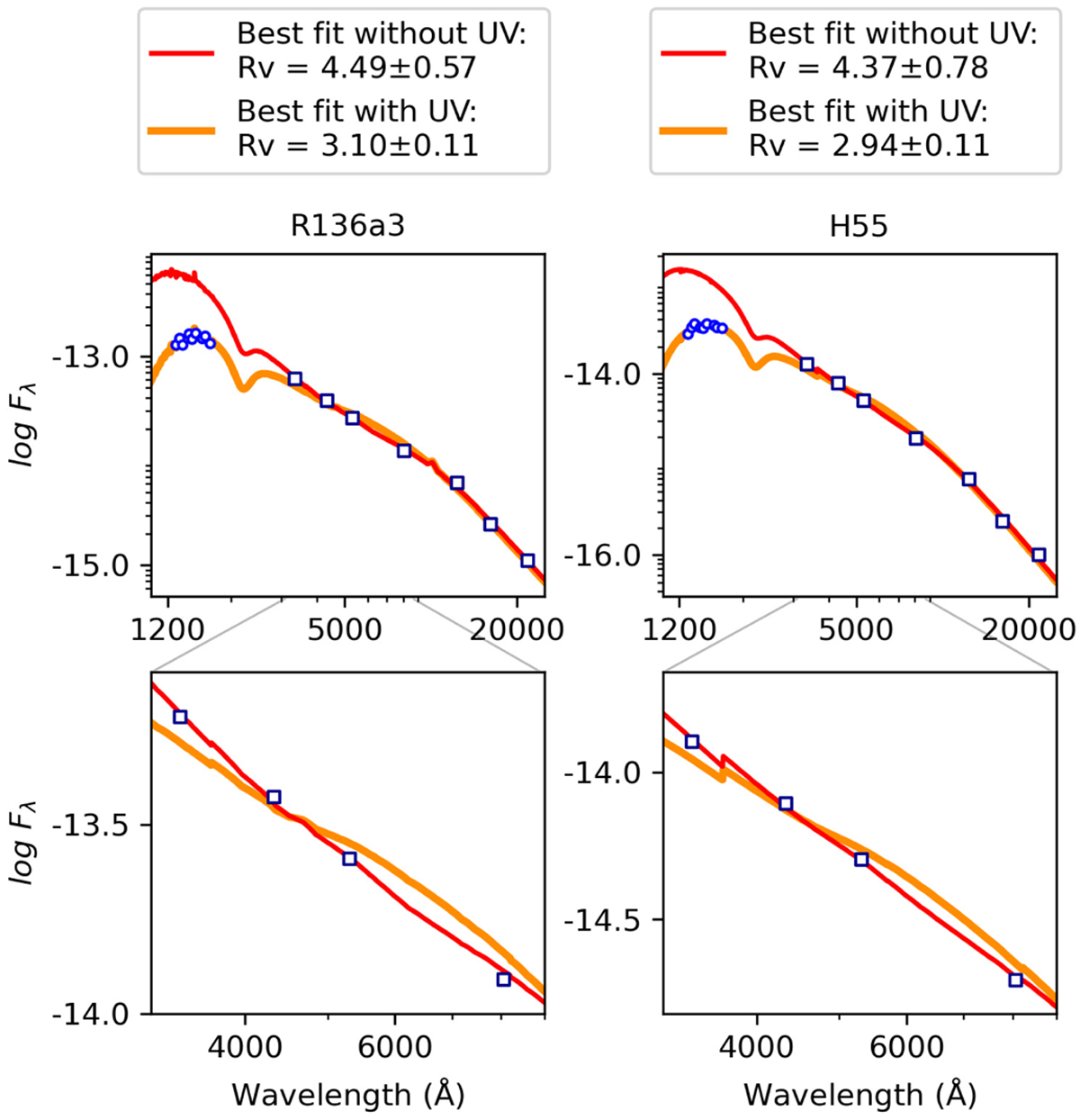
Example fits of SEDs of the stars R136a3 (left; WNh) and H55 (right; O2 V((f*))z), adopting the standard Galactic law of F99. The figure shows that this law is not suitable for our analysis: the Galactic dependence of UV extinction on Rv does not hold for sightlines towards R136. In other words, the reddened flux cannot be modelled accurately over the full wavelength range: an RV based on the optical and NIR photometry gives a total mismatch with the observed UV fluxes, whereas a much lower value – that can reproduce the UV fluxes – gives a very poor fit to the observed slope in the optical. The top panels display the flux from UV to NIR; the bottom panels zoom in on the optical regime for which UBVI photometry is available. Circles and squares indicate observed fluxes in the UV, and optical or NIR, respectively. The best-fitting reddened model including the UV is shown in orange; the best fit excluding the UV constraints in red. For this example, we used the law of F99, but the same behaviour is seen with other RV -dependent Galactic laws.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


