Fig. 4.
Download original image
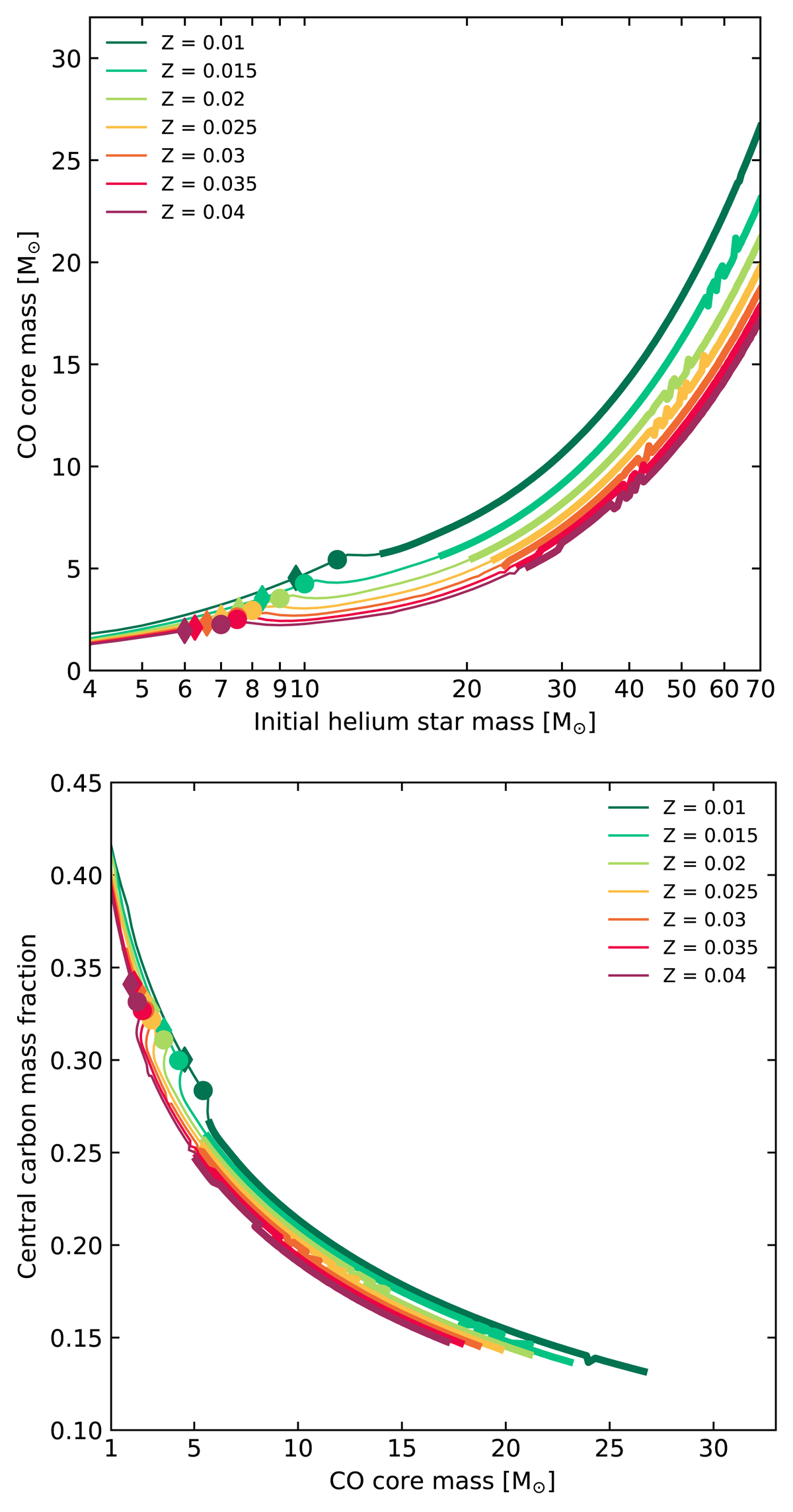
Properties of the carbon-oxygen core at the end of helium burning. Top: carbon-oxygen core mass at the end of helium burning, as a function of initial helium star mass. Bottom: central carbon abundance at the end of helium burning, as a function of carbon-oxygen core mass. Thin lines represent models where core carbon burning occurs convectively, whereas thick lines represent models where carbon burning occurs radiatively. The dots on each line indicate, for each metallicity, the initial helium star mass at which the transition between WN- and WC-type mass loss is observed to occur in the models. The rhombi indicate the value of the minimum initial mass above which helium stars are observable as WN-type stars, obtained via Eq. (8). Helium stars below this limit do not have optically thick WR winds and have overestimated mass-loss rates.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


