Fig. 8
Download original image
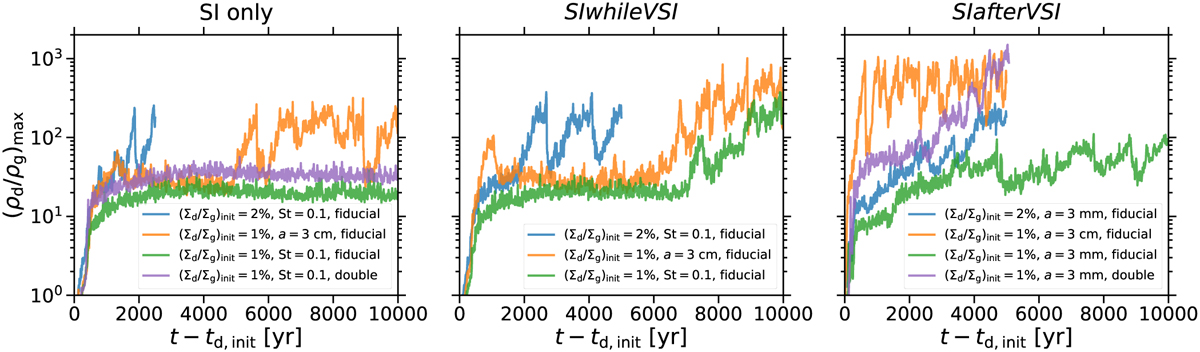
Maximum dust-to-gas volume density ratio (ρd/ρg)max as a function of time after the dust particle initialisation t – td,init. In the left, middle, and right panels, respectively, simulations of the streaming instability only, of the scenario SIwhileVSI, and of the scenario SIafterVSI with different initial dust-to-gas surface density ratios (Σd/Σg)init, fixed dust sizes a or Stokes numbers St, and resolutions (fiducial or double) can be seen. Increasing any of the three parameters causes the maximum volume density ratio to increase as well. In addition, the maximum is larger if a dust size of a = 3 cm rather than a Stokes number of 0.1 is considered, as is evident from the left and middle panels. Neither the simulation of the streaming instability with the doubled resolution nor the corresponding one with the fiducial resolution develop into a strong-clumping phase, with the maximum volume density ratio being greater by a factor of a few in the former simulation. In comparison, the maximum is enhanced by more than an order of magnitude during the strong-clumping phase in the double-resolution simulation of SIafterVSI than in respective fiducial-resolution simulation.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


