Fig. 4.
Download original image
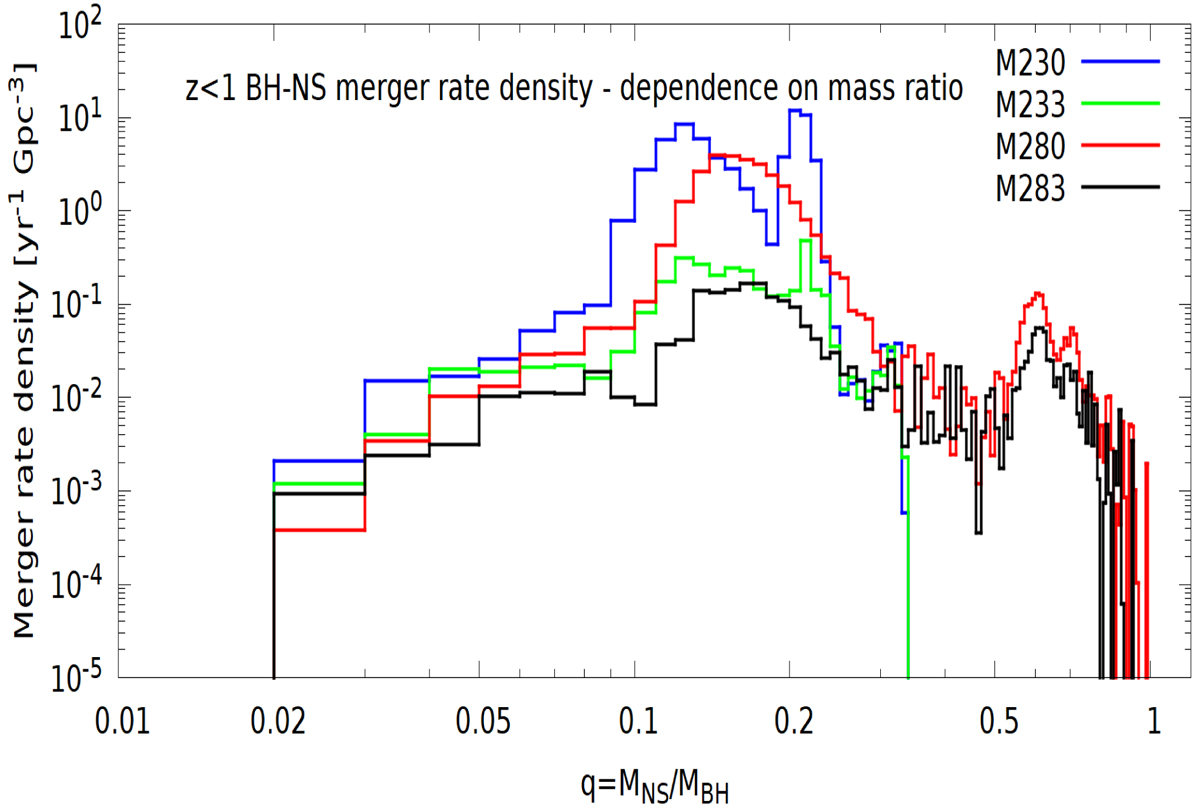
Mass ratio distribution for BH-NS mergers in the low-redshift Universe (z < 1). For each BH-NS system, we calculated the mass ratio q = MNS/MBH ∈ [0, 1]. Values indicate merger rate densities estimated from the systems within each q bin, that is to say dRate dt−1dV−1dq−1Δq, with Δq = 0.01. For transparency purposes, we use simple merger rate density as the vertical axis label. Most mergers have rather small mass ratios q ∼ 0.1 − 0.2, but there are also extreme mass ratio systems such as 56 M⊙ BH + 1.3 M⊙ NS (q = 0.023). For models with the delayed supernova engine (M280 and M283), there is a secondary peak for high mass ratios q > 0.4, which consists mostly of double compact objects with both components in the FMG (see Sect. 4).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


